Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
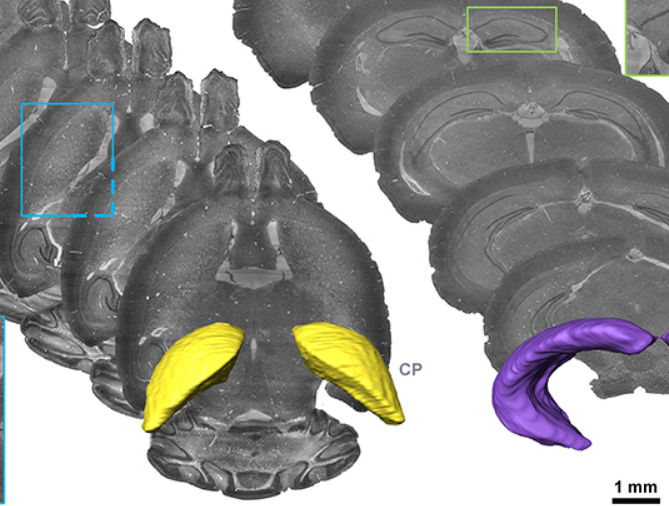
Precise Cerebral Vascular Atlas in Stereotaxic Coordinates of Whole Mouse Brain
Understanding amazingly complex brain functions and pathologies requires a complete cerebral vascular atlas in stereotaxic coordinates. Making a precise atlas for cerebral arteries and veins has been a century-old objective in neuroscience and neuropathology. Using micro-optical sectioning tomography (MOST) with a modified Nissl staining method, we acquired five mouse brain data sets containing arteries, veins, and microvessels. Based on the brain-wide vascular spatial structures and brain re... Read more
Benyi Xiong, Anan Li, Yang Lou, Shangbin Chen, Ben Long, Jie Peng, Zhongqin Yang, Tonghui Xu, Xiaoquan Yang, Xiangning Li, Tao Jiang, Qingming Luo and Hui Gong
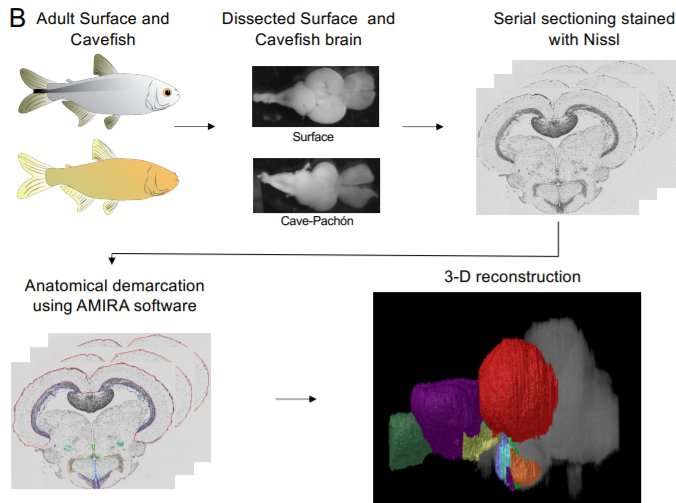
A shift in environmental conditions impacts the evolution of complex developmental and behavioral traits. The Mexican cavefish, Astyanax mexicanus, is a powerful model for examining the evolution of development, physiology, and behavior because multiple cavefish populations can be compared to an extant and ancestral-like surface population of the same species. Many behaviors have diverged in cave populations of A. mexicanus, and previous studies have shown that cavefish ha... Read more
Cody Loomis, View ORCID ProfileRobert Peuß, James Jaggard, Yongfu Wang, Sean McKinney, Stephen Raftopoulos, Austin Raftopoulos, Daniel Whu, Matthew Green, Suzanne E. McGaugh, Nicolas Rohner, Alex C. Keene, Erik R. Duboue
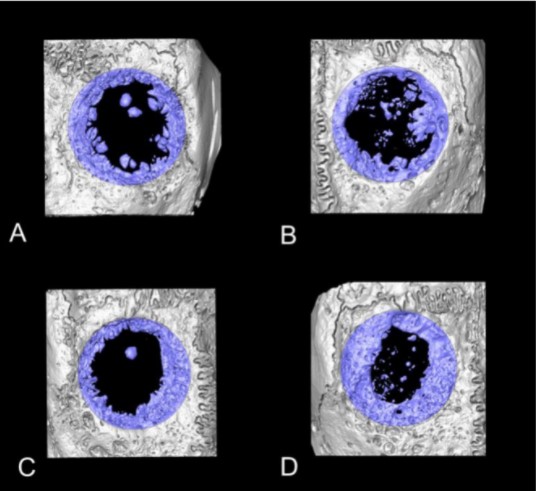
Collagen-Based Matrices for Osteoconduction: A Preclinical In Vivo Study
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of additional hydroxyapatite (HA) in collagen-based matrices (CM) and membrane placement on bone formation in calvarial defects.
Critical size defects in the calvaria of 16 New Zealand White Rabbits were randomly treated with CM or mineralized collagen-based matrices (mCM). Half of the sites were covered with a collagen membrane. Animals were euthanized after 12 weeks of healing. The samples were studied by micro-CT and histology. New... Read more
Hiroki Katagiri, Yacine El Tawil, Niklaus P. Lang, Jean-Claude Imber, Anton Sculean, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi and Nikola Saulacic
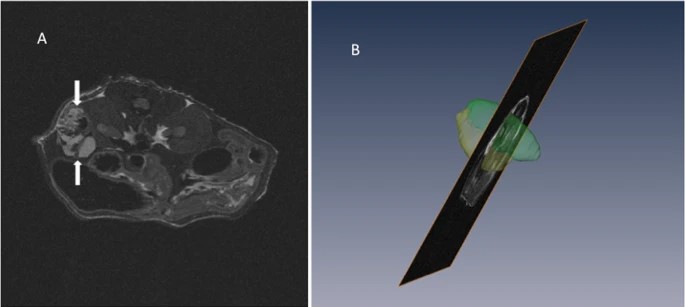
Recent treatment developments for metastatic renal cell carcinoma offer combinations of immunotherapies or immunotherapy associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). There is currently no argument to choose one solution or another. Easy-to-use markers to assess longitudinal responses to TKI are necessary to determine when to switch to immunotherapies. These new markers will enable an earlier adaptation of therapeutic strategy in order to prevent tumor development, unnecessary toxicity an... Read more
Alexandre Ingels, Ingrid Leguerney, Paul-Henry Cournède, Jacques Irani, Sophie Ferlicot, Catherine Sébrié, Baya Benatsou, Laurène Jourdain, Stephanie Pitre-Champagnat, Jean-Jacques Patard & Nathalie Lassau
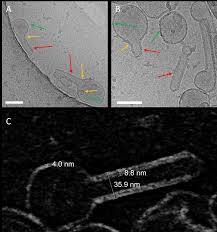
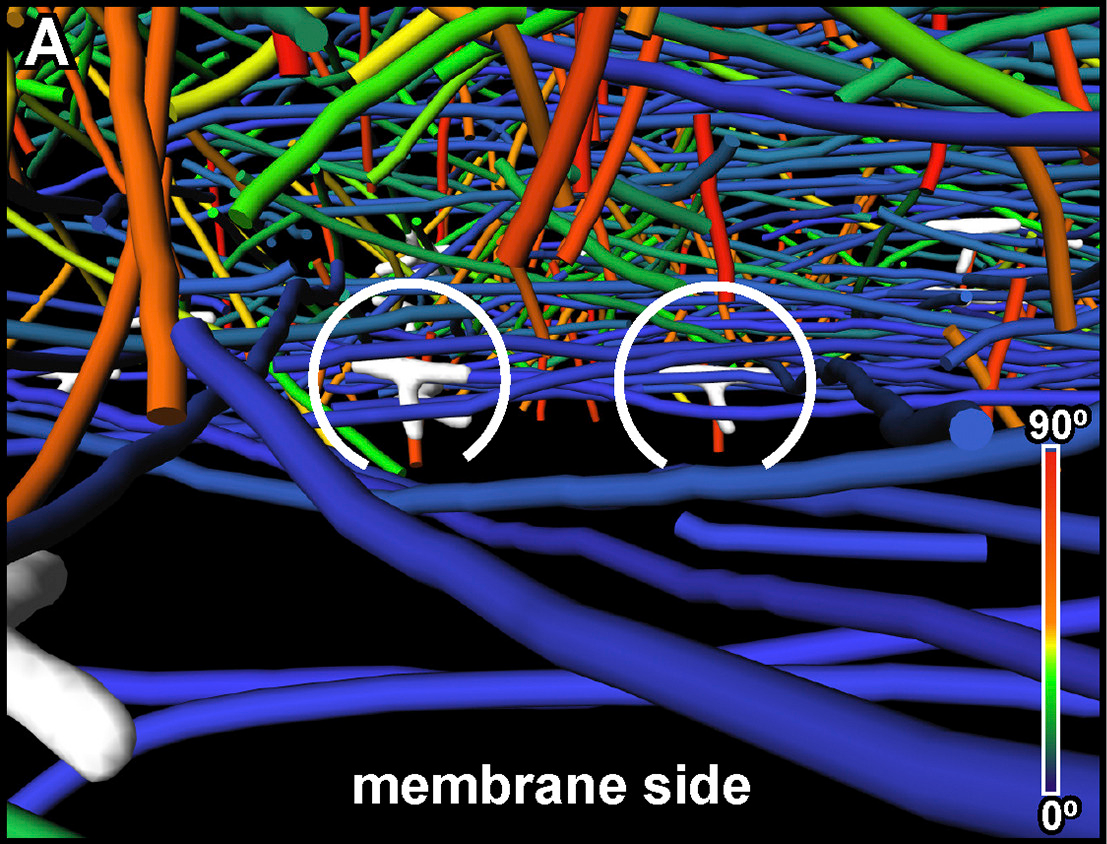
Influenza A matrix protein M1 is sufficient to induce lipid membrane deformation
The matrix protein M1 of the Influenza A virus is considered to mediate viral assembly and budding at the plasma membrane (PM) of infected cells. In order for a new viral particle to form, the PM lipid bilayer has to bend into a vesicle towards the extracellular side. Studies in cellular models have proposed that different viral proteins might be responsible for inducing membrane curvature in this context (including M1), but a clear consensus has not been reached. In this study, we use a comb... Read more
Ismail Dahmani, Kai Ludwig, Salvatore Chiantia
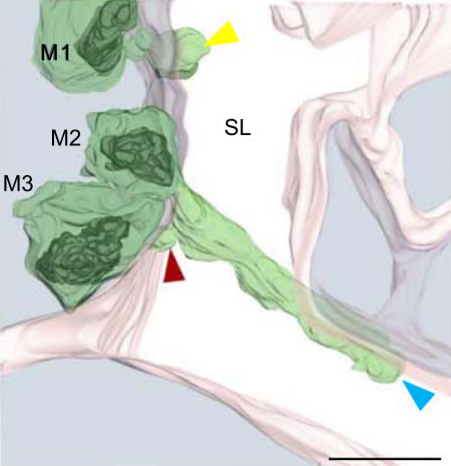
Multiple membrane extrusion sites drive megakaryocyte migration into bone marrow blood vessels
Platelets, cells central to hemostasis and thrombosis, are formed from parent cell megakaryocytes. Although the process is highly efficient in vivo, our ability to generate them in vitro is still remarkably inefficient. We proposed that greater understanding of the process in vivo is needed and used an imaging approach, intravital correlative light electron microscopy, to visualize platelet generation in bone marrow in the living mouse. In contrast to current understanding, we found that most... Read more
Edward Brown, Leo M Carlin, Claus Nerlov, Cristina Lo Celso, Alastair W Poole
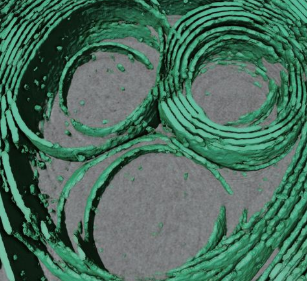
Membrane architecture of pulmonary lamellar bodies revealed by post-correlation on-lamella cryo-CLEM
Lamellar bodies (LBs) are surfactant rich organelles in alveolar type 2 cells. LBs disassemble into a lipid-protein network that reduces surface tension and facilitates gas exchange at the air-water interface in the alveolar cavity. Current knowledge of LB architecture is predominantly based on electron microscopy studies using disruptive sample preparation methods. We established a post-correlation on-lamella cryo-correlative light and electron microscopy approach for cryo-FIB milled lung ce... Read more
Steffen Klein, Benedikt H. Wimmer, Sophie L. Winter, Androniki Kolovou, Vibor Laketa, Petr Chlanda
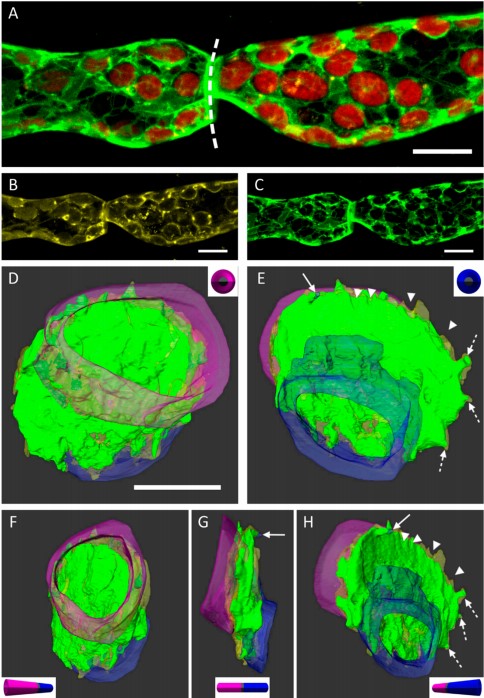
3D Dissection of Structural Membrane-Wall Contacts in Filamentous Moss Protonemata
Cell-to-cell contact is essential for communication and development of multicellular organisms. A prerequisite is the passage through membranes. That way, molecular exchange and information flow is regulated via hormones, membrane proteins and pores.
In plants, the rigid cell walls prevent large membrane contact areas between protoplasts. Only plasmodesmata, minute channels between adjacent cells, form direct connections. Often, molecular data of the proteins involved are manifold but t... Read more
Dominik Harant and Ingeborg Lang
The Architecture of Traveling Actin Waves Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography
Actin waves are dynamic supramolecular structures involved in cell migration, cytokinesis, adhesion, and neurogenesis. Although wave-like propagation of actin networks is a widespread phenomenon, the actin architecture underlying wave propagation remained unknown. In situ cryo-electron tomography of Dictyostelium cells unveils the wave architecture and provides evidence for wave progression by de novo actin nucleation. Subtomogram averaging reveals the structu... Read more
Marion Jasnin, Florian Beck, Mary Ecke, Yoshiyuki Fukuda, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Wolfgang Baumeister, Günther Gerisch
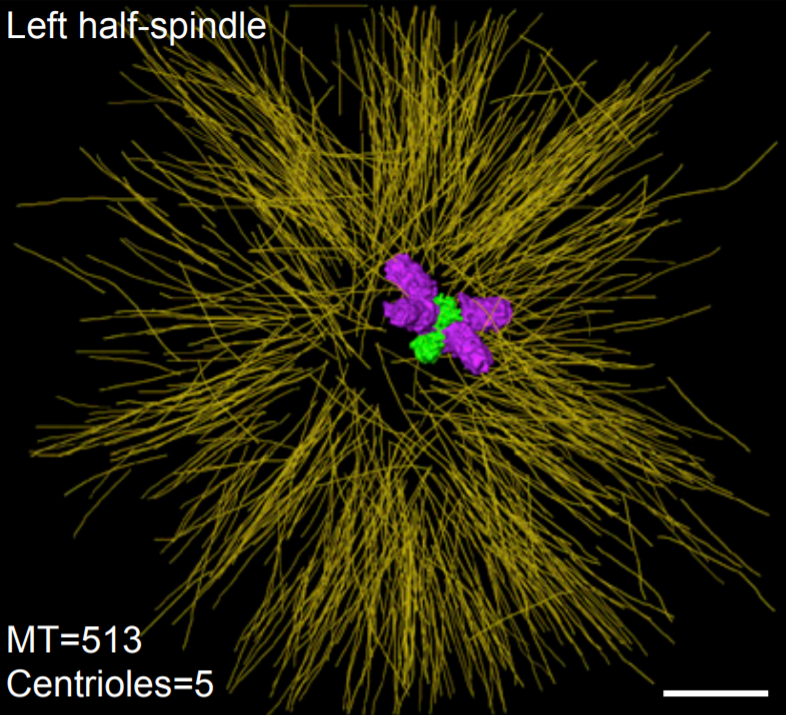
Asymmetric Centriole Numbers at Spindle Poles Cause Chromosome Missegregation in Cancer
Chromosomal instability is a hallmark of cancer and correlates with the presence of extra centrosomes, which originate from centriole overduplication.
Overduplicated centrioles lead to the formation of centriole rosettes, which mature into supernumerary centrosomes in the subsequent cell cycle. While extra centrosomes promote chromosome missegregation by clustering into pseudo-bipolar spindles, the contribution of centriole rosettes to chromosome missegregation is unknown. We us... Read more
Marco R.Cosenza, Anna Cazzola, Annik Rossberg, Nicole L. Schieber, Gleb Konotop, Elena Bausch, Alla Slynko, Tim Holland-Letz, Marc S.Raab, Taronish Dubash, Hanno Glimm, Sven Poppelreuther, Christel Herold-Mende, Yannick Schwab, Alwin Krämer
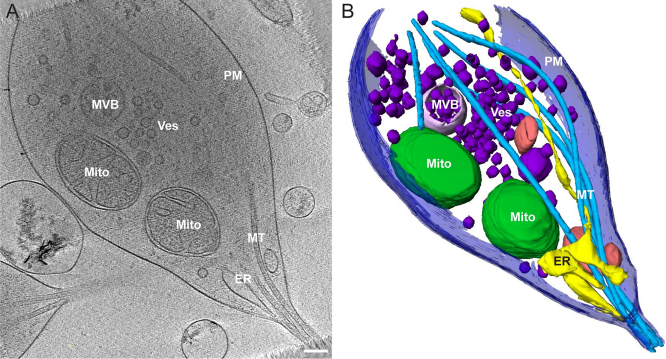
Morphology of mitochondria in spatially restricted axons revealed by cryo-electron tomography
Neurons project axons to local and distal sites and can display heterogeneous morphologies with limited physical dimensions that may influence the structure of large organelles such as mitochondria. Using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET), we characterized native environments within axons and presynaptic varicosities to examine whether spatial restrictions within these compartments influence the morphology of mitochondria. Segmented tomographic reconstructions revealed distinctive morphologi... Read more
Tara D. Fischer, Pramod K. Dash, Jun Liu, M. Neal Waxham
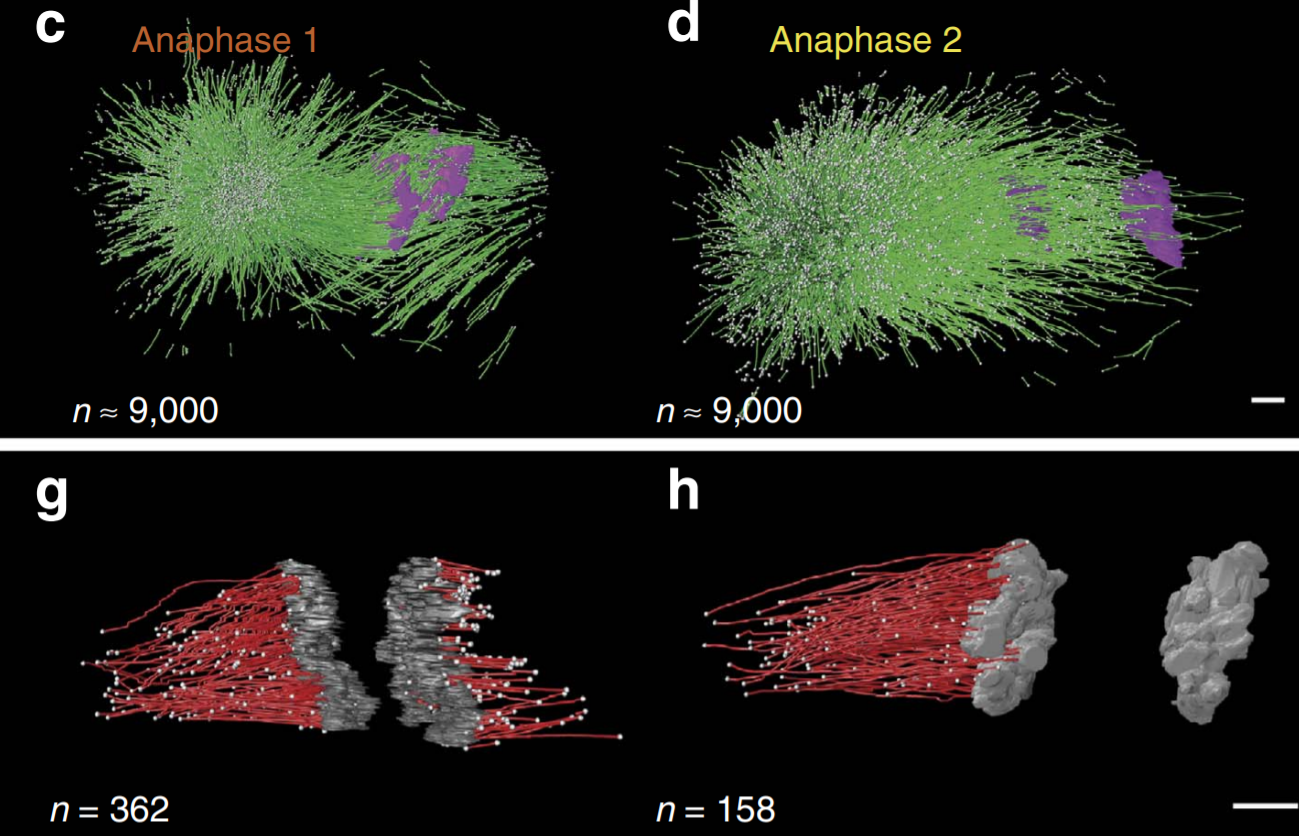
C. elegans chromosomes connect to centrosomes by anchoring into the spindle network
The mitotic spindle ensures the faithful segregation of chromosomes. Here we combine the first large-scale serial electron tomography of whole mitotic spindles in early C. elegans embryos with live-cell imaging to reconstruct all microtubules in 3D and identify their plus- and minus-ends. We classify them as kinetochore (KMTs), spindle (SMTs) or astral microtubules (AMTs) according to their positions, and quantify distinct properties of each class. While our light microscopy and muta... Read more
Stefanie Redemann, Johannes Baumgart, Norbert Lindow, Michael Shelley, Ehssan Nazockdast, Andrea Kratz, Steffen Prohaska, Jan Brugués, Sebastian Fürthauer & Thomas Müller-Reichert
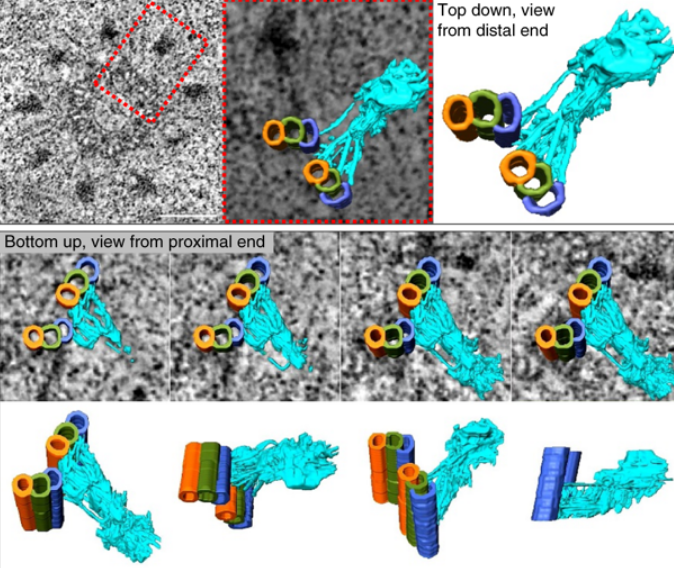
Centrioles are vital cellular structures that form centrosomes and cilia. The formation and function of cilia depends on a set of centriole’s distal appendages. In this study, we use correlative super resolution and electron microscopy to precisely determine where distal appendage proteins localize in relation to the centriole microtubules and appendage electron densities. Here we characterize a novel distal appendage protein ANKRD26 and detail, in high resolution, the initial steps of dist... Read more
Mathew Bowler, Dong Kong, Shufeng Sun, Rashmi Nanjundappa, Lauren Evans, Veronica Farmer, Andrew Holland, Moe R. Mahjoub, Haixin Sui & Jadranka Loncarek
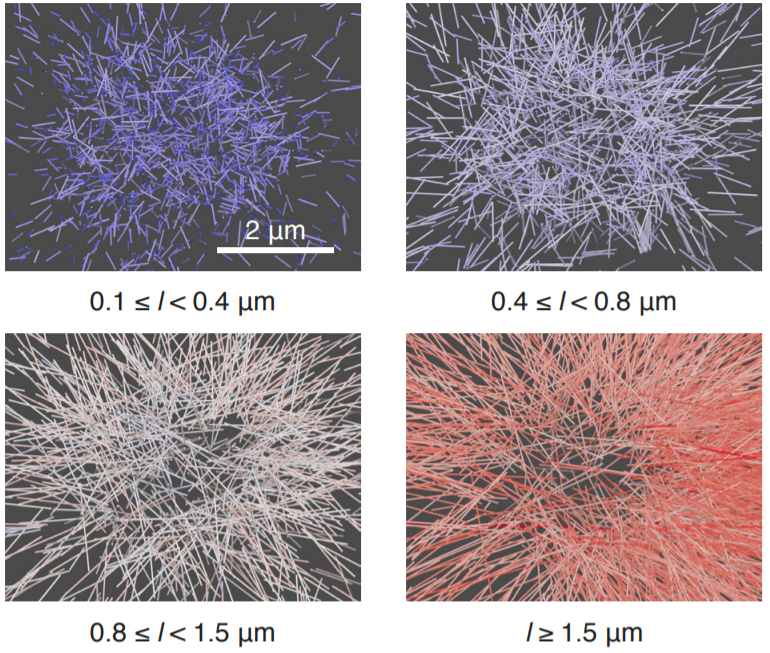
Soluble tubulin is locally enriched at mitotic centrosomes in C. elegans
During mitosis, the centrosome expands its capacity to nucleate microtubules. Understanding the mechanisms of centrosomal microtubule nucleation is, however, constrained by a lack of knowledge of the amount of soluble and polymer tubulin at mitotic centrosomes. Here we combined light microscopy and serial-section electron tomography to measure the amount of dimer and polymer at mitotic centrosomes in early C. elegans embryos. We show that a C. elegans one-cell stage centrosome at metaphase co... Read more
Johannes Baumgart, Marcel Kirchner, Stefanie Redemann, Jeffrey Woodruff, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Frank Julicher, Anthony Hyman, Thomas Mueller-Reichert, Jan Brugues
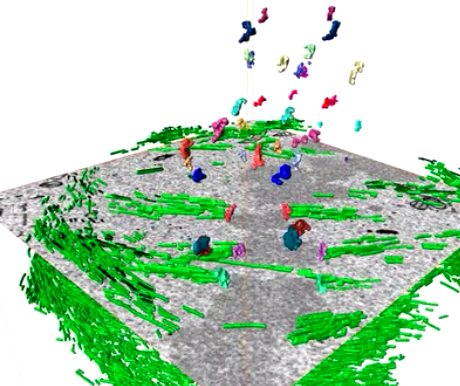
Serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) is a powerful method to analyze cells in 3D. Here, working at the resolution limit of the method, we describe a correlative light–SBF-SEM workflow to resolve microtubules of the mitotic spindle in human cells. We present four examples of uses for this workflow that are not practical by light microscopy and/or transmission electron microscopy. First, distinguishing closely associated microtubules within K-fibers; second, resolving brid... Read more
Faye M. Nixon, Thomas R. Honnor, Nicholas I. Clarke, Georgina P. Starling, Alison J. Beckett, Adam M. Johansen, Julia A. Brettschneider, Ian A. Prior, Stephen J. Royle
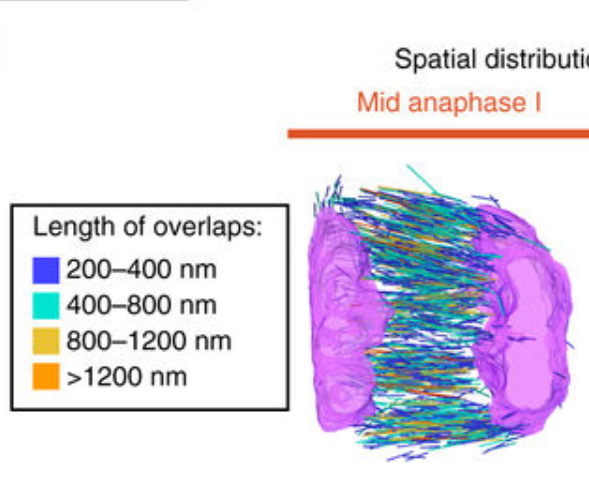
Chromosome segregation occurs by microtubule pushing in oocytes
During cell division, spindle microtubules ensure an equal repartition of chromosomes between the two daughter cells. While the kinetochore-dependent mechanisms that drive mitotic chromosome segregation are well understood, in oocytes of most species atypical spindles assembled in absence of centrosomes entail poorly understood mechanisms of chromosome segregation. In particular, the structure(s) responsible for force generation during meiotic chromosome separation in oocytes is unclear. Usin... Read more
Kimberley Laband, Rémi Le Borgne, Frances Edwards, Marine Stefanutti, Julie C. Canman, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Julien Dumont

Each pulmonary segment is an anatomical and functional unit. However, it is fundamentally difficult to precisely distinguish every pulmonary segment using the conventional pulmonary intersegmental planes from computed tomography images. Building arteriopulmonary segments is likely to be an effective way to identify pulmonary segments.
The three-dimensional reconstructed images showed the branches of the pulmonary artery ramified up to their eighth order covering the entire lung as well... Read more
Huijie Gao, Chao Liu
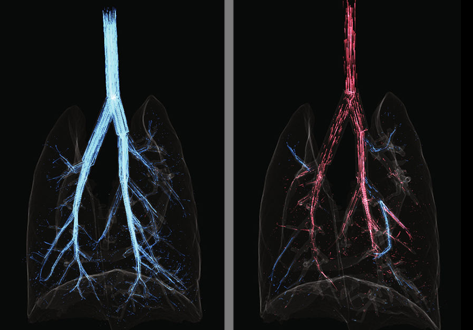
Cardiogenic Airflow in the Lung Revealed Using Synchrotron-Based Dynamic Lung Imaging
The beating heart is known to produce pressure and airflow oscillations in the lungs of mammals. This phenomenon is often disregarded as detailed measurement of its effects in the lung have hitherto not been possible. Previous studies have attempted to measure the effect of these oscillations on gas mixing. However, the results have proven inconclusive, due to the lack of a direct measurement tool capable of flow measurement throughout the entire bronchial tree. Here we present the first deta... Read more
Stephen Dubsky, Jordan Thurgood, Andreas Fouras, Bruce R. Thompson & Gregory J. Sheard
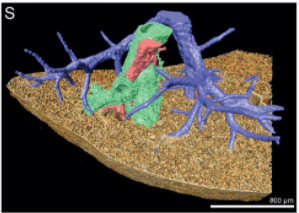
Multiscale Co‐reconstruction of Lung Architectures and Inhalable Materials Spatial Distribution
Pulmonary diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, lower respiratory infections, and lung cancer are listed in the top ten causes of deaths globally with more than 10 million mortality per year. Apart from oral administration, the Dry Powder Inhalation (DPI) for pulmonary administration provides an important alternative route for targeted treatment of these pulmonary diseases. […] Furthermore, there is a growing demand on und... Read more
Xian Sun, Xiaochuan Zhang, Xiaohong Ren, Hongyu Sun, Li Wu, Caifen Wang, Xiaohui Ye, Peter York, Zhaobing Gao, Hualiang Jiang, Jiwen Zhang, Xianzhen Yin
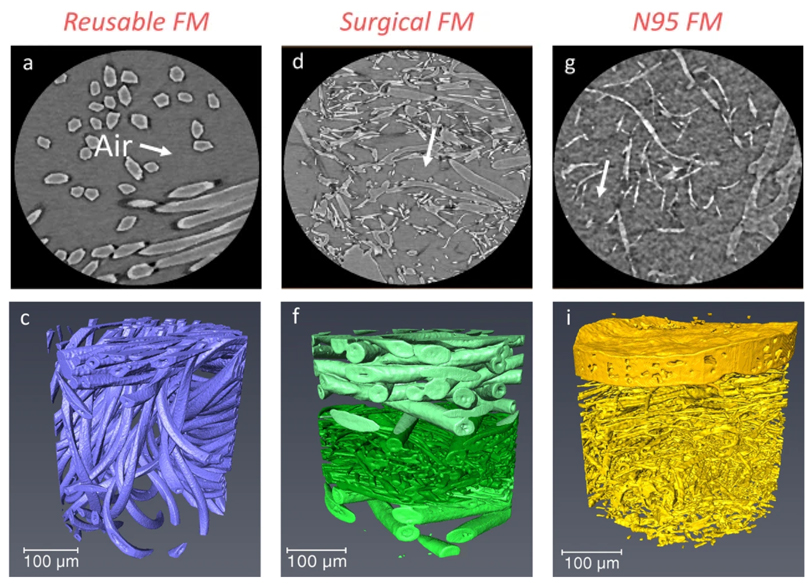
Microstructure analysis and image-based modelling of face masks for COVID-19 virus protection
Until March 2021, around 120 million coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infected cases and over 2.6 million deaths have been reported worldwide. […] Recent investigations have implied that face masks help to reduce the disease transmission and therefore slow down the growth of the epidemic curve. However, there are still ongoing debates on the efficacy of wearing masks […] since there is a general lack of information relating to the material structure of commonly used face masks.Read more
Wenjia Du, Francesco Iacoviello, Tacson Fernandez, Rui Loureiro, Daniel J. L. Brett & Paul R. Shearing
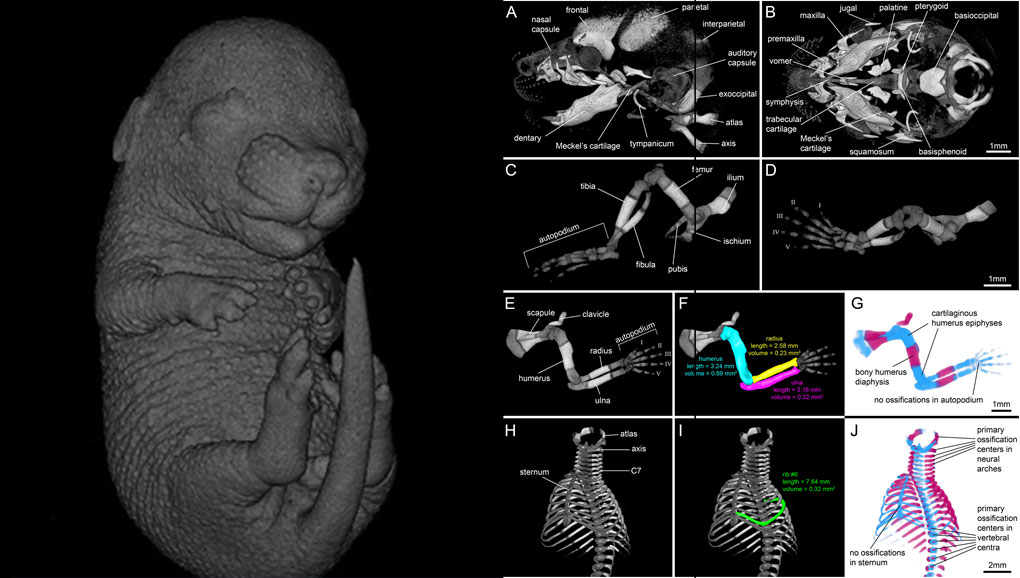
For decades, clearing and staining with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red has been the gold standard to image vertebrate skeletal development. Here, we present an alternate approach to visualise bone and cartilage based on X-ray microCT imaging, which allows the collection of genuine 3D data of the entire developing skeleton at micron resolution.
Our novel protocol is based on ethanol fixation and staining with Ruthenium Red, and efficiently contrasts cartilage matrix, as demonstrated in wh... Read more
Simone Gabner, Peter Böck, Dieter Fink, Martin Glösmann, Stephan Handschuh