Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
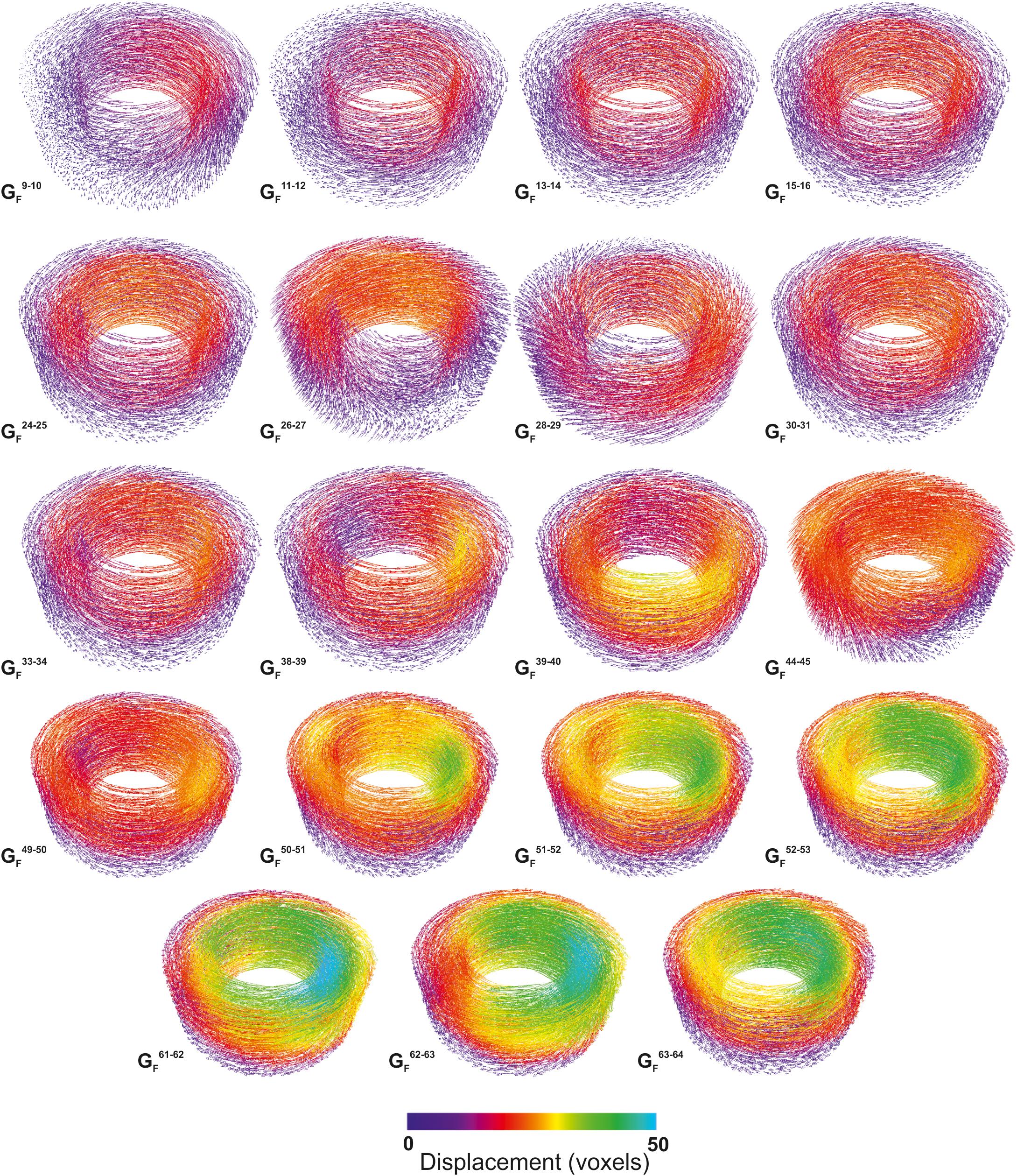
Quantifying Microstructural Evolution in Moving Magma
Many of the grand challenges in volcanic and magmatic research are focused on understanding the dynamics of highly heterogeneous systems and the critical conditions that enable magmas to move or eruptions to initiate. However, we are usually unable to observe the processes directly. Here we give a short synopsis of the new capabilities and highlight the potential insights that in situ observation can provide. We present the first 3D data showing the evolving textural heterogeneity within a sh... Read more
Katherine J. Dobson1, Anja Allabar, Eloise Bretagne, Jason Coumans, Mike Cassidy, Corrado Cimarelli, Rebecca Coats, Thomas Connolley, Loic Courtois, Donald B. Dingwell, Danilo Di Genova, Benjamin Fernando, Julie L. Fife, Frey Fyfe, Stephan Gehne, Thomas Jones, Jackie E. Kendrick, Helen Kinvig, Stephan Kolzenburg, Yan Lavallée, Emma Liu, Edward W. Llewellin, Amber Madden-Nadeau, Kamel Madi, Federica Marone, Cerith Morgan, Julie Oppenheimer, Anna Ploszajski, Gavin Reid, Jenny Schauroth, Christian M. Schlepütz, Catriona Sellick, Jérémie Vasseur, Felix W. von Aulock, Fabian B. Wadsworth, Sebastian Wiesmaier and Kaz Wanelik
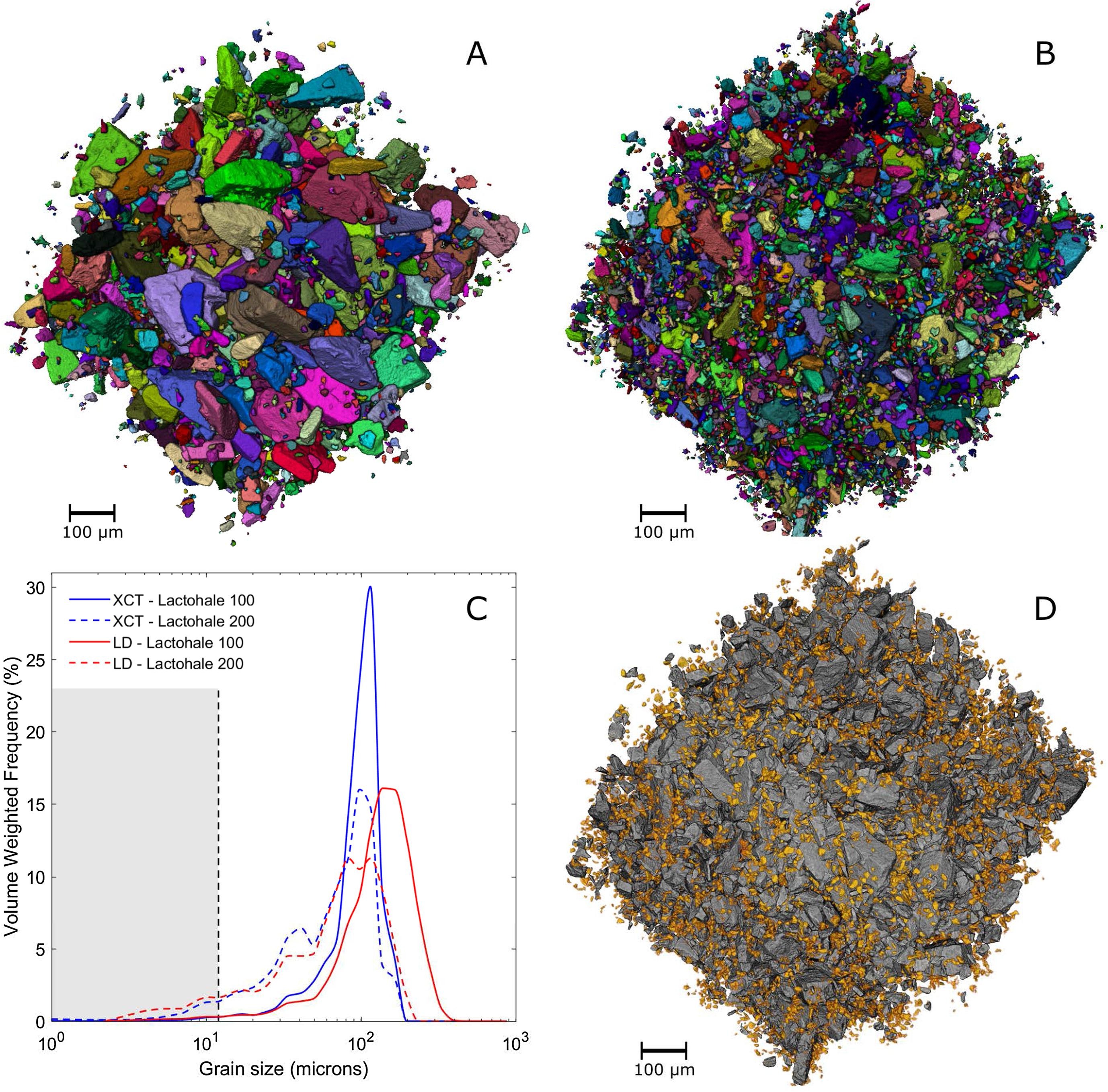
3D characterisation of dry powder inhaler formulations
Carrier-based dry powder inhaler (DPI) formulations need to be accurately characterised for their particle size distributions, surface roughnesses, fines contents and flow properties. Understanding the micro-structure of the powder formulation is crucial, yet current characterisation methods give incomplete information. Commonly used techniques like laser diffraction (LD) and optical microscopy (OM) are limited due to the assumption of sphericity and can give variable results depending on par... Read more
P. Gajjar, I.D. Styliari, T.T.H. Nguyen, J. Carr, X. Chen, J.A. Elliott, R.B. Hammond, T.L. Burnett, K. Roberts, P.J. Withers, D.Murnane
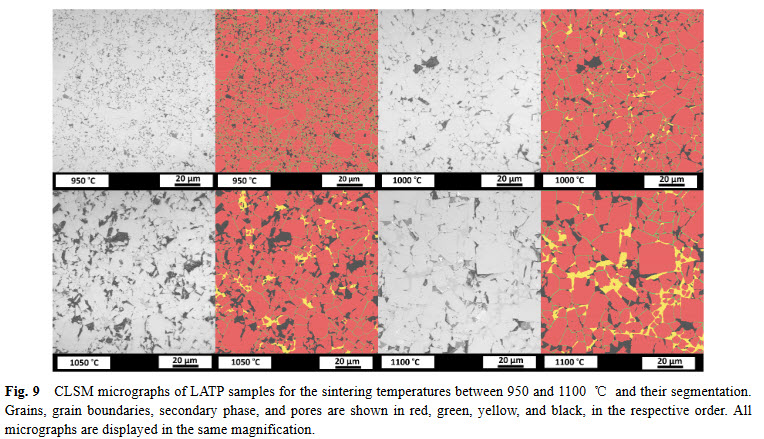
Lithium aluminum titanium phosphate (LATP) is one of the materials under consideration as an electrolyte in future all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. In ceramic processing, the presence of secondary phases and porosity play an important role. In a presence of more than one secondary phase and pores, image analysis must tackle the difficulties about distinguishing between these microstructural features. In this study, we study the phase evolution of LATP ceramics sintered at temperatures b... Read more
Deniz Cihan GUNDUZ, Roland SCHIERHOLZ, Shicheng YUa, Hermann TEMPEL, Hans KUNGL, Rüdiger-A. EICHEL
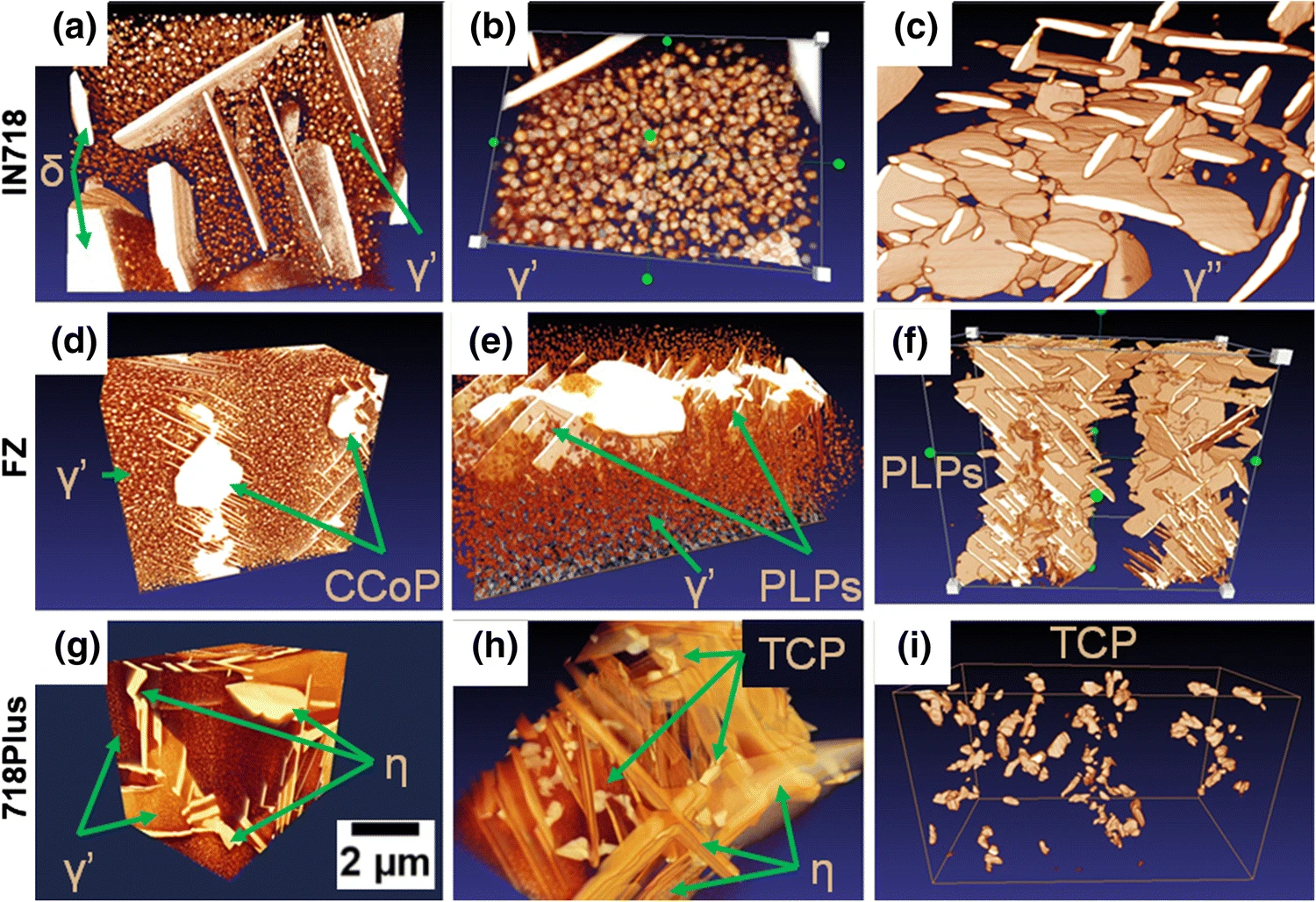
Inconel 718 (IN718) is the most popular precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloy introduced by the Huntington Alloys Division of INCO in 1959 (Ref Read more
Oskar Dziuba, Grzegorz Cempura, Agnieszka Wusatowska-Sarnek & Adam Kruk
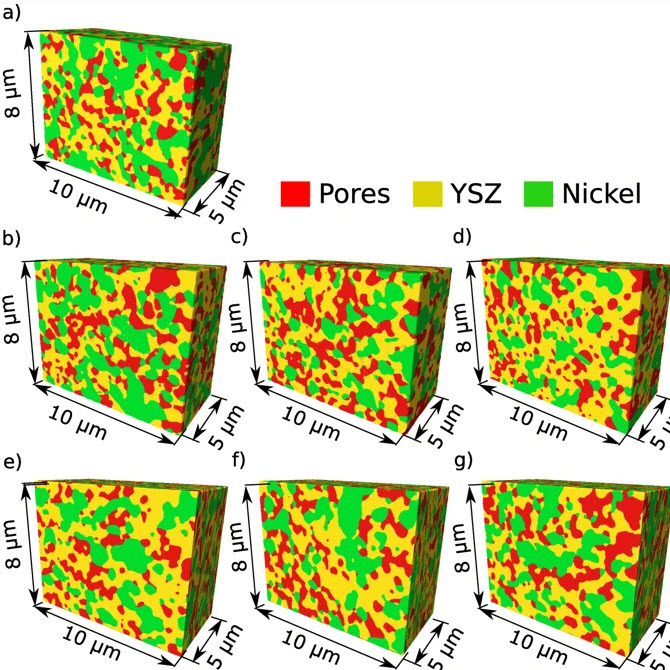
An Anisotropic Microstructure Evolution in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen directly into electricity. A single cell usually has a form of a flat plate in which an impervious and dense ion-conducting electrolyte is sandwiched between two porous catalytic electrodes: an anode and a cathode. Fuel is fed to the anode side, and the air is supplied to the cathode. The gasses cannot mix to avoid unproductive combustion. Instead, gasses hit catalyst material, lose their... Read more
Grzegorz Brus, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S. Szmyd
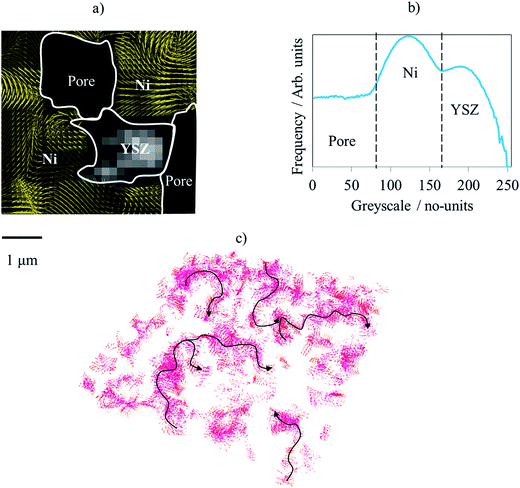
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
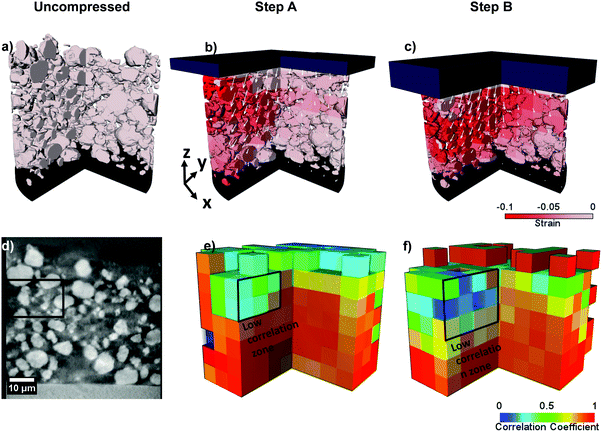
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
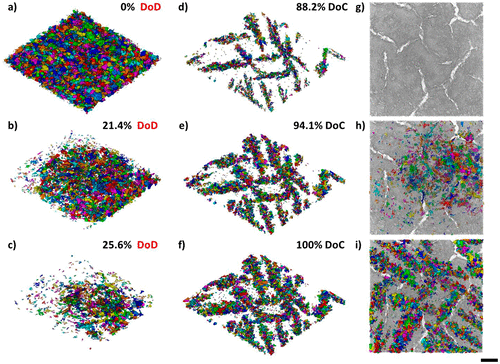
Four-Dimensional Studies of Morphology Evolution in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
Lithium sulfur (Li–S) batteries have great potential as a successor to Li-ion batteries, but their commercialization has been complicated by a multitude of issues stemming from their complex multiphase chemistry. In situ X-ray tomography investigations enable direct observations to be made about a battery, providing unprecedented insight into the microstructural evolution of the sulfur cathode and shedding light on the reaction kinetics of the sulfur phase. Here, for the first time, the mor... Read more
Chun Tan, Thomas M. M. Heenan, Ralf F. Ziesche, Sohrab R. Daemi, Jennifer Hack, Maximilian Maier, Shashidhara Marathe, Christoph Rau, Daniel J. L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing
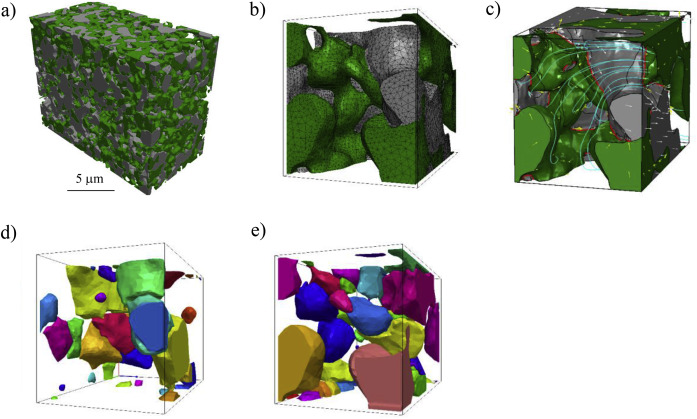
The electrode microstructural properties significantly influence the efficiency and durability of many electrochemical devices including solid oxide fuel cells. Despite the possibility of simulating the electrochemical phenomena within real three-dimensional microstructures, the potential of such 3D microstructural information has not yet been fully exploited. We introduce here a completely new methodology for the advanced characterization of inhomogeneous current distribution base... Read more
A.Bertei, V.Yufit, F.Tariq, N.P.Brandon
The use of contrast enhancement techniques in X-ray imaging of lithium–ion battery electrodes
Understanding the microstructural morphology of Li–ion battery electrodes is crucial to improving the electrochemical performance of current Li–ion battery systems and in developing next-generation power systems. The use of 3D X-ray imaging techniques, which are continuously evolving, provides a noninvasive platform to study the relationship between electrode microstructure and performance at various time and length scales. In addition to characterizing a weakly (X-ray) absorbing graphite... Read more
Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo , Donal P. Finegan , Jeff Gelb , Christian Holzner , Daniel J.L. Brett , Paul R. Shearing
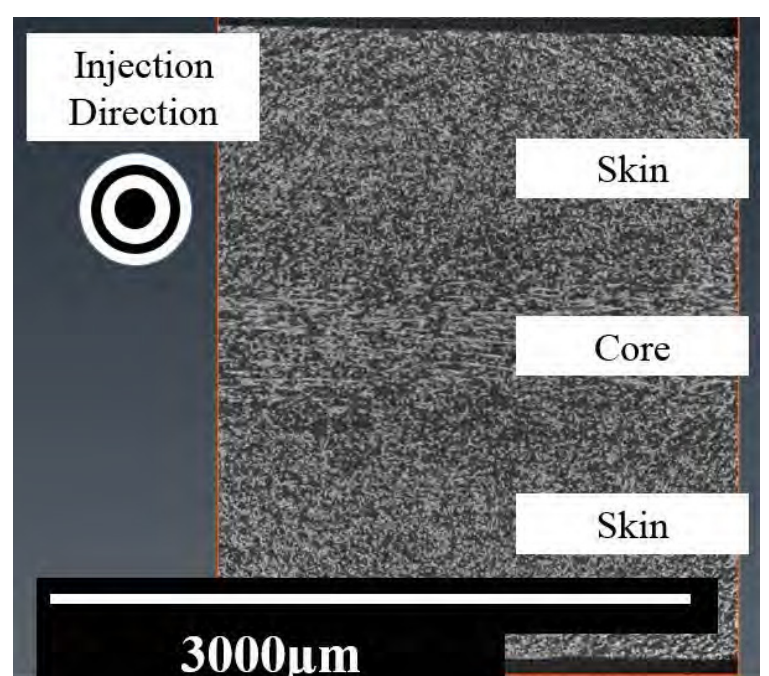
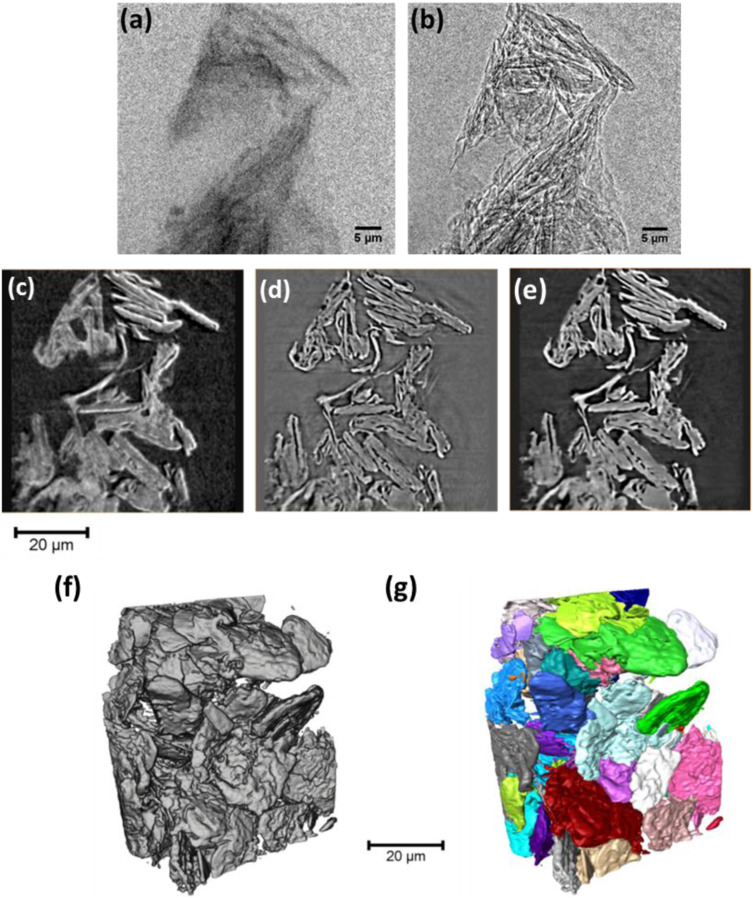
For many years, SFRPs (short fibre reinforced polyamides) have been used in the automotive industry as a means to reduce vehicle weight. However, their complex anisotropic and heterogeneous microstructure requires sophisticated material characterisation and simulation. This study aims at presenting the simulation strategy adopted by an automotive company address these challenges. The manufacturing process is first simulated and correlated with tomography analysis. Then, based on the numerical... Read more
Pablo Wilson, Peter Heyes
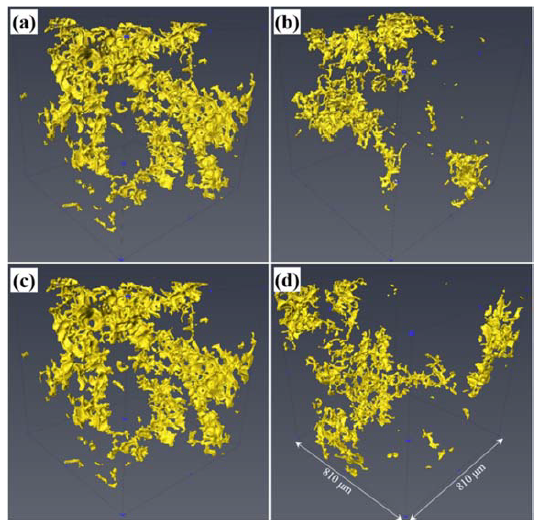
The effect of ultrasonic melting processing on three-dimensional architecture of intermetallic phases and pores in two multicomponent cast Al-5.0Cu 0.6Mn-0.5 Fe alloys is characterized using conventional microscopy and synchrotron X-ray microtomography. (…) The results show that ultrasonic melt processing (USP) significantly reduce the volume fraction, grain size, interconnectivity, and equivalent diameter of the intermetallic phases in both alloys. The volume fraction of pores in both ... Read more
Yuliang Zhao, Dongfu Song, Bo Lin, Chun Zhang, Donghai Zheng, Zhi Wang, Weiwen Zhang
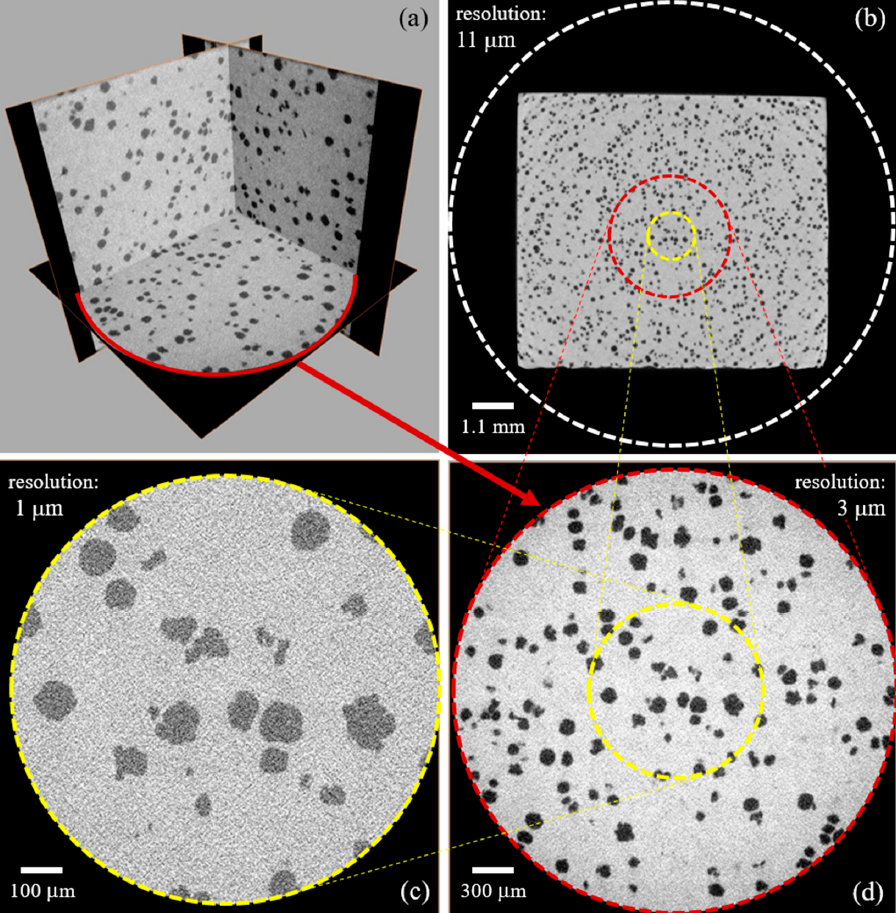
We describe in detail a methodology to estimate the effective elastic parameters of nodular cast iron, using micro-tomography in conjunction with multiscale finite elements. We discuss the adjustment of the image acquisition parameters, address the issue of the representative-volume choice, and present a brief discussion on image segmentation. In addition, the finite-element computational implementation developed to estimate the effective elastic parameters from segmented microstructural imag... Read more
Andre Pereira, Marcio Costa, Carla Anflor, Juan Pardal and Ricardo Leiderman
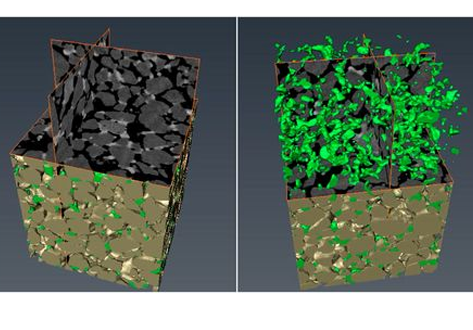
We introduce the application of microbial-induced calcite precipitation via the ureolytic soil bacterium Sporosarcina Pasteurii in freeze-dried form, as a means of enhancing overall MICP efficiency and reproducibility for geotechnical engineering applications. We show that the execution of urea hydrolysis and CaCO3 precipitation persist as a “cell-free” mechanism upon the complete breakdown of rehydrated cell clusters. Further, strength and stiffness parameters of bio-cemented ... Read more
Dimitrios Terzis, Lyesse Laloui
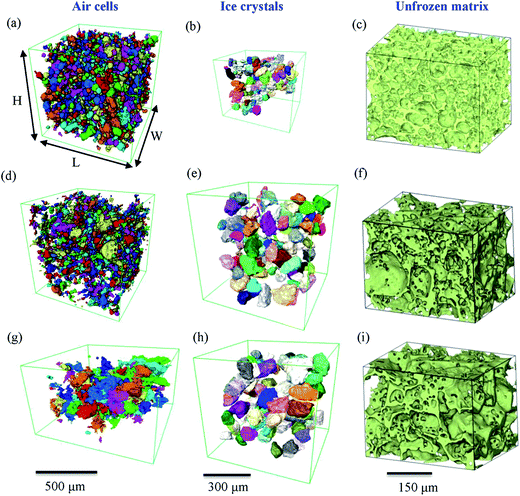
The microstructure of food affects our sensorial perception, its attractiveness, and the manufactured product’s shelf-life.
Microstructural evolution in soft matter directly influences not only the material’s mechanical and functional properties, but also our perception of that material’s taste. Using synchrotron X-ray tomography and cryo-SEM we investigated the time–temperature evolution of ice cream’s microstructure. This was enabled via three adv... Read more
Enyu Guo, Guang Zeng, Daniil Kazantsev, Peter Rockett, Julian Bent, Mark Kirkland, Gerard Van Dalen, David S. Eastwood, David StJohn and Peter D. Lee
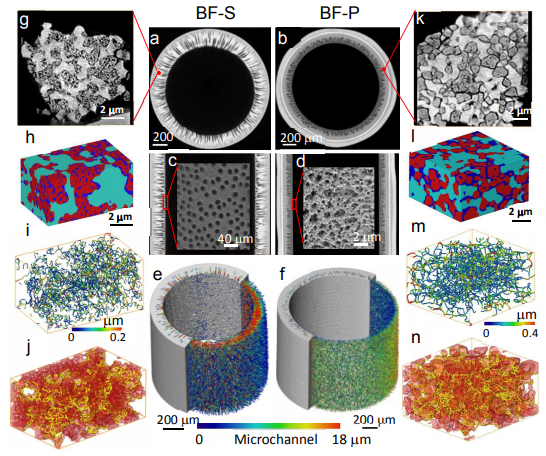
Mass transport can significantly limit the rate of reaction and lead to concentration polarization in electrochemical devices, especially under the conditions of high operating current density.
In this study we investigate hierarchically structured micro-tubular solid
oxide fuel cells (MT-SOFC) fabricated by phase inversion technique and quantitatively assess the mass transport and electrochemical performance improvement compared to a conventional tubular SOFC. We present pioneer... Read more
Xuekun Lu, Tao Li, Antonio Bertei, Jason I S Cho , Thomas M.M. Heenan , Rabuni Mohamad, Kang Li, Dan JL Brett, Paul R Shearing
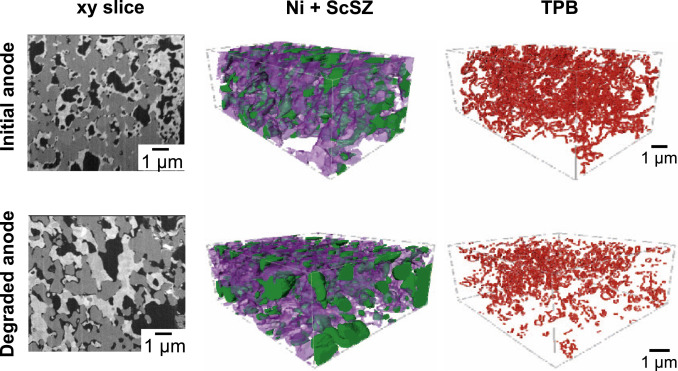
Nickel/zirconia-based nanostructured electrodes for solid oxide fuel cells suffer from poor stability even at intermediate temperature.
This study quantifies the electrochemical and microstructural degradation of nanostructured electrodes by combining 3D tomography, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and mechanistic modeling. For the first time, the electrochemical degradation of nanostructured electrodes is quantified according to the fractal nature of the three-phase bounda... Read more
A. Bertei, E. Ruiz-Trejo, K. Kareh, V. Yufit, X. Wang, F. Tariq, N.P. Brandon,
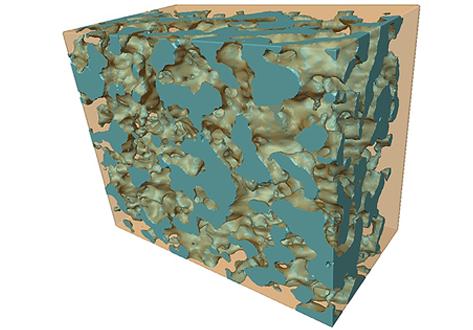
A simple chemical bath deposition is used to coat a complex porous ceramic scaffold with a conformal Ni layer.
The resulting composite is used as a solid oxide fuel cell electrode, and its electrochemical response is measured in humidified hydrogen. X‐ray tomography is used to determine the microstructural characteristics of the uncoated and Ni‐coated porous structure, which include the surface area to total volume, the radial pore size, and the size of the necks between the pores.... Read more
Dr. Enrique Ruiz‐Trejo, Milla Puolamaa, Brian Sum, Dr. Farid Tariq, Dr. Vladimir Yufit, Prof. Nigel P. Brandon
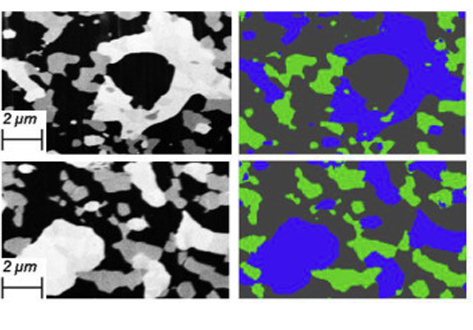
Quantification of the degradation of Ni-YSZ anodes upon redox cycling
Ni-YSZ anodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells are vulnerable to microstructural damage during redox cycling leading to a decrease in the electrochemical performance.
- Quantification of redox damage by coupling 3D tomography, EIS and nanoindentation.
- YSZ fracture, Ni detachment and agglomeration led to irreversible mechanical damage.
- Ni nanoparticles obtained upon redox cycling improve electrochemical performance.
- Loss in TPB densi... Read more
Bowen Song, Enrique Ruiz-Trejo, Antonio Bertei, Nigel P.Brandon
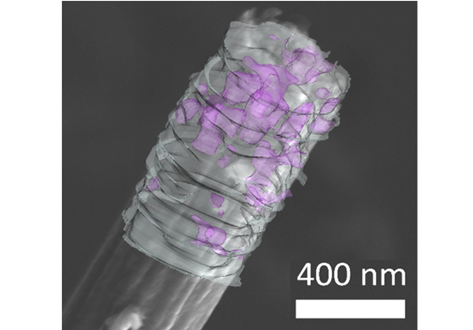
Flexible all-fiber electrospun supercapacitor
Electrospun all-fiber flexible supercapacitor with nanofiber electrodes/separator.
- Increased graphitic degree with the addition of MnACAC and thermal decomposition.
- Enhanced capacitive performance with the addition of MnO.
- Quantified nanofiber alignment and increased bias with MnO over undoped fibers.
- FIBSEM tomography of nanofibers showing MnO disitribution in carbon nanofibers.
We present an all-fiber flexible supercapacitor with compo... Read more
Xinhua Liu, Max Naylor Marlow, Samuel J. Cooper, Bowen Song, Xiaolong Chen, Nigel P. Brandon, Billy Wu
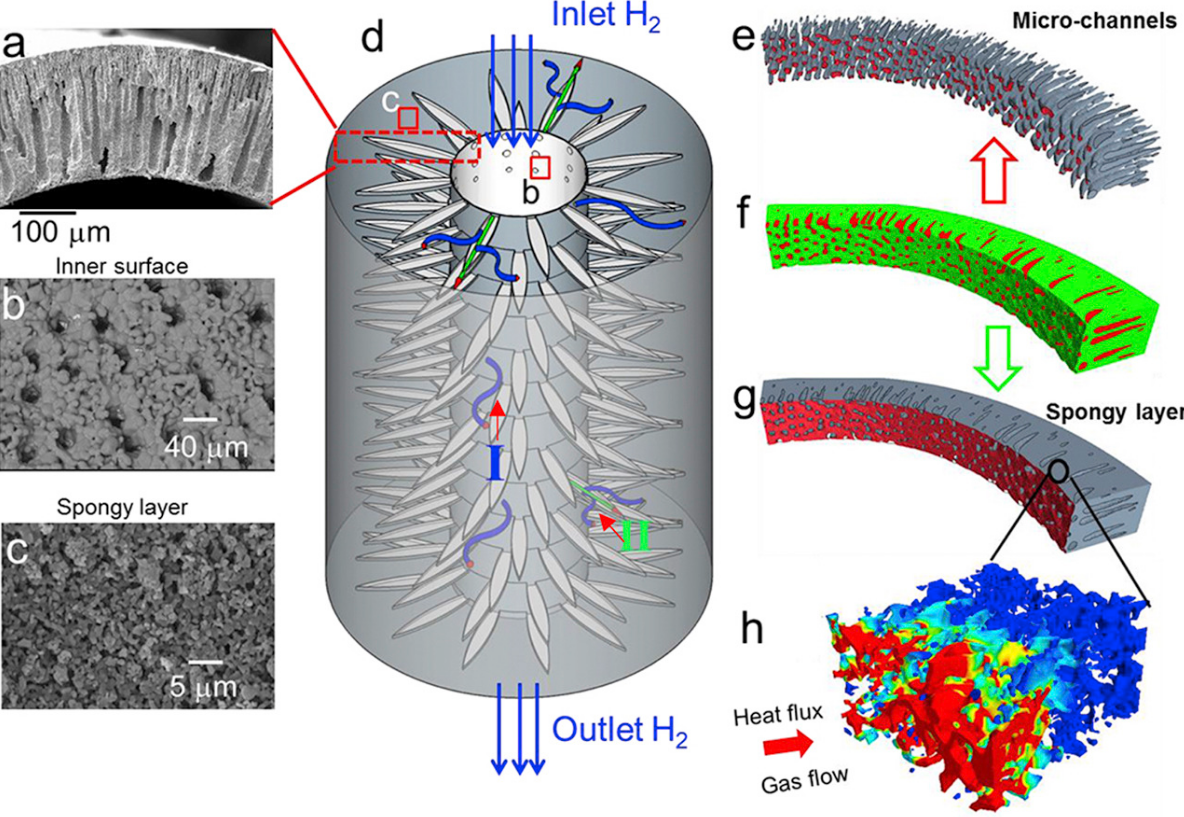
Our parametric study shows that increasing the porosity in the spongy layer beyond 10% enhances the effective transport parameters of the spongy layer at an exponential rate, but linearly for the full anode. For the first time, local and global mass transport properties are correlated to the microstructure, which is of wide interest for rationalizing the design optimization of SOFC electrodes and more generally for hierarchical materials in batteries and membranes.
Read more
Xuekun Lu, Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo, Antonio Bertei, Tao Li, Kang Li, Dan J.L. Brett, Paul R.Shearing