3D computational anatomy of the scaphoid and its waist for use in fracture treatment
A detailed understanding of scaphoid anatomy helps anatomic fracture reduction and optimal screw position. Therefore, we analyzed the size and shape variations of the cartilage and osseous surface, the distribution of volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), and if the vBMD values differ between a peripheral and a central screw pathway?
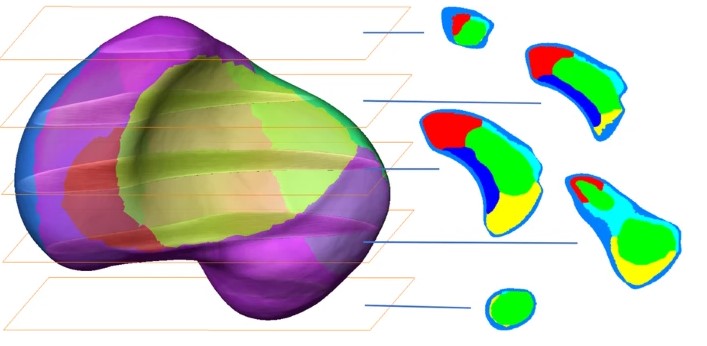
Forty-three fresh frozen hand specimens (17 females, 26 males) were analysed with high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) and dissected to compute a 3D-statistical osseous and cartilage surface model and a 3D-averaged vBMD model of the scaphoid. 3D patterns were analysed using principal component analysis (PCA). vBMD was analysed via averaging HR-pQCT grey values and virtual bone probing along a central and peripheral pathway.
High anatomical variations regarding the osseous and cartilage surfaces were associated with three distinct concentrically arranged zones with notable different vBMD. The complex scaphoid anatomy with its waist might alter the strategy of fracture fixation, education and research.