Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
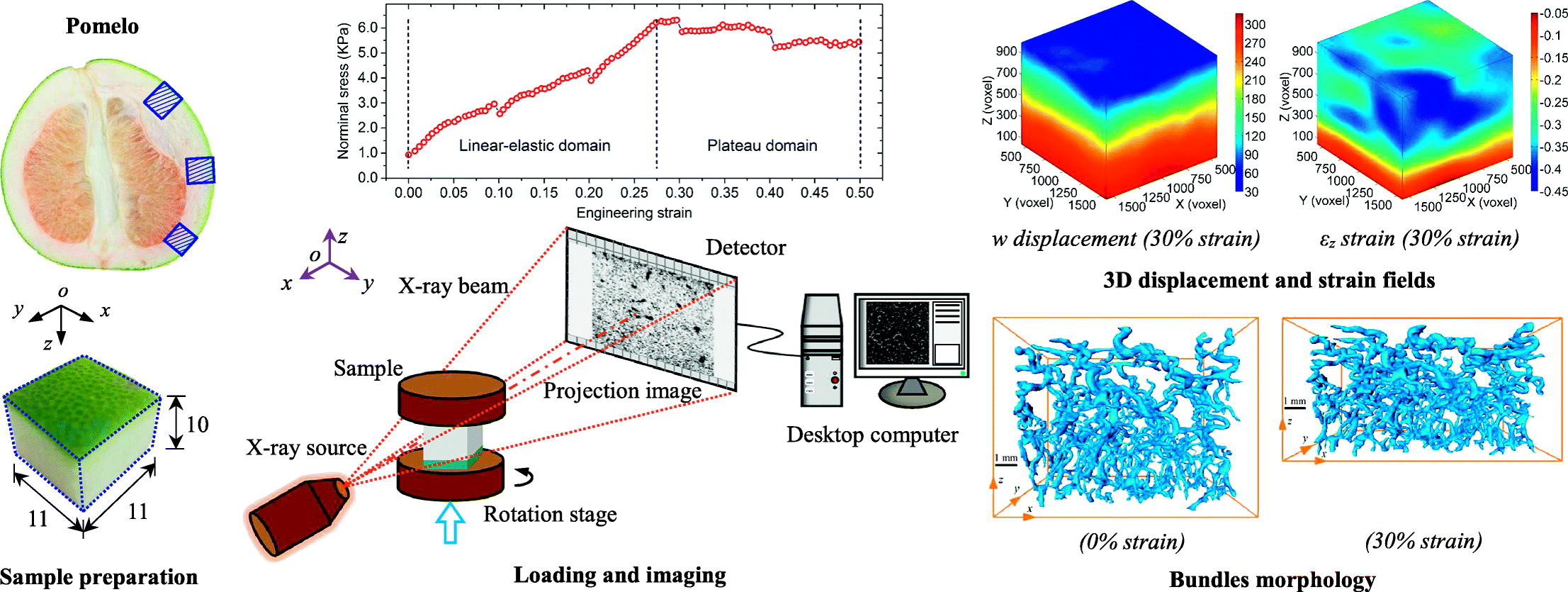
Among natural cellular materials, pomelo peels, having a foam-like hierarchical microstructure, represent an ideal model for developing materials with high energy absorption efficiency. In this work, by combining X-ray tomographic imaging technique and digital volume correlation (DVC), in-situ stepwise uniaxial compression tests were performed to quantify the internal morphological evolution and kinematic responses of pomelo peel samples during compression.
Read more
B.Wang, B.Pan, G.Lubineau
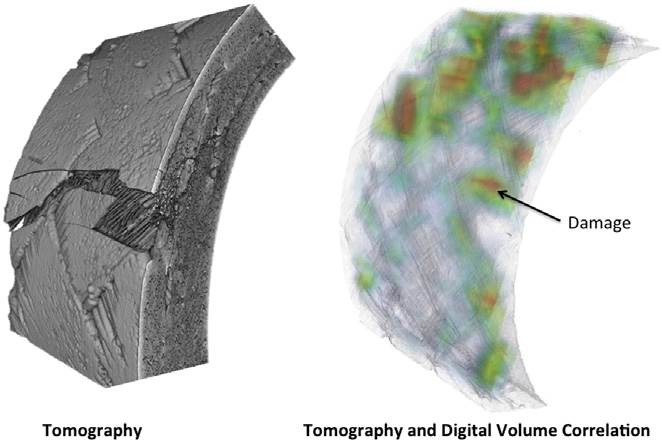
In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite
SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composites are candidate materials for fuel cladding in Generation IV nuclear fission reactors and as accident tolerant fuel clad in current generation plant.
Experimental methods are needed that can detect and quantify the development of mechanical damage, to support modelling and qualification tests for these critical components. In situ observations of damage development have been obtained of tensile and C-ring mechanical test specimens of a braided nuclear gr... Read more
L. Saucedo-Mora, T. Lowe, S. Zhao, P.D. Lee, P.M. Mummery, T.J. Marrow
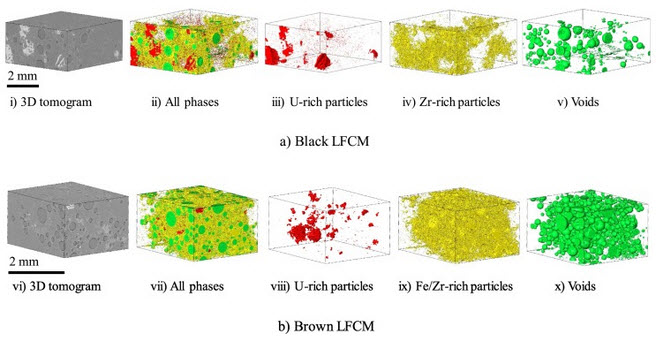
Decommissioning of the damaged Chernobyl nuclear reactor Unit 4 is a top priority for the global community. Before such operations begin, it is crucial to understand the behaviour of the hazardous materials formed during the accident. Since those materials formed under extreme and mostly unquantified conditions, modelling alone is insufficient to accurately predict their physical, chemical and, predominantly, mechanical behaviour. Meanwhile, knowledge of the mechanical characteristics of thos... Read more
C.Paraskevoulakos, J.P.Forna-Kreutzer, K.R.Hallam, C.P.Jones, T.B.Scott, C.Gausse, D.J.Bailey, C.A.Simpson, D.Liu, C.Reinhard, C.L.Corkhill, M.Mostafavi
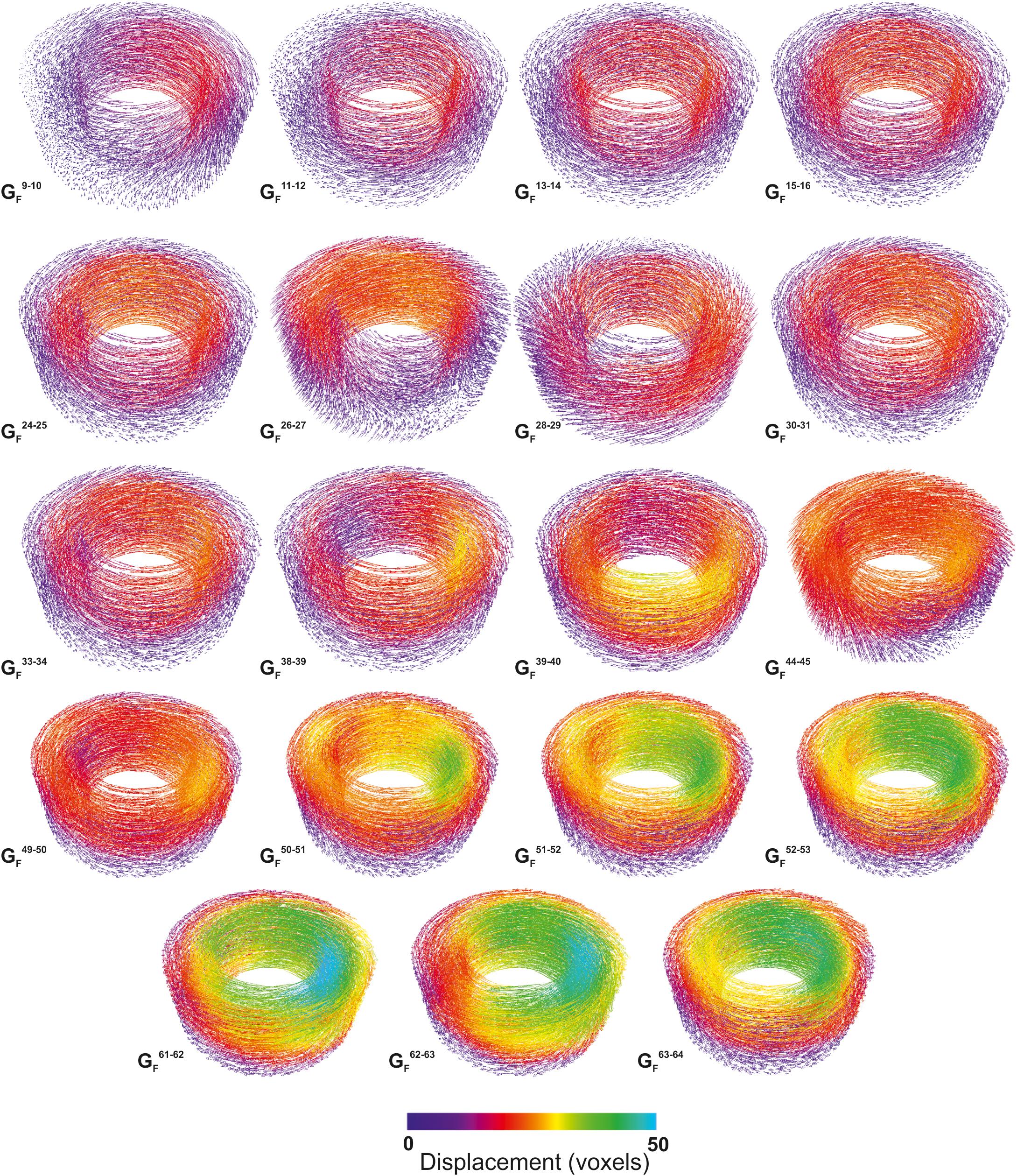
Quantifying Microstructural Evolution in Moving Magma
Many of the grand challenges in volcanic and magmatic research are focused on understanding the dynamics of highly heterogeneous systems and the critical conditions that enable magmas to move or eruptions to initiate. However, we are usually unable to observe the processes directly. Here we give a short synopsis of the new capabilities and highlight the potential insights that in situ observation can provide. We present the first 3D data showing the evolving textural heterogeneity within a sh... Read more
Katherine J. Dobson1, Anja Allabar, Eloise Bretagne, Jason Coumans, Mike Cassidy, Corrado Cimarelli, Rebecca Coats, Thomas Connolley, Loic Courtois, Donald B. Dingwell, Danilo Di Genova, Benjamin Fernando, Julie L. Fife, Frey Fyfe, Stephan Gehne, Thomas Jones, Jackie E. Kendrick, Helen Kinvig, Stephan Kolzenburg, Yan Lavallée, Emma Liu, Edward W. Llewellin, Amber Madden-Nadeau, Kamel Madi, Federica Marone, Cerith Morgan, Julie Oppenheimer, Anna Ploszajski, Gavin Reid, Jenny Schauroth, Christian M. Schlepütz, Catriona Sellick, Jérémie Vasseur, Felix W. von Aulock, Fabian B. Wadsworth, Sebastian Wiesmaier and Kaz Wanelik
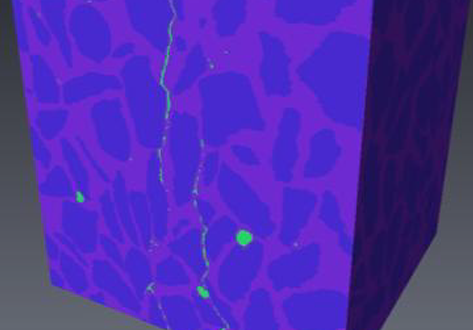
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
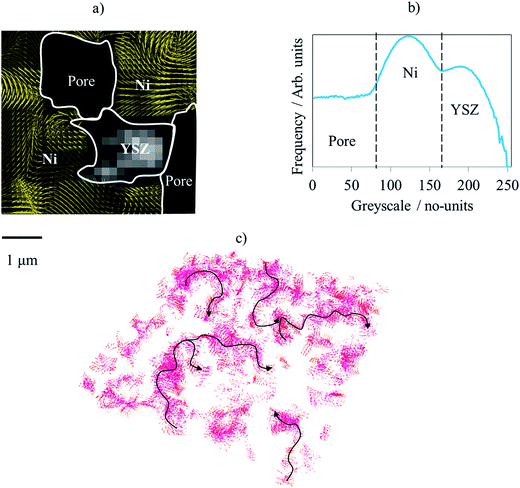
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
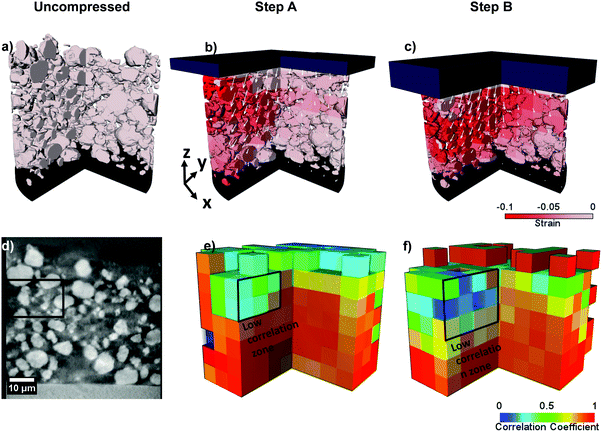
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing