Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
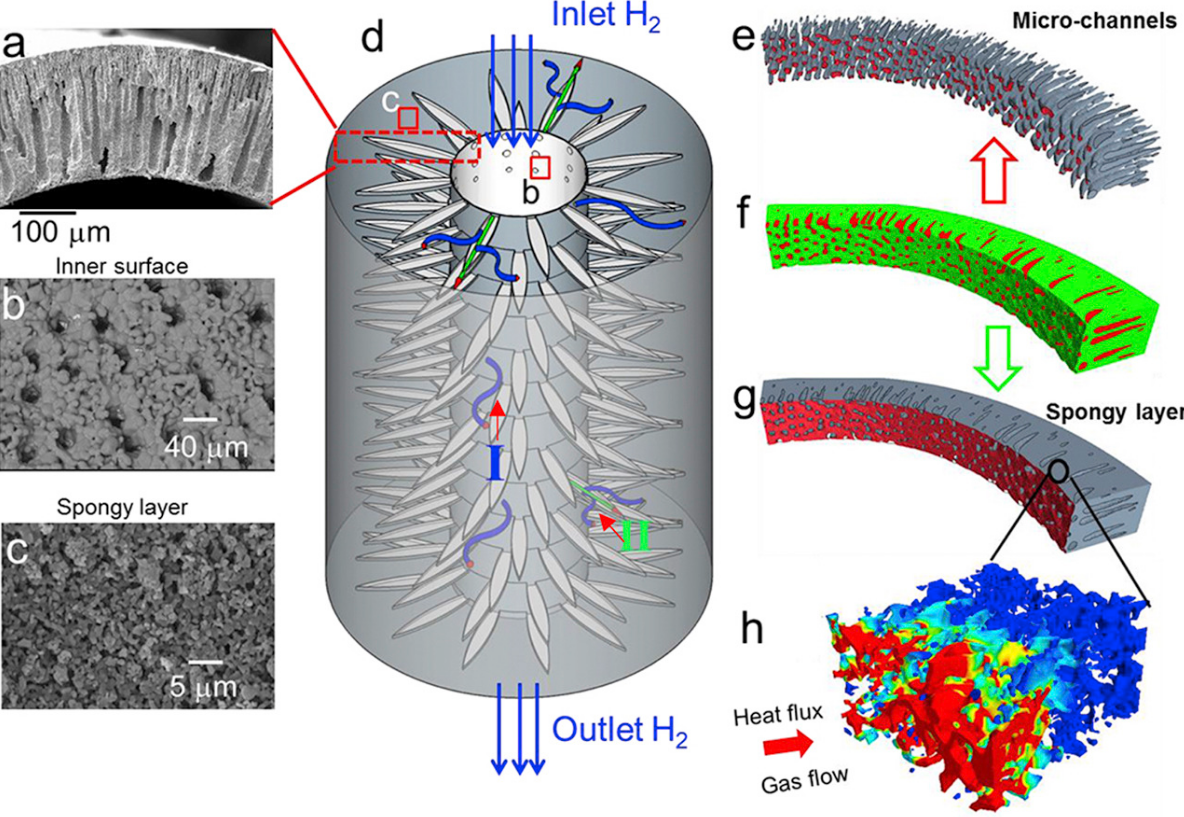
Our parametric study shows that increasing the porosity in the spongy layer beyond 10% enhances the effective transport parameters of the spongy layer at an exponential rate, but linearly for the full anode. For the first time, local and global mass transport properties are correlated to the microstructure, which is of wide interest for rationalizing the design optimization of SOFC electrodes and more generally for hierarchical materials in batteries and membranes.
Read more
Xuekun Lu, Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo, Antonio Bertei, Tao Li, Kang Li, Dan J.L. Brett, Paul R.Shearing
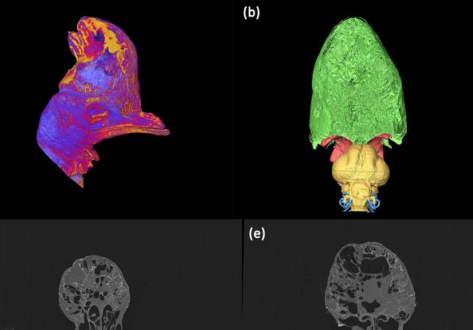
Cranial ornaments such as keratinous horns and bony casques are commonplace amongst birds and take a variety of diverse forms. Possible functions include display, thermoregulation, vocalisation and intraspecific combat, yet few hypotheses have been directly tested. Here we investigate the anatomy and mechanics of the casque of the Southern Cassowary (Casuarius casuarius), and test functional hypotheses using CT-based virtual dissection.
In particular, we determine the nature of pneumat... Read more
Charlotte A. Brassey , Thomas O’Mahoney
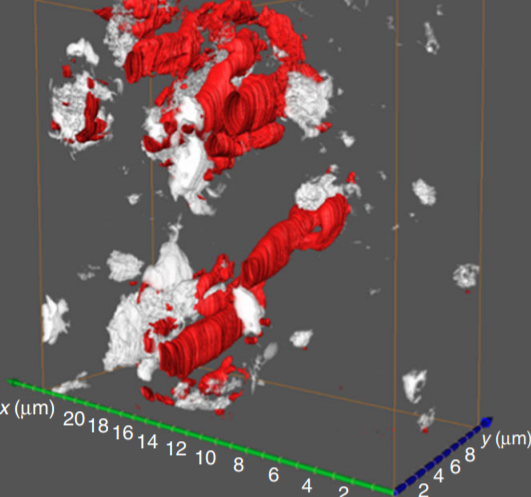
Durable and self-hydrating tungsten carbide-based composite polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
Proton conductivity of the polymer electrolyte membranes in fuel cells dictates their performance and requires sufficient water management. Here, we report a simple, scalable method to produce well-dispersed transition metal carbide nanoparticles. We demonstrate that these, when added as an additive to the proton exchange Nafion membrane, provide significant enhancement in power density and durability over 100 hours, surpassing both the baseline Nafion and platinum-containing recast Nafion ... Read more
Weiqing Zheng, Liang Wang, Fei Deng, Stephen A. Giles, Ajay K. Prasad, Suresh G. Advani, Yushan Yan & Dionisios G. Vlachos
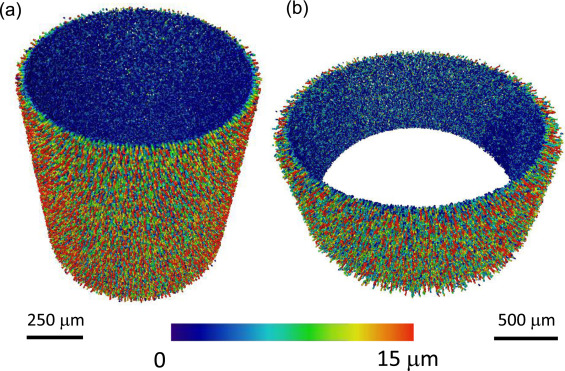
In this study, a series of alumina hollow fibers have been prepared with varied polymer binder (polyethersulfone, PESf) concentration and new polymer-based internal coagulant (aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol, PVA). For the first time, the micro-channels were characterized in 3D using X-ray CT to determine micro-channel densities and diameters in the radial direction, as well as the 2D measurement of the pore size in the sponge-like layer.
Read more
Tao Li, Xuekun Lu, Bo Wang, Zhentao Wu, Kang Li, Dan J.L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing
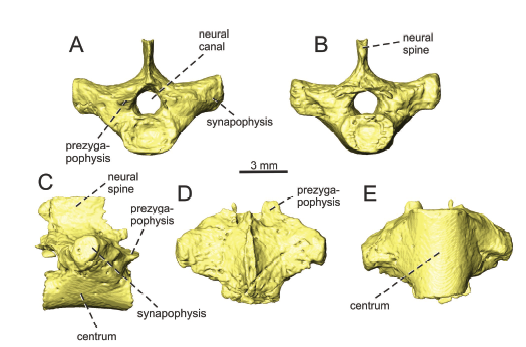
An eosauropterygian skeleton found in the Middle Triassic (upper Anisian) Gutenstein Formation of the Fatric Unit (Demänovská dolina Valley, Low Tatra Mountains, Slovakia) represents the earliest known occurrence of marine tetrapods in the Western Carpathians. The specimen represents a partly articulated portion of the postcranial skeleton (nine dorsal vertebrae, coracoid, ribs, gastral ribs, pelvic girdle, femur and one zeugopodial element). It is assigned to the Pachypleurosauria, more pr... Read more
ANDREJ ČERŇANSKÝ, NICOLE KLEIN, JÁN SOTÁK, MÁRIO OLŠAVSKÝ, JURAJ ŠURKA, and PAVEL HERICH
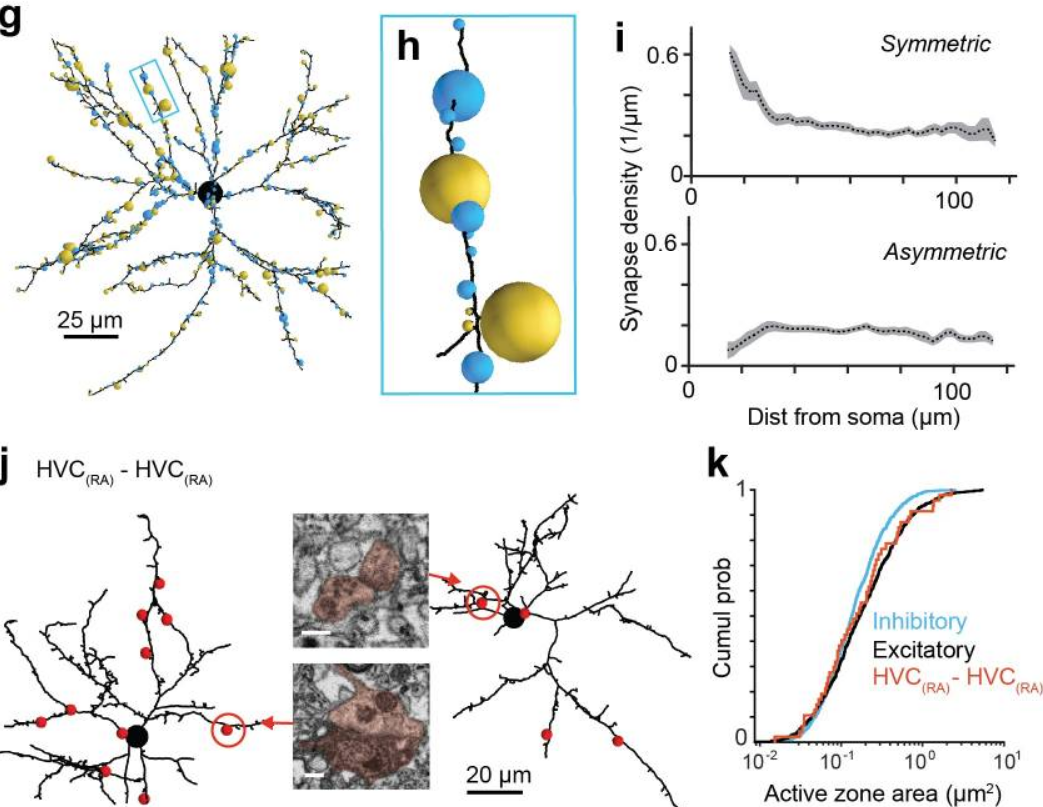
EM connectomics reveals axonal target variation in a sequence-generating network
The sequential activation of neurons has been observed in various areas of the brain, but in no case is the underlying network structure well understood. Here we examined the circuit anatomy of zebra finch HVC, a cortical region that generates sequences underlying the temporal progression of the song. We combined serial block-face electron microscopy with light microscopy to determine the cell types targeted by HVC(RA) neurons, which control song timing. Close to their soma, axons... Read more
Jörgen Kornfeld, Sam E Benezra, Rajeevan T Narayanan, Fabian Svara, Robert Egger, Marcel Oberlaender, Winfried Denk, Michael A Long
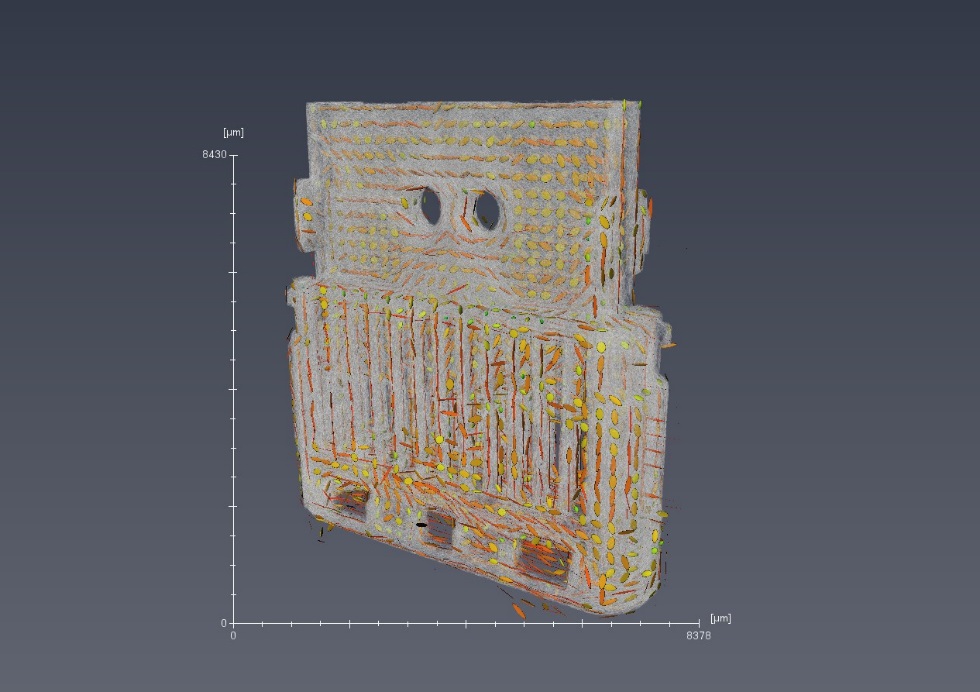
Glass fiber length and orientation analysis of reinforced polymers (GFRP)
Royal DSM is a global science-based company active in health, nutrition and
materials. Within DSM’s Materials Cluster DSM Engineering Plastics is a global player in specialty plastics. These materials are used in components for the electrical and electronics, automotive, flexible food packaging and consumer goods industries.
A typical product made of DSM Engineering Plastics’ polymer portfolio are USB-C connectors. Key performance indicators for this application are dimension... Read more
Jennifer Schillings, Arno Wilbers and Joachim Loos, DSM Materials Science Center, Geleen, The Netherlands
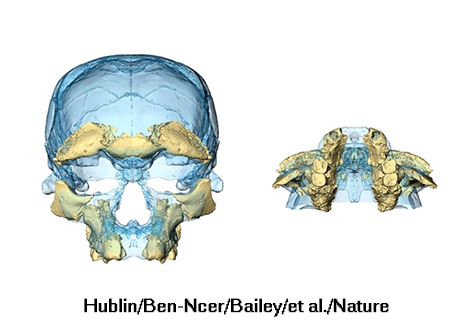
Scientists discover the oldest Homo sapiens fossils at Jebel Irhoud, Morocco
New finds of fossils and stone tools from the archaeological site of Jebel Irhoud, Morocco, push back the origins of our species by one hundred thousand years and show that by about 300 thousand years ago important changes in our biology and behaviour had taken place across most of Africa.
Read more
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig, Germany)
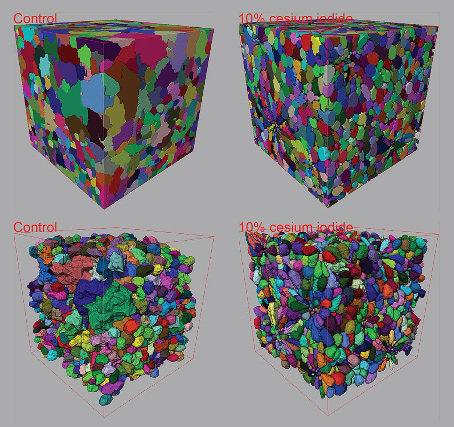
Contrast-enhanced 3D micro-CT of plant tissues using different impregnation techniques
X-ray micro-CT has increasingly been used for 3D imaging of plant structures. At the micrometer reso-lution however, limitations in X-ray contrast often lead to datasets with poor qualitative and quantitative measures, especially within dense cell clusters of plant tissue specimens. The current study developed protocols for delivering a cesium based contrast enhancing solution to varying plant tissue specimens for the purpose of improving 3D tissue structure characterization within plant spec... Read more
Zi Wang, Pieter Verboven and Bart Nicolai, Department of Biosystems KU Leuven – University of Leuven Willem de Croylaan, Leuven Belgium
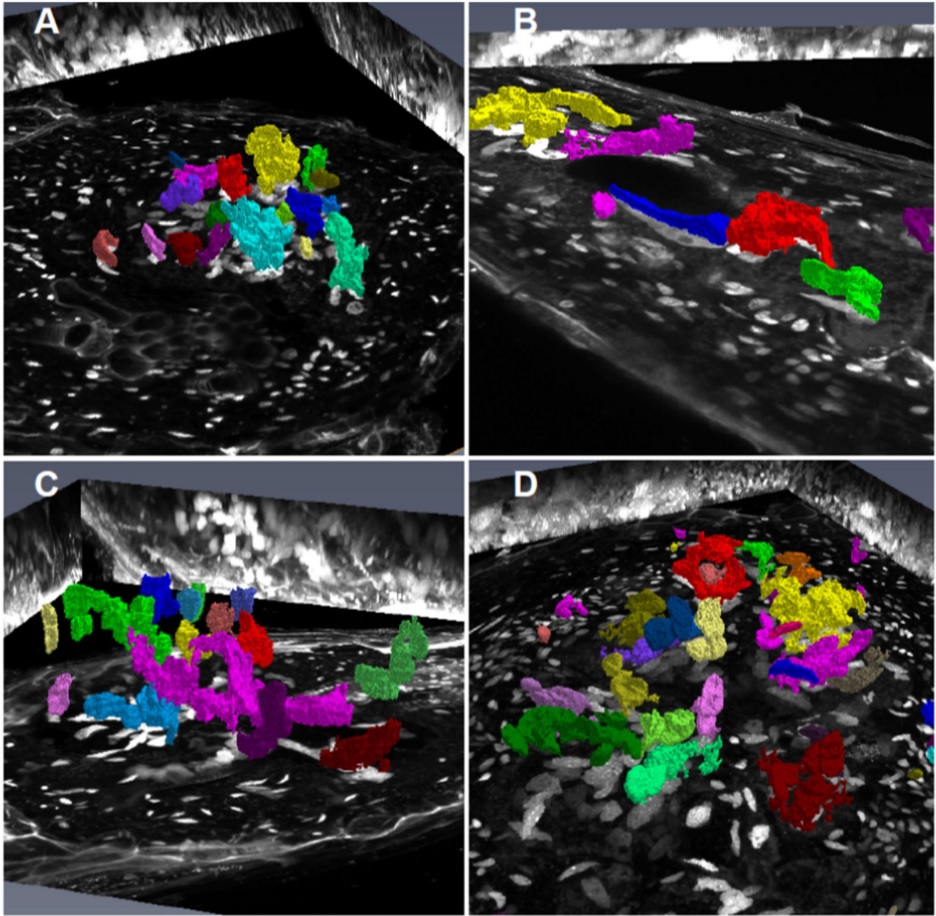
Root-knot nematodes induce galls that contain giant-feeding cells harboring multiple enlarged nuclei within the roots of host plants. It is recognized that the cell cycle plays an essential role in the set-up of a peculiar nuclear organization that seemingly steers nematode feeding site induction and development. Functional studies of a large set of cell cycle genes in transgenic lines of the model host Arabidopsis thaliana have contributed to better understand the role of the cell cycle comp... Read more
Antonino de Souza Junior José Dijair, Pierre Olivier, Coelho Roberta R., Grossi-de-Sa Maria F., Engler Gilbert, de Almeida Engler Janice / Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, Université Côte d’Azur, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Institut Sophia Agrobiotech, Sophia-Antipolis, France
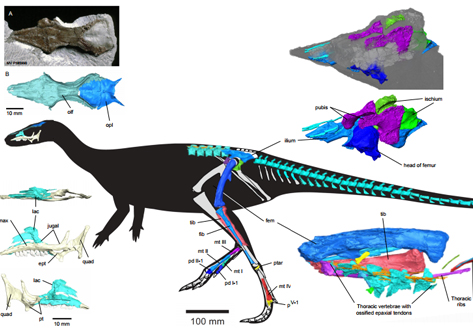
Revealing the skeleton of polar dinosaur using synchrotron computed tomography
Leaellynasaura amicagraphica was a small, bipedal, herbivorous dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (~106 million years ago) of Australia within the Antarctic Circle of that time.
Synchrotron scans, and the resulting 3D reconstruction of the skull and post-cranial skeleton, provide a unique view of the morphology of Leaellynasaura, and allows this material to be 3D printed for display.
Read more
1University College London, UK; Monash University, Melbourne, Australia; Museum Victoria, Melbourne, Australia
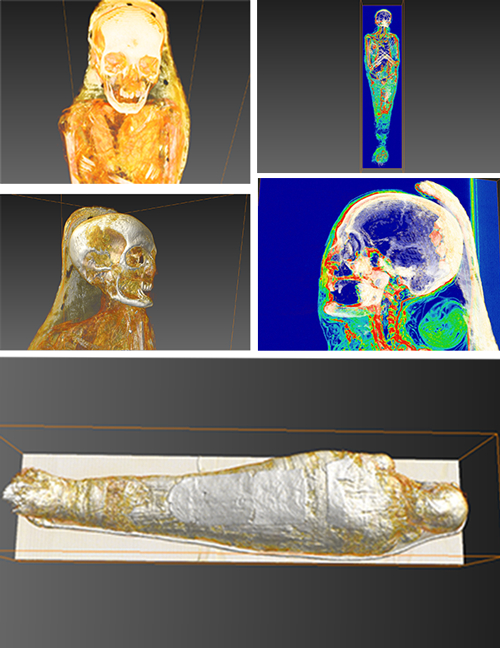
AMSC Research, LLC uses Amira software to understand processes and rituals of Egyptian mummification
“Scanning is important, but it is really just the first step in an immersive exploration of artifacts” says Elias. Raw data from scans taken of mummies (or other archaeological subject matter) is delivered to AMSC Research as files in a language known as DICOM. Next, these are converted into a visually readable form for analytical purposes and to launch the creative modeling process.
Elias uses Amira software to analyze scan data. Mummies are biological entities, so apart f... Read more
Dr. Jonathan Elias, AMSC Research, LLC
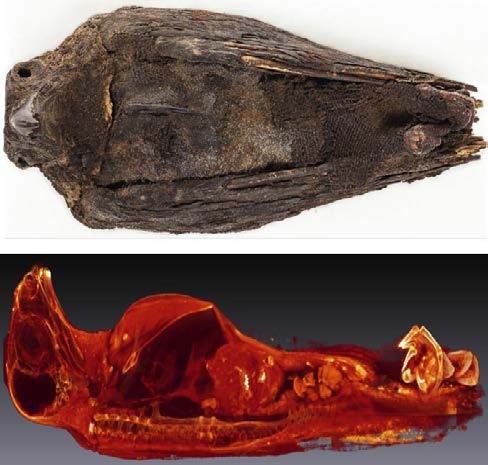

Entering this special exhibit at the Oriental Institute Museum at the University of Chicago, you will immediately feel transported into the ancient Nile delta marshlands with its lush green flora.
The combination of colors, video footage, bird songs, and ancient artifacts will give you the impression that you have just traveled through time and space.
At the start of the exhibit, you will find one of their most impressive artifacts, an empty shell of an ostrich egg from 3100 B... Read more
Rozenn Bailleul-LeSuer, The University of Chicago, Department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations

The University of Birmingham uses Avizo software to explore the North Sea as it was 10,000 years ago
The IBM Visual and Spatial Technology Centre (VISTA) specialize in large scale data capture, analysis and visualization for the Arts and Humanities at the University of Birmingham, UK. The VISTA Centre supports interdisciplinary academic research and application development for visualization, spatial analysis and imaging using state-ofthe- art technology.
Avizo software is a fundamental tool that provides new opportunities for data... Read more
IBM Visual and Spatial Technology Centre, Institute of Archaeology, Birmingham Archaeology, University of Birmingham, UK
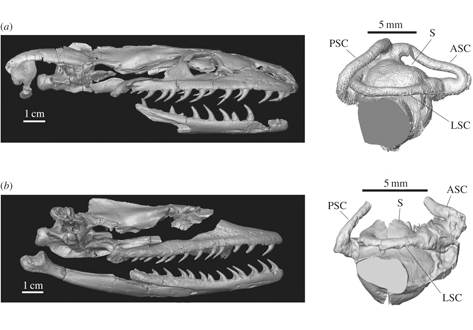
Madtsoiids are among the most basal snakes, with a fossil record dating back to the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian). Most representatives went extinct by the end of the Eocene, but some survived in Australia until the Late Cenozoic. Yurlunggur and Wonambi are two of these late forms, and also the best-known madtsoiids to date. A better understanding of the anatomy and palaeoecology of these taxa may shed light on the evolution and extinction of this poorly known group of s... Read more
Alessandro Palci, Mark N. Hutchinson, Michael W. Caldwell, John D. Scanlon, Michael S. Y. Lee
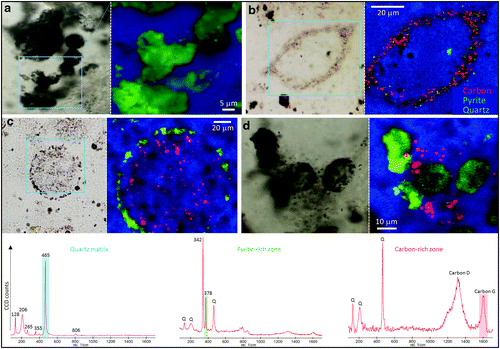
Volcanogenic Pseudo-Fossils from the ∼3.48 Ga
The ∼3.48 billion-year-old Dresser Formation, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia, is a key geological unit for the study of Earth’s earliest life and the habitats it occupied. Here, we describe a new suite of spheroidal to lenticular microstructures that morphologically resemble some previously reported Archean microfossils. Correlative microscopy shows that these objects have a size distribution, wall ultrastructure, and chemistry that are incompatible with a microfossil origin and in... Read more
Wacey David , Noffke Nora , Saunders Martin , Guagliardo Paul , and Pyle David M
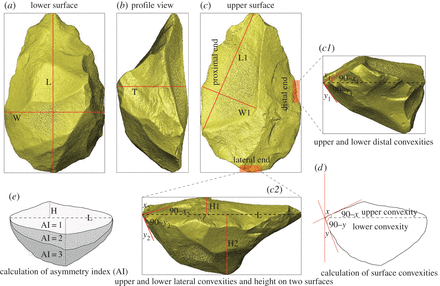
Prepared core technology illustrates in-depth planning and the presence of a mental template during the core reduction process. This technology is, therefore, a significant indicator in studying the evolution of abstract thought and the cognitive abilities of hominids. Here, we report on Victoria West cores excavated from the Canteen Kopje site in central South Africa, with a preliminary age estimate of approximately 1 Ma (million years ago) for these cores. Technological analysis shows tha... Read more
Hao Li, Kathleen Kuman, Matt G. Lotter, George M. Leader, Ryan J. Gibbon
The first Neanderthal remains from an open-air Middle Palaeolithic site in the Levant
The late Middle Palaeolithic (MP) settlement patterns in the Levant included the repeated use of caves and open landscape sites. The fossil record shows that two types of hominins occupied the region during this period—Neandertals and Homo sapiens. Until recently, diagnostic fossil remains were found only at cave sites. Because the two populations in this region left similar material cultural remains, it was impossible to attribute any open-air site to either species. In this study... Read more
Ella Been, Erella Hovers, Ravid Ekshtain, Ariel Malinski-Buller, Nuha Agha, Alon Barash, Daniella E. Bar-Yosef Mayer, Stefano Benazzi, Jean-Jacques Hublin, Lihi Levin, Noam Greenbaum, Netta Mitki, Gregorio Oxilia, Naomi Porat, Joel Roskin, Michalle Soudack, Reuven Yeshurun, Ruth Shahack-Gross, Nadav Nir, Mareike C. Stahlschmidt, Yoel Rak & Omry Barzilai
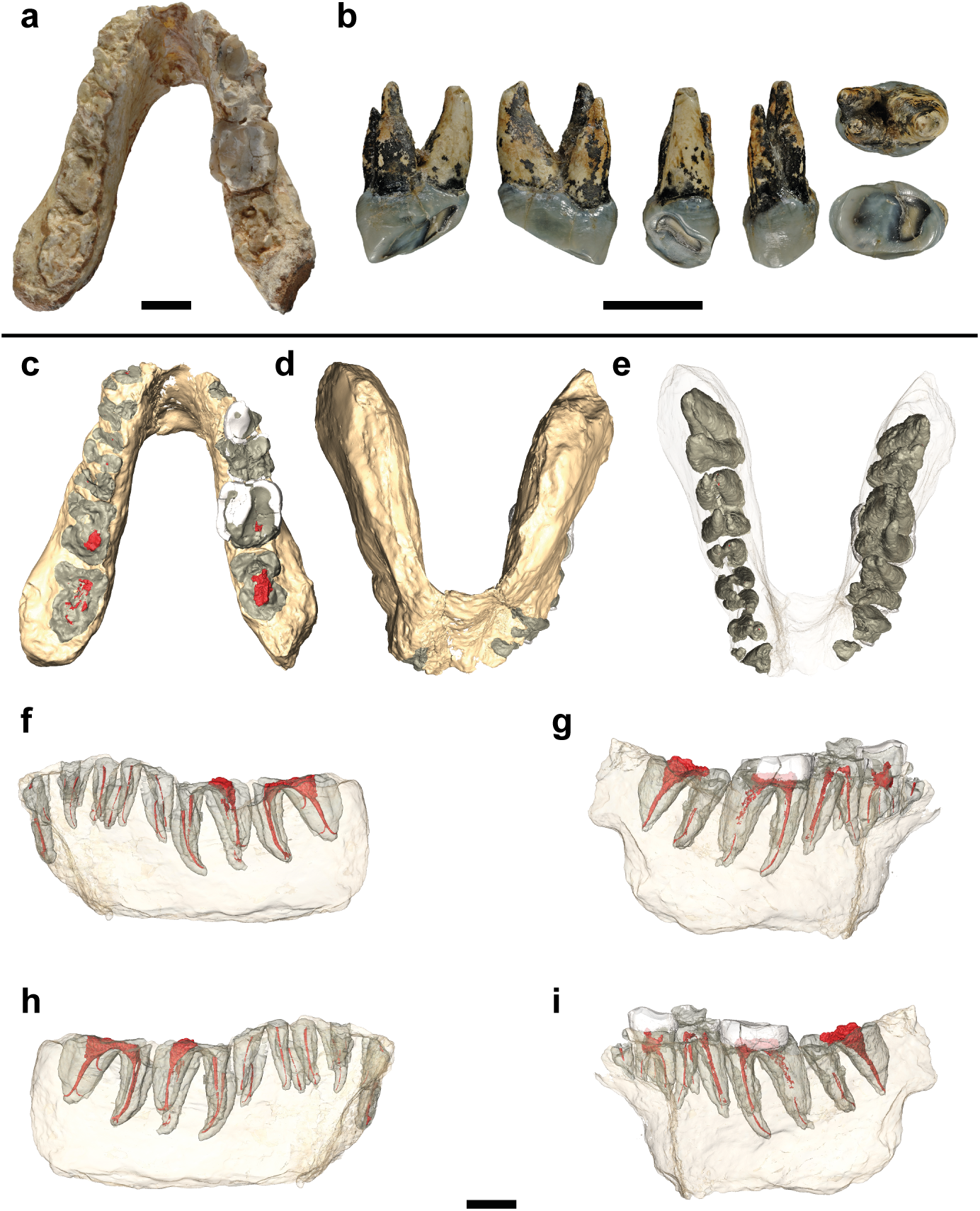
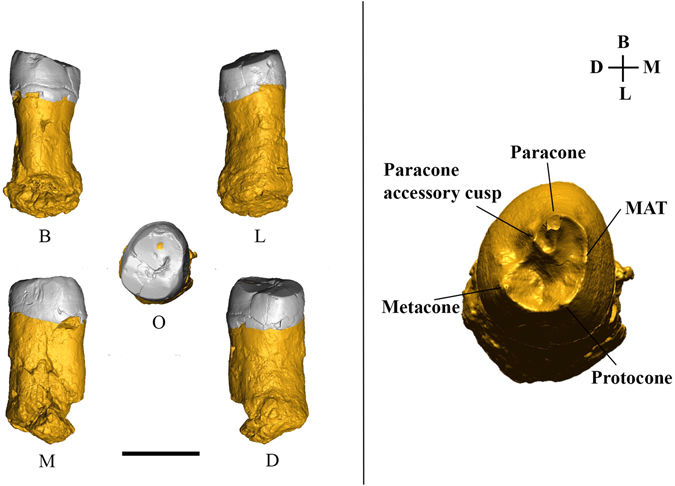
Potential hominin affinities of Graecopithecus from the Late Miocene of Europe
The split of our own clade from the Panini is undocumented in the fossil record. To fill this gap we investigated the dentognathic morphology of Graecopithecus freybergi from Pyrgos Vassilissis (Greece) and cf. Graecopithecus sp. from Azmaka (Bulgaria), using new μCT and 3D reconstructions of the two known specimens. Pyrgos Vassilissis and Azmaka are currently dated to the early Messinian at 7.175 Ma and 7.24 Ma. Mainly based on its external preservation and the previou... Read more
Jochen Fuss, Nikolai Spassov, David R. Begun, Madelaine Böhme
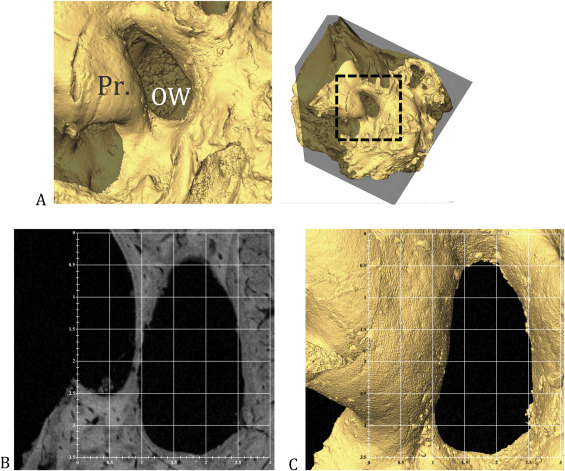
Echoes from the past: New insights into the early hominin cochlea from a phylo-morphometric approach
Investigation on cochlear variation, an indirect evidence of auditory capacities among early hominins and extant catarrhine species, in order to assess (i) the phylogenetic signal of relative external cochlear length (RECL) and oval window area (OWA), the evolutionary model with the highest probability of explaining our observed data, some hominin ancestral nodes for RECL and OWA. RECL has a high phylogenetic signal under a Brownian motion model, and is closely correlated with body mass. Our... Read more
José Braga, Priscille Bouvier, Jordan Romeyer Dherbey, Patricia Balaresque, Laurent Risser , Jean-Michel Loubes , Jean Dumoncel , Benjamin Duployer , Christophe Tenailleau
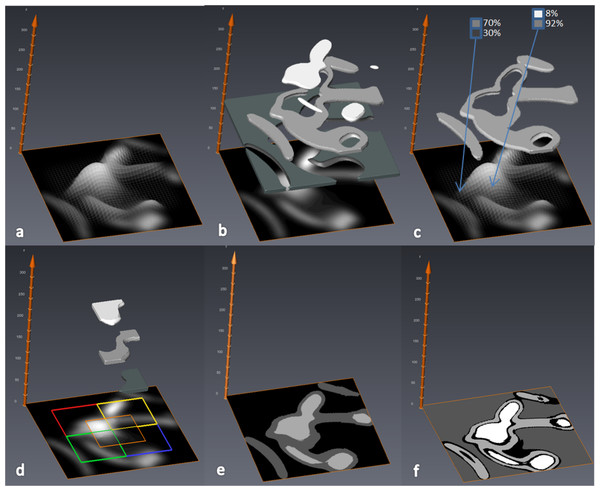
MIA-Clustering: a novel method for segmentation of paleontological material
Paleontological research increasingly uses high-resolution micro-computed tomography (μCT) to study the inner architecture of modern and fossil bone material to answer important questions regarding vertebrate evolution. This non-destructive method allows for the measurement of otherwise inaccessible morphology. Digital measurement is predicated on the accurate segmentation of modern or fossilized bone from other structures imaged in μCT scans, as errors in segmentation can result in inaccur... Read more
Christopher J. Dunmore, Gert Wollny, Matthew M. Skinner