Microstructure Characterization by X-Ray Computed Tomography of C/C-SiC Ceramic Composites Fabricated with Different Carbon Fiber Architectures
Fan Wan, Talha, J. Pirzada, Rongjun Liu, Yanfei Wang, Changrui Zhang, Thomas James Marrow - College of Aerospace Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China - Department of Materials, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
![Microstructure Characterization by X-Ray Computed Tomography of C/C-SiC Ceramic Composites Fabricated with Different Carbon Fiber Architectures]()
The microstructure morphologies have been characterized by high resolution laboratory X-ray computed tomography in Carbon Fiber Reinforced Carbon and Silicon Carbide (C/C-SiC) ceramic composites fabricated by Gaseous Silicon Infiltration (GSI) from C/C preforms of three different architectures: 3D stitched cloth fabric; 3D orthogonal woven fabric; and needled short-cut felt. Each composites’ microstructure was influenced by the structure of the C/C preform. By incorporating tomography with gravimetric analysis, the 3D distribution of the SiC was visualized, showing a connected SiC network in the needled short-cut felt, and more heterogeneous SiC formation on the surfaces of the fiber bundles in the stitched and woven fabrics. The needled short-cut felt provided the largest contact surface for the GSI reaction and generated ~56% volume fraction of SiC, which is almost twice and three times that achieved in the stitched and woven fabrics respectively. Differences in the open and closed pore distributions were also measured by mercury intrusion porosimetry and tomography.
How Amira-Avizo Software is used
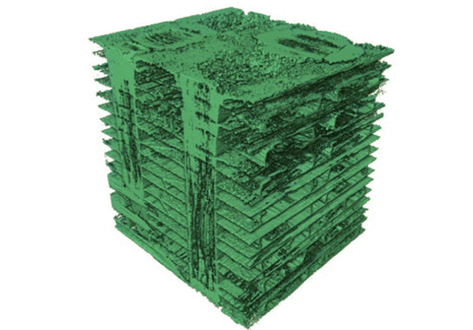
Fig 2: 3D visualizations of C/C preforms by threshold segmentation of tomographs: (a) 3D stitched cloth fabric, architecture ①; (b) 3D orthogonal woven fabric, architecture ②; (c) needled short-cut felt, architecture ③. The carbon is shown in (i), and the porosity in (ii) (cropped by 0.7 mm at top and bottom to show internal structure). In (iii), a central subsection of the porosity (0.42 mm thickness) is shown.
Fig 3: 3D visualizations of the C/C-SiC composites, presented as orthogonal slices of the tomography data: (a) 3D stitched cloth fabric, architecture ①; (b) 3D orthogonal woven fabric, architecture ②; (c) needled short-cut felt, architecture ③
Fig 5: 3D visualizations of C/C-SiC composites, by threshold segmentation of tomographs obtained after acid dissolution to remove Si: (a) 3D stitched cloth fabric, architecture ①; (b) 3D orthogonal woven fabric, architecture ②; (c) needled short-cut felt, architecture ③. The labeled volumes are (i) carbon, (ii) SiC, and (iii) porosity (representing dissolved Si)
Fig 6: Analysis of porosity: (a) pore size distributions for (i) open pores detected from MIP and (ii) closed pores observed in matrix by XCT; (b) 3D visualizations of the closed pores in architecture ① (3D stitched cloth fabric), architecture ② (3D orthogonal woven fabric) and architecture ③ (needled short-cut felt)