Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
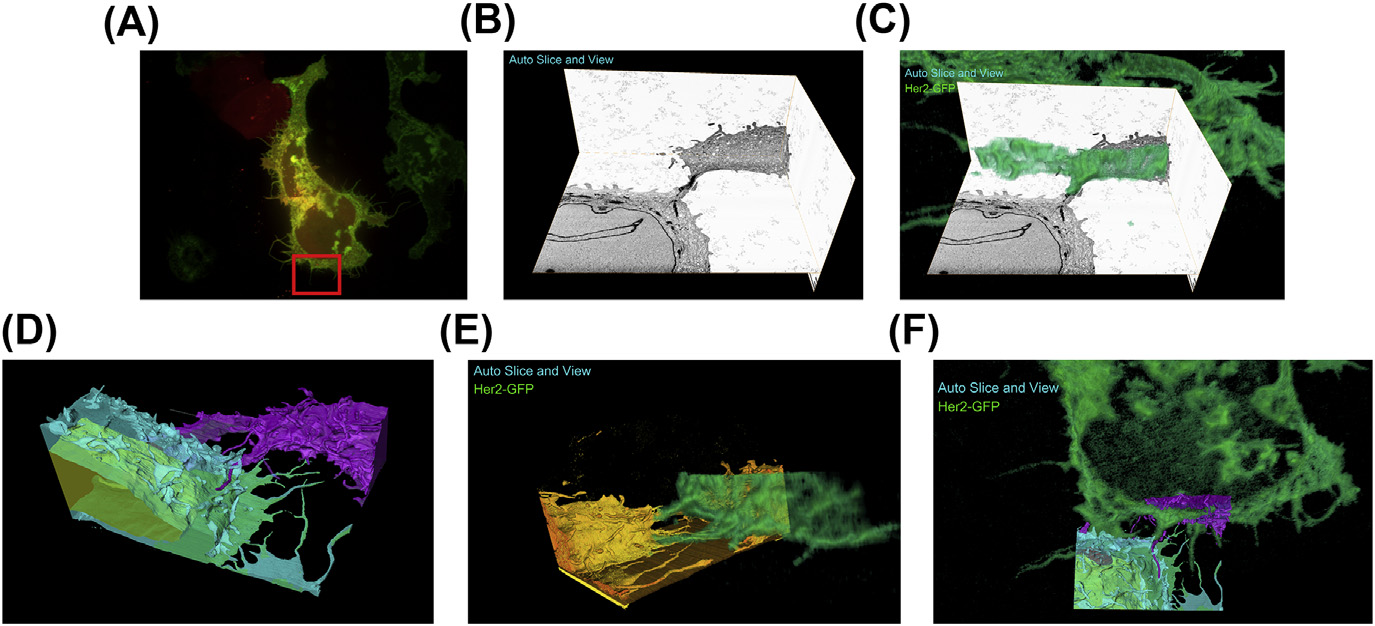
A fully integrated, three-dimensional fluorescence to electron microscopy correlative workflow
While fluorescence microscopy provides tools for highly specific labeling and sensitive detection, its resolution limit and lack of general contrast has hindered studies of cellular structure and protein localization. Recent advances in correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM), including the fully integrated CLEM workflow instrument, the Thermo Scientific CorrSight with MAPS, have allowed for a more reliable, reproducible, and quicker approach to correlate three-dimensional time-lapse... Read more
Claudia S. Lopez, Cedric Bouchet-Marquis, Christopher P. Arthur, Jessica L. Riesterer, Gregor Heiss, Guillaume Thibault, Lee Pullan, Sunjong Kwon, Joe W. Gray

The molecular basis for sarcomere organization in vertebrate skeletal muscle
Sarcomeres are force-generating and load-bearing devices of muscles. A precise molecular picture of how sarcomeres are built underpins understanding their role in health and disease. Here, we determine the molecular architecture of native vertebrate skeletal sarcomeres by electron cryo-tomography.
Our reconstruction reveals molecular details of the three-dimensional organization and interaction of actin and myosin in the A-band, I-band, and Z-disc and demonstrates that α-actinin cros... Read more
Zhexin Wang, Michael Grange, Thorsten Wagner, Ay Lin Kho, Mathias Gautel, Stefan Raunser
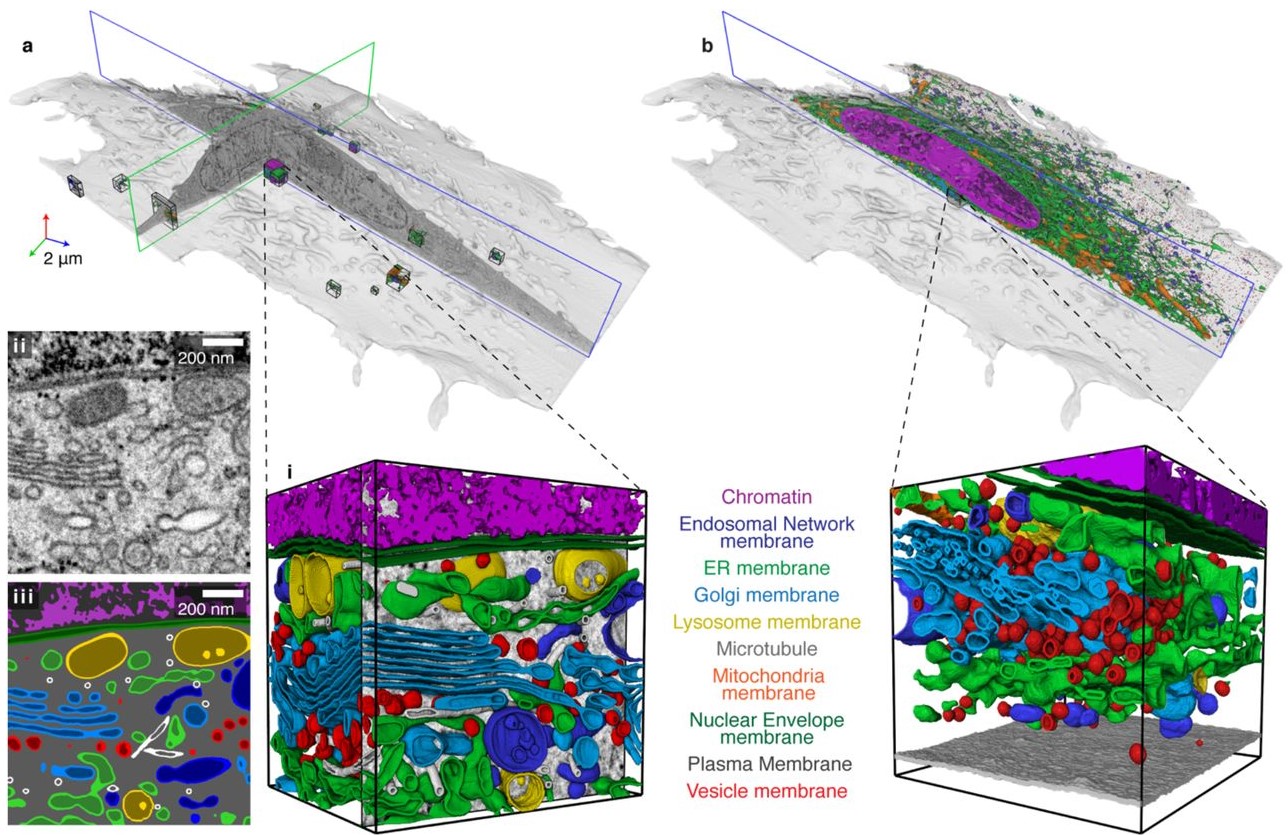
Automatic whole cell organelle segmentation in volumetric electron microscopy
Cells contain hundreds of different organelle and macromolecular assemblies intricately organized relative to each other to meet any cellular demands. Obtaining a complete understanding of their organization is challenging and requires nanometer-level, three-dimensional reconstruction of whole cells. Even then, the immense size of datasets and large number of structures to be characterized requires generalizable, automatic methods.
To meet this challenge, we developed an analy... Read more
Larissa Heinrich, Davis Bennett, David Ackerman, Woohyun Park, John Bogovic, View ORCID ProfileNils Eckstein, Alyson Petruncio, Jody Clements, C. Shan Xu, Jan Funke, Wyatt Korff, Harald F. Hess, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Stephan Saalfeld, Aubrey V. Weigel, COSEM Project Team
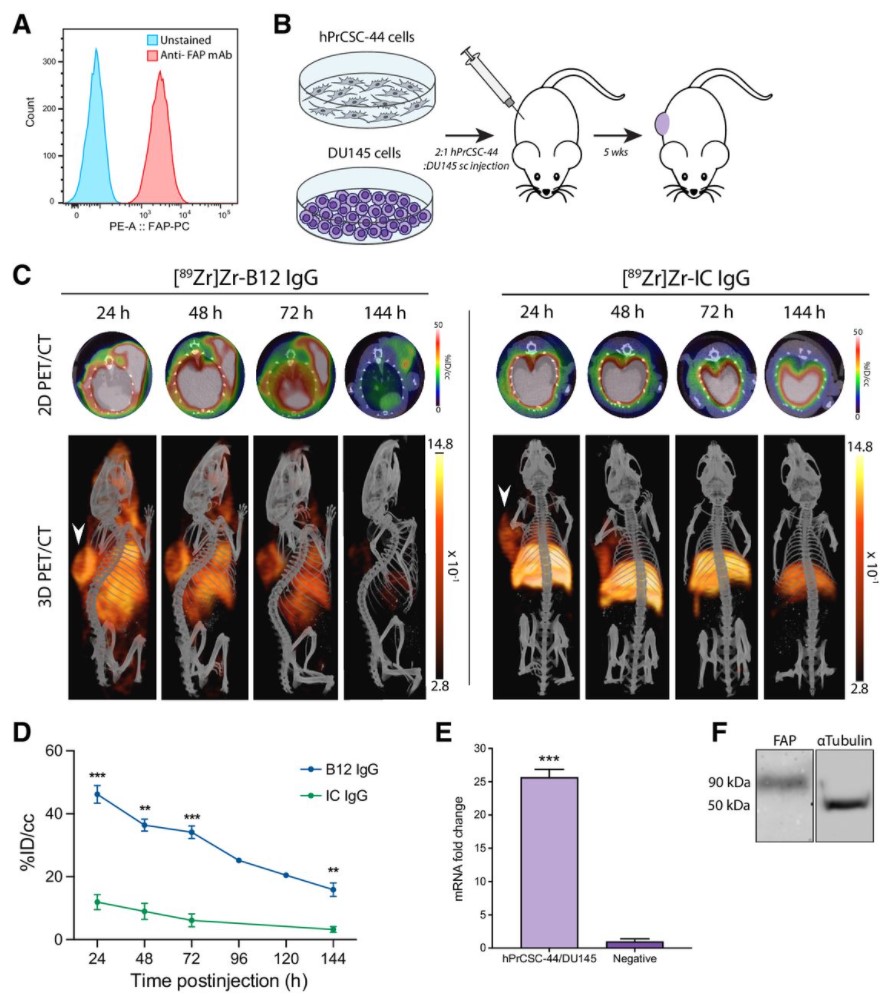
Malignant cells are surrounded by a complex and supportive tumor microenvironment that consists of immune cells, extracellular matrix, vasculature, and fibroblasts. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are the major cell type in the reactive stroma and are known to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis. Fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) is a transmembrane serine protease expressed by CAFs in the microenvironment of epithelial tumors.
Meta-analysis of FAP expression and clinical ... Read more
Hallie M. Hintz, Joseph P. Gallant, Donald J. Vander Griend, Ilsa M. Coleman, Peter S. Nelson and Aaron M. LeBeau
Precise methods for quantifying drug accumulation in brain tissue are currently very limited, challenging the development of new therapeutics for brain disorders. Transcardial perfusion is instrumental for removing the intravascular fraction of an injected compound, thereby allowing for ex vivo assessment of extravasation into the brain. However, pathological remodeling of tissue microenvironment can affect the efficiency of transcardial perfusion, which has been largely overlooked.
We... Read more
Serhii Kostrikov, Kasper B. Johnsen, Thomas H. Braunstein, Johann M. Gudbergsson, Frederikke P. Fliedner, Elisabeth A. A. Obara, Petra Hamerlik, Anders E. Hansen, Andreas Kjaer, Casper Hempel & Thomas L. Andresen
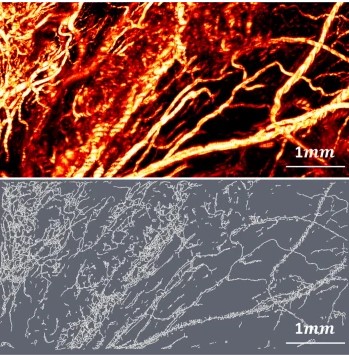
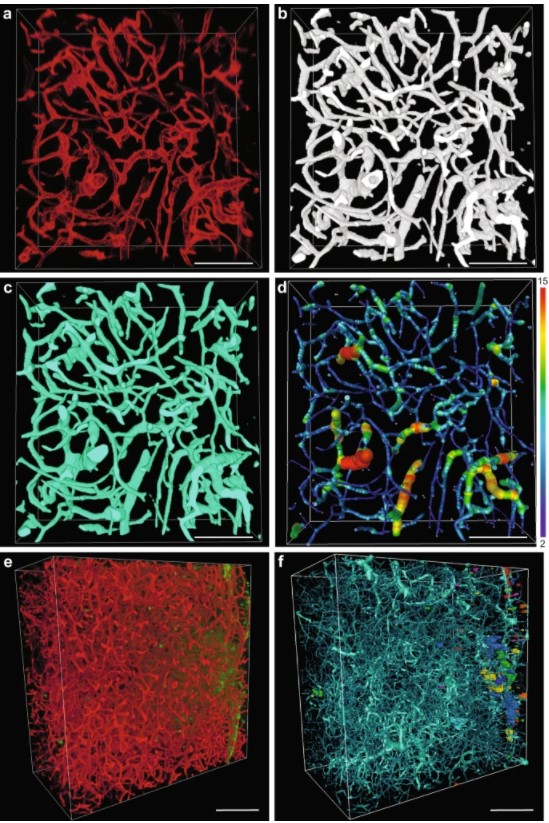
Optical Resolution Photoacoustic Microscopy of Ovary and Fallopian Tube
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among gynecological cancers, but is poorly amenable to preoperative diagnosis. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of “optical biopsy,” using high-optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) to quantify the microvasculature of ovarian and fallopian tube tissue. The technique is demonstrated using excised human ovary and fallopian tube specimens imaged immediately after surgery.
This report describes the first applicatio... Read more
Bin Rao, Xiandong Leng, Yifeng Zeng, Yixiao Lin, Ruimin Chen, Qifa Zhou, Andrea R. Hagemann, Lindsay M. Kuroki, Carolyn K. McCourt, David G. Mutch, Matthew A. Powell, Ian S. Hagemann & Quing Zhu
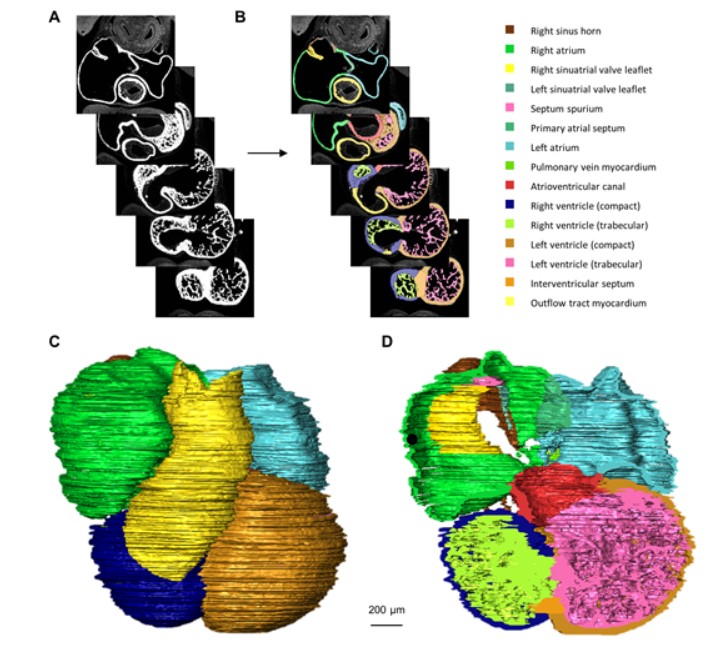
Quantified growth of the human embryonic heart
The size and growth patterns of the components of the human embryonic heart have remained largely undefined.
To provide these data, three-dimensional heart models were generated from immunohistochemically stained sections of ten human embryonic hearts ranging from Carnegie stage 10 to 23. Fifty-eight key structures were annotated and volumetrically assessed. Sizes of the septal foramina and atrioventricular canal opening were also measured. The heart grows exponentially throughout embr... Read more
Jaeike W. Faber, Jaco Hagoort, Antoon F. M. Moorman, Vincent M. Christoffels, Bjarke Jensen
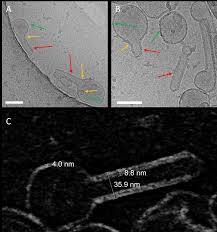
Influenza A matrix protein M1 is sufficient to induce lipid membrane deformation
The matrix protein M1 of the Influenza A virus is considered to mediate viral assembly and budding at the plasma membrane (PM) of infected cells. In order for a new viral particle to form, the PM lipid bilayer has to bend into a vesicle towards the extracellular side. Studies in cellular models have proposed that different viral proteins might be responsible for inducing membrane curvature in this context (including M1), but a clear consensus has not been reached. In this study, we use a comb... Read more
Ismail Dahmani, Kai Ludwig, Salvatore Chiantia
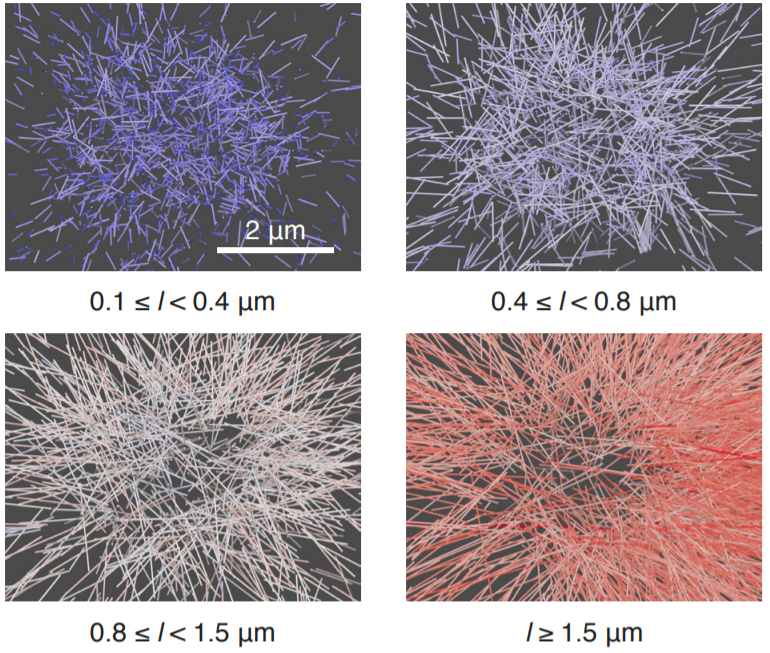
Soluble tubulin is locally enriched at mitotic centrosomes in C. elegans
During mitosis, the centrosome expands its capacity to nucleate microtubules. Understanding the mechanisms of centrosomal microtubule nucleation is, however, constrained by a lack of knowledge of the amount of soluble and polymer tubulin at mitotic centrosomes. Here we combined light microscopy and serial-section electron tomography to measure the amount of dimer and polymer at mitotic centrosomes in early C. elegans embryos. We show that a C. elegans one-cell stage centrosome at metaphase co... Read more
Johannes Baumgart, Marcel Kirchner, Stefanie Redemann, Jeffrey Woodruff, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Frank Julicher, Anthony Hyman, Thomas Mueller-Reichert, Jan Brugues

Each pulmonary segment is an anatomical and functional unit. However, it is fundamentally difficult to precisely distinguish every pulmonary segment using the conventional pulmonary intersegmental planes from computed tomography images. Building arteriopulmonary segments is likely to be an effective way to identify pulmonary segments.
The three-dimensional reconstructed images showed the branches of the pulmonary artery ramified up to their eighth order covering the entire lung as well... Read more
Huijie Gao, Chao Liu
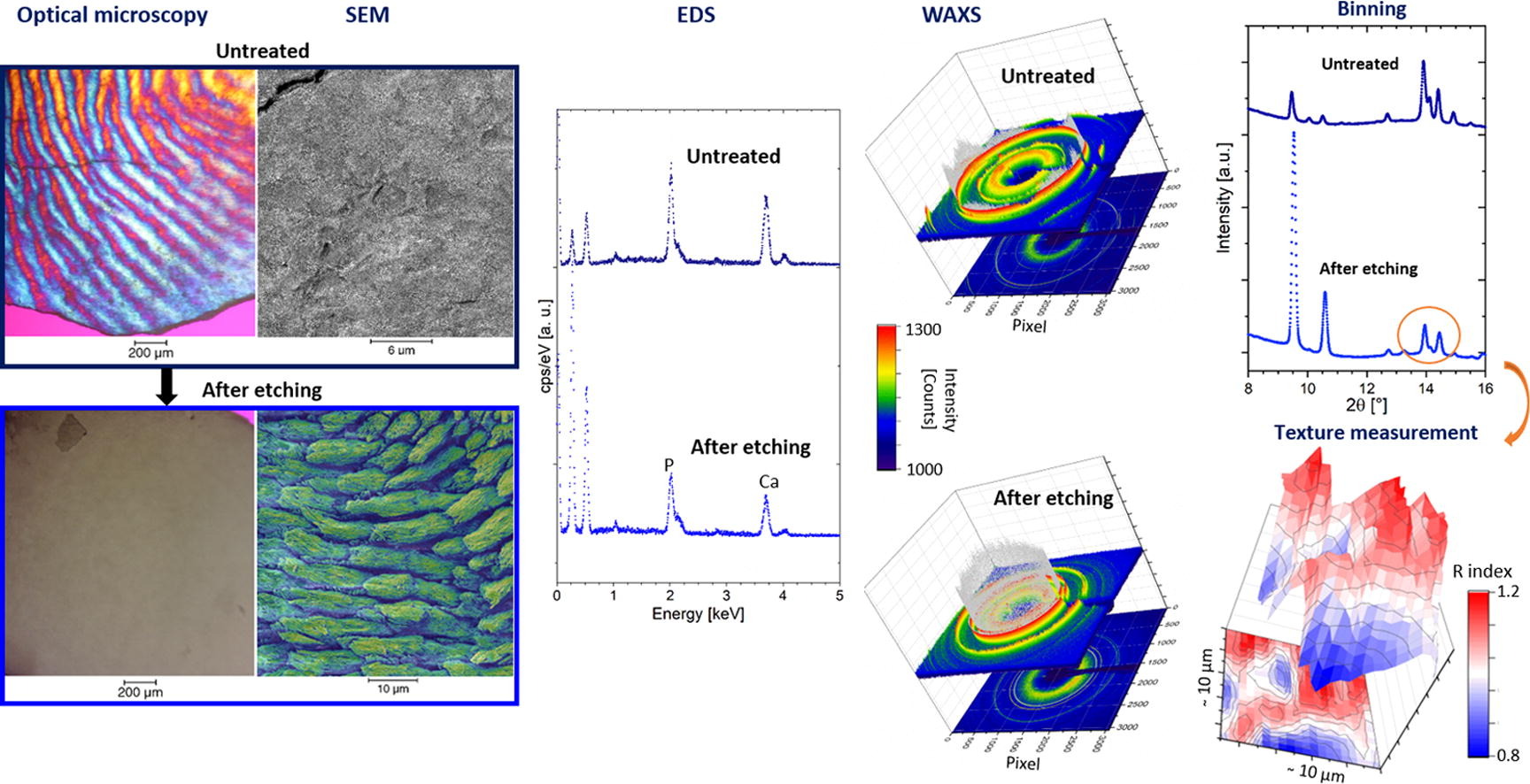
Enamel caries is a highly prevalent worldwide disease that involves the demineralisation of the outer tooth structure. In this study, we report the analysis of artificially demineralised human enamel sections (‘slices’) etched using lactic acid (2% v/v) in comparison with healthy enamel using correlative techniques of optical and electron microscopy, as well as scanning diffraction. Demineralisation of the enamel was characterised at the micron to sub-micron scale. The structure of the he... Read more
Cyril Besnard, Robert A. Harper, Thomas E. J. Moxham, Jonathan D. James, Malte Storm, Enrico Salvati, Gabriel Landini, Richard M. Shelton, Alexander M.Korsunsky
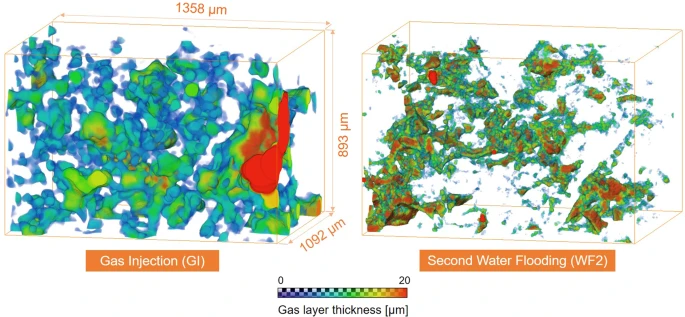
Pore-scale mechanisms of CO2 storage in oilfields
Rapid implementation of global scale carbon capture and storage is required to limit temperature rises to 1.5 °C this century. Depleted oilfields provide an immediate option for storage, since injection infrastructure is in place and there is an economic benefit from enhanced oil recovery. To design secure storage, we need to understand how the fluids are configured in the microscopic pore spaces of the reservoir rock. We use high-resolution X-ray imaging to study the flow of oil, water and ... Read more
Abdulla Alhosani, Alessio Scanziani, Qingyang Lin, Ali Q. Raeini, Branko Bijeljic & Martin J. Blunt
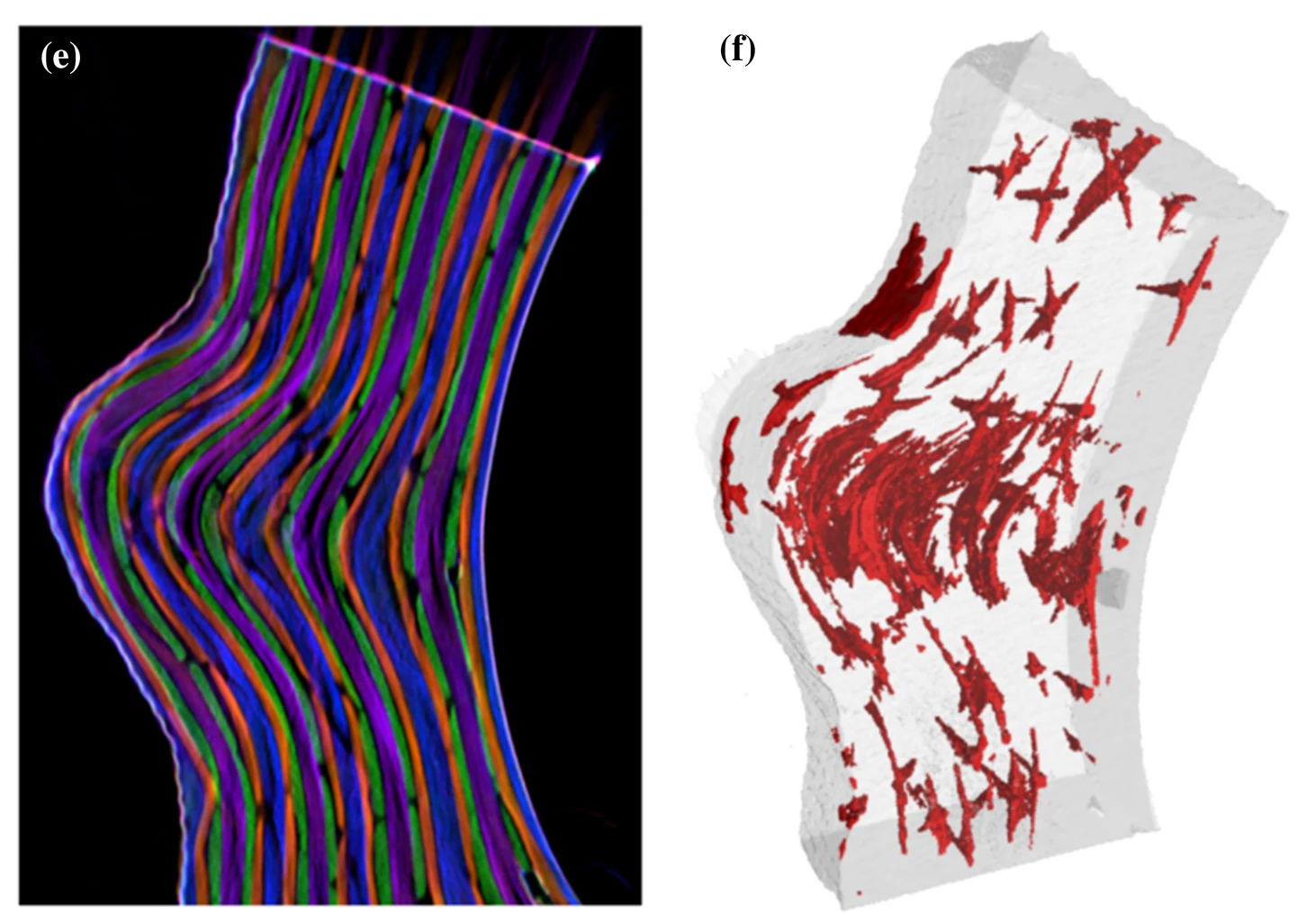
The high strength at moderate weight in combination with superior corrosion and fatigue properties makes carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) an attractive material for lightweight applications in aerospace. Nonetheless, besides several benefits, CFRP components also bear significant risks like a low resistance to impact damage. […] In this work, we present a multimodal approach to three-dimensionally quantify and visualize fiber orientation and resin-rich areas in carbon-fiber-reinf... Read more
Jonathan Glinz, Jan Šleichrt, Daniel Kytýř, Santhosh Ayalur-Karunakaran, Simon Zabler, Johann Kastner & Sascha Senck

Defect structure process maps for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Accurate detection, characterization, and prediction of defects has great potential for immediate impact in the production of fully-dense and defect free metal additive manufacturing (AM) builds. Accordingly, this paper presents Defect Structure Process Maps (DSPMs) as a means of quantifying the role of porosity as an exemplary defect structure in powder bed printed materials. Synchrotron-based micro-computed tomography (μSXCT) was used to demonstrate that metal AM defects follow predictable... Read more
Jerard V.Gordon, Sneha P.Narra, Ross W.Cunningham, He Liu, Hangman Chen, Robert M.Suter, Jack L.Beuth, Anthony D.Rollett
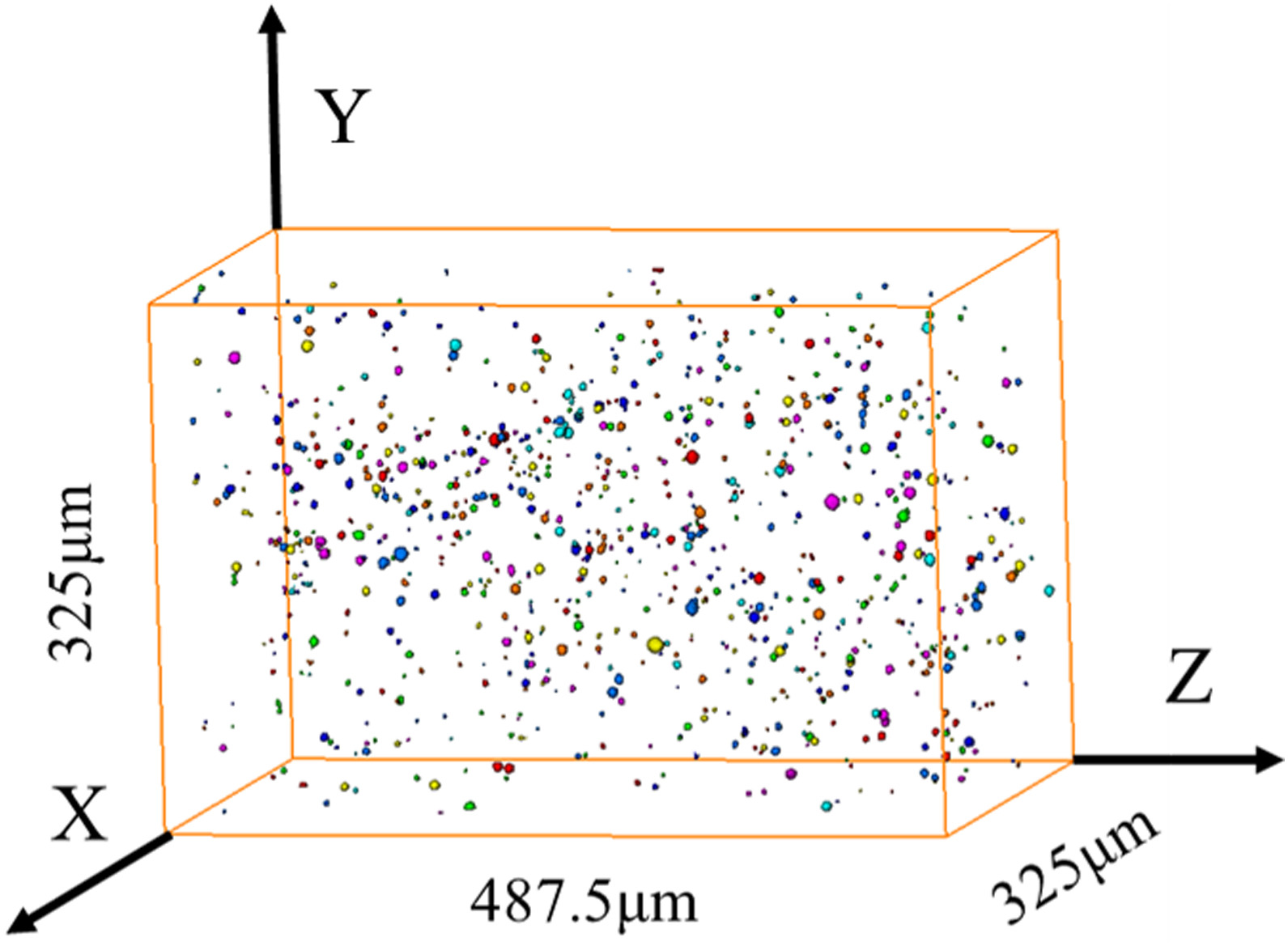
Three-dimensional characterization of typical inclusions in steel
The non-metallic inclusions are mostly harmful to the propertiesof the steel products. The effective characterization of the size, morphology, and distribution of the inclusions in steel is a key issue to remove and control the inclusions in the Read more
Zhiqiang Shang, Tao Li; Shufeng Yang, Jianchuan Yan, Han Guod
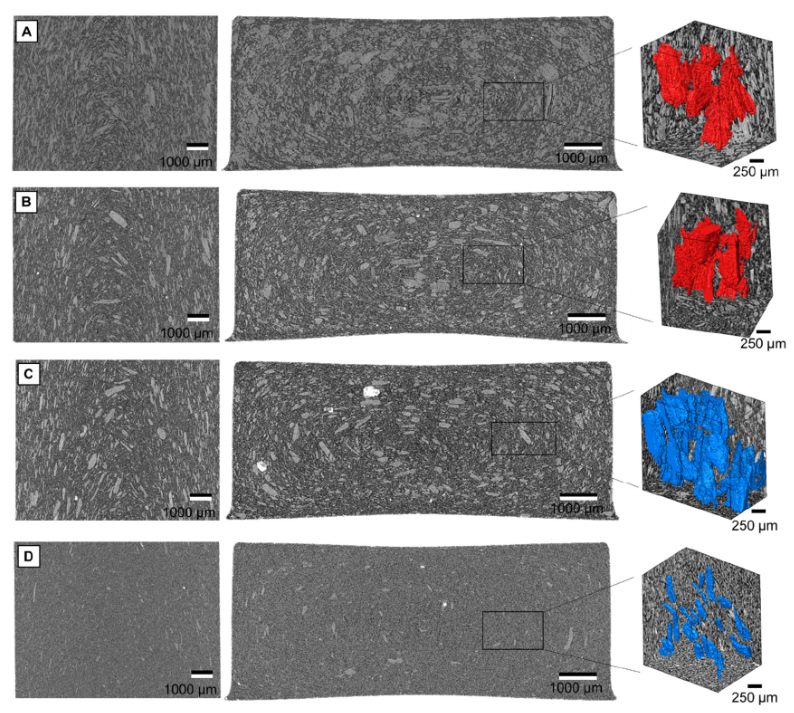
In this study, various wood material sources were used for the manufacture of wood-polymer composites (WPC). The materials were categorised as virgin wood particles (VWP), reprocessed WPC particles (RWP) and recycled thermoset composite particles (RCP) and derived from two virgin wood sources, three-layer particle boards, medium-density fibre boards (MDF) boards,or two different wood/polypropylene composites. All produced wood-polypropylene compounds contained 60% wood material and were manu... Read more
Kim Christian Krause, D, Philipp Sauerbier, Tim Koddenberg and Andreas Krause
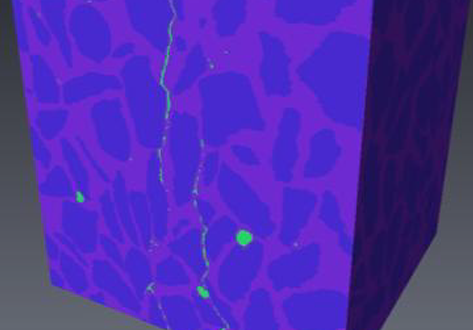
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
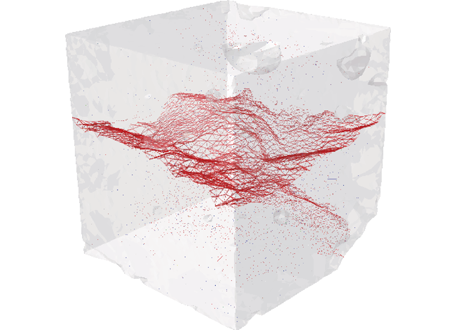
Three-Dimensional In Situ XCT Characterisation and FE Modelling of Cracking in Concrete
An improved understanding of 3D cracking in concrete can be achieved by multiscale experiments and numerical modelling based on realistic microstructures, for the development of materials with higher strength, durability, and fracture resistance.
Three-dimensional (3D) characterisation and modelling of cracking in concrete have been always of great importance and interest in civil engineering. In this study, an in situ microscale X-ray computed tomography (XCT) test was carried out to ... Read more
Wenyuan Ren, Zhenjun Yang, Rajneesh Sharma, Samuel A. McDonald, Paul M. Mummery
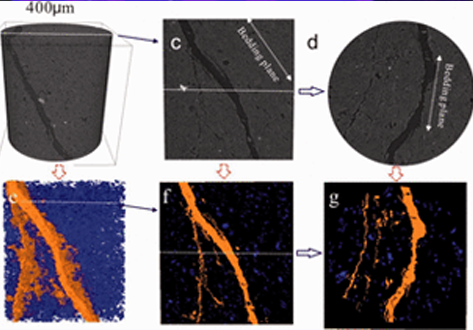
Experimental study on the cracking process of layered shale using X-ray microCT
The cracking process in Longmaxi formation shale was experimentally studied during uniaxial compressive loading. Both the evolution of the three-dimensional fracture network and the micromechanics of failure in the layered shale were examined as a function of the inclination angle of the bedding plane. To visualize the cracking process, the test devices presented here used an industrial X-ray CT scanner that enabled scanning during the uniaxial compressive loading. Scanning electron microscop... Read more
Institue of Geomechanic, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Laboratory of Shale Oil & Gas, Beijing, China
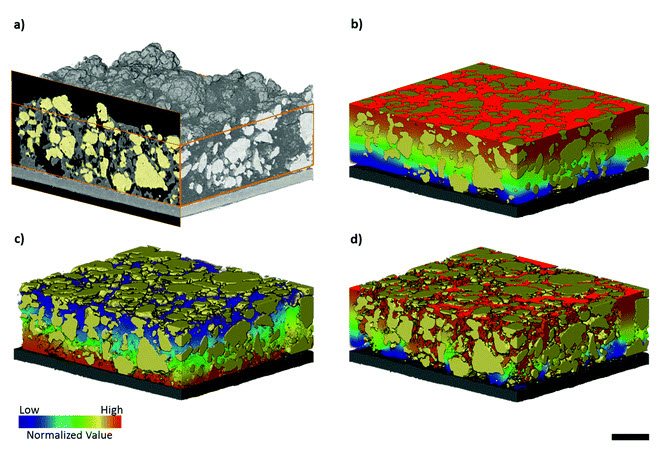
Three-dimensional image based modelling of transport parameters in lithium–sulfur batteries
An elemental sulfur electrode was imaged with X-ray micro and nano computed tomography and segmented into its constituent phases. Morphological parameters including phase fractions and pore and particle size distributions were calculated directly from labelled image data, and flux based simulations were performed to determine the effective molecular diffusivity of the pore phase and electrical conductivity of the conductive carbon and binder phase, D... Read more
Chun Tan, Matthew D. R. Kok , Sohrab R. Daemi , Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
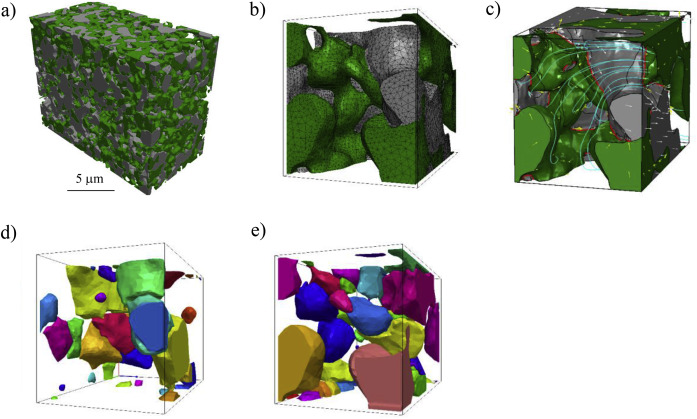
The electrode microstructural properties significantly influence the efficiency and durability of many electrochemical devices including solid oxide fuel cells. Despite the possibility of simulating the electrochemical phenomena within real three-dimensional microstructures, the potential of such 3D microstructural information has not yet been fully exploited. We introduce here a completely new methodology for the advanced characterization of inhomogeneous current distribution base... Read more
A.Bertei, V.Yufit, F.Tariq, N.P.Brandon