Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
In this study, the researchers investigated the compressive failure mechanisms in flax fiber composites, a promising eco-friendly alternative to synthetic composite materials, through both numerical simulations and experimental analysis. They examined the reasons behind the low compressive strength in comparison to tensile strength, focusing on the compressive-to-tensile strength ratio. A novel thermodynamically consistent continuum damage micromechanics model was introduced to capture the ev... Read more
Vedad Tojaga, Alexandros Prapavesis, Jonas Faleskog, T. Christian Gasser, Aart W. van Vuure, Sören Östlund
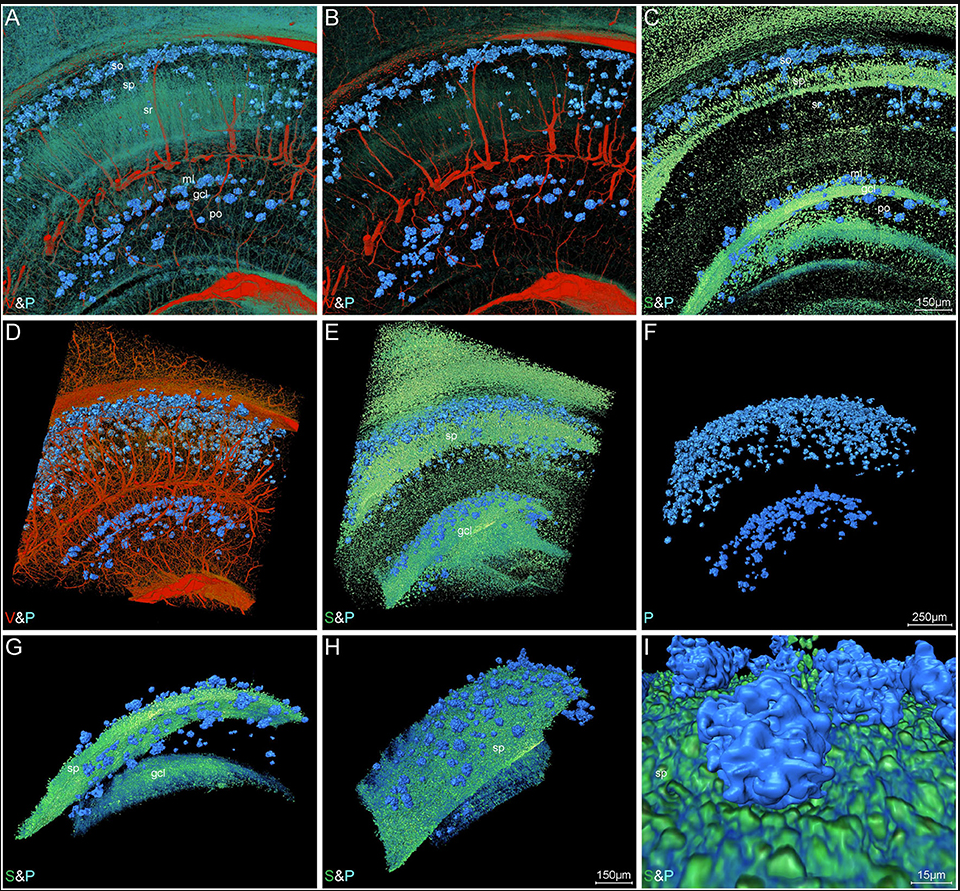
High-Resolution Digital Panorama of Multiple Structures in Whole Brain of Alzheimer's Disease Mice
Our study placed emphasis on solving problems in processing high-throughput bright field images and made attempt in developing a method for the extraction and reconstruction of multiple structures. This will facilitate a better understanding of the cerebral anatomical features under the pathological state of AD and shows extensive application prospect in drug efficacy assessment from brain-wide level.
Simultaneously visualizing Amyloid-β (Aβ) plaque with its surrounding brain structu... Read more
Xianzhen Yin, Xiaochuan Zhang, Jingjing Zhang, Weicheng Yang, Xian Sun, Haiyan Zhang, Zhaobing Gao, Hualiang Jiang

Fossil fruits formerly described as cashews from the Oligocene of Peru are reinvestigated based on the original specimens and newly collected materials. The recovery of an outer spiny layer, preserved in the sedimentary molds surrounding the locule casts, indicates that these disseminules do not represent Anacardium. Imagery from nano-CT scans of the specimens documents a distinctive morphology which does not resemble any fruits or seeds of Anacardiaceae. We describe the morphology in more de... Read more
STEVEN R. MANCHESTER, BEHNAZ BALMAKI
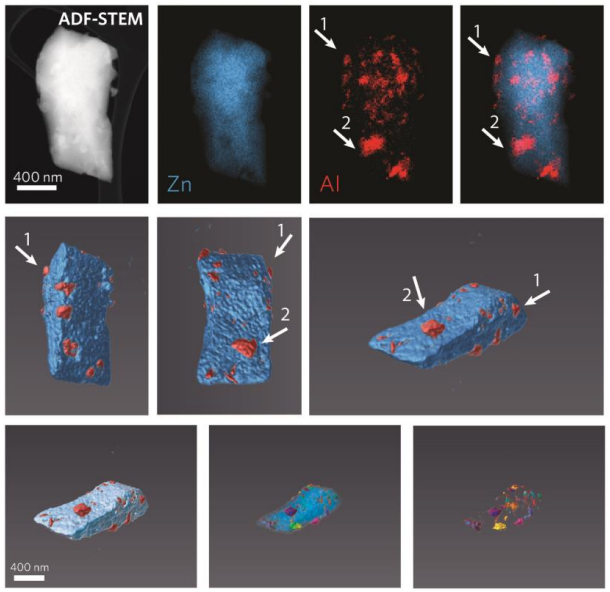
Metal-Organic Framework Crystal-Glass Composites
The majority of research into metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) focuses on their crystalline nature. However, in recent research the vitrification of a number of MOFs has been revealed. We propose that the solid-liquid phase transitions involved in MOF-glass formation can provide unique opportunities for the creation of a new class of functional, stable and porous composite materials. Described herein is the design, synthesis, and characterisation of novel metal-organic framework (MOF) crystal-... Read more
Jingwei Hou, Christopher W. Ashling, Sean M. Collins, Andraž Krajnc, Chao Zhou, Louis Longley, Duncan N. Johnstone, Philip A. Chater, Shichun Li, François-Xavier Coudert, David A. Keen, Paul A. Midgley, Gregor Mali, Vicki Chen, Thomas Bennett
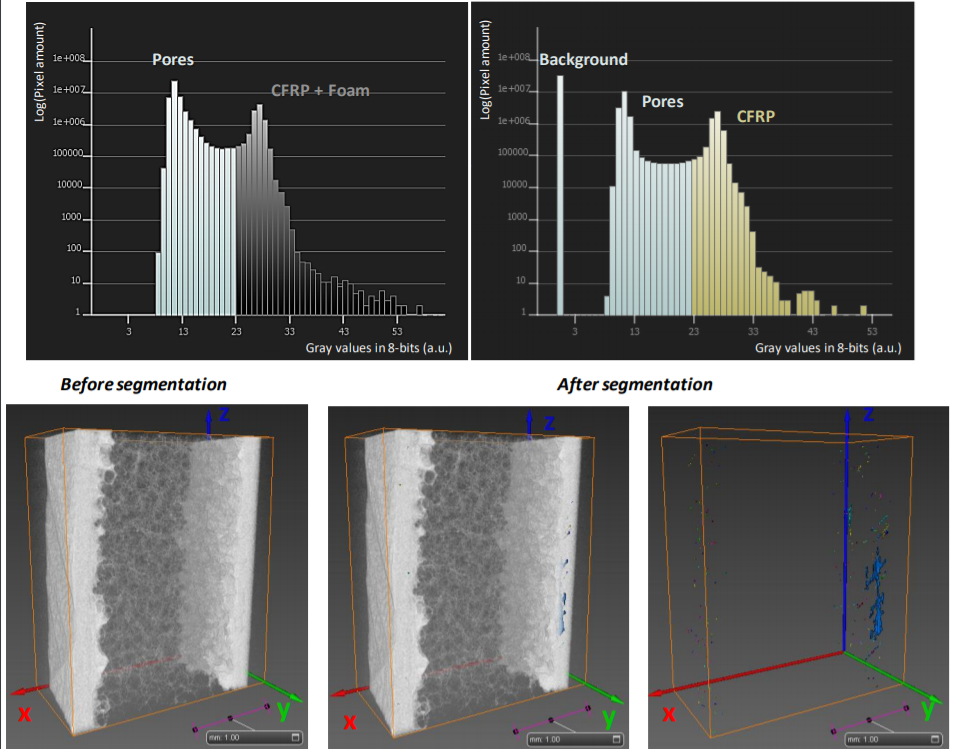
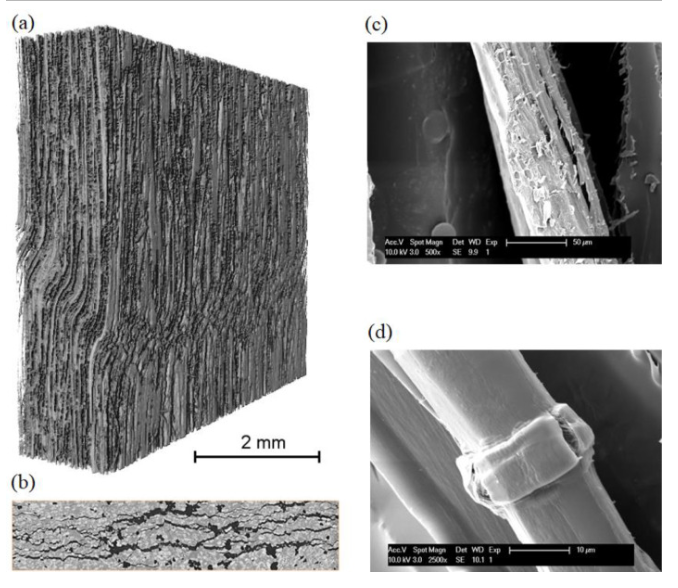
The aim of the current study is to propose a versatile, non-destructive inspection strategy to evaluate the structure of two different aircraft carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) -based composite configurations, which are widely used for structural elements, respectively layered composite and sandwich structure. X-ray computed tomography (CT) has been used as a flexible method for assessment of porosity levels in CFRP components in both types of configuration, permitting to investigate th... Read more
Elena Dilonardo, Michele Nacucchi, Fabio De Pascalis, Mauro Zarrelli, Cinzia Giannini
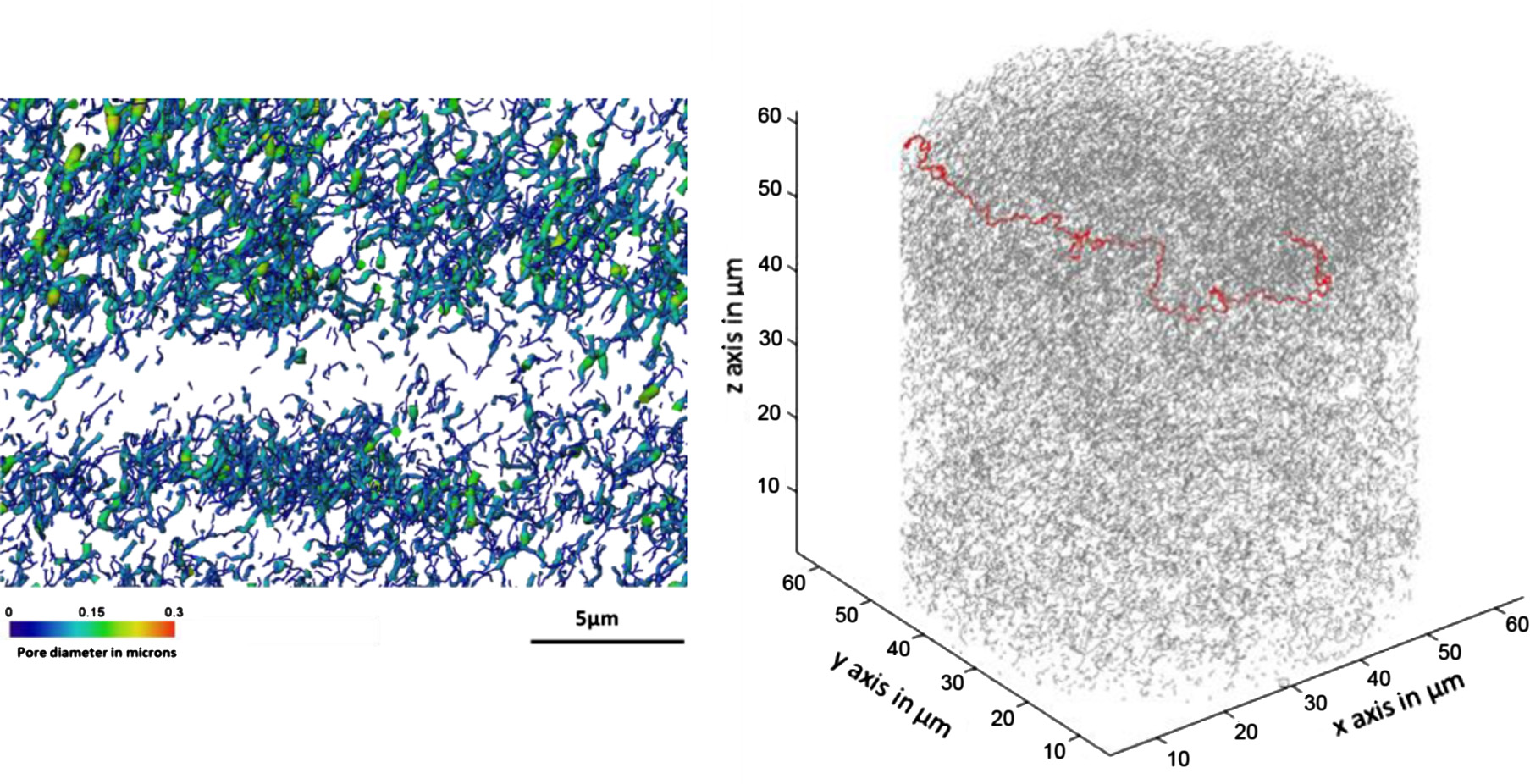
Microstructural analysis of TRISO particles using multi-scale X-ray computed tomography
TRISO particles, a composite nuclear fuel built up by ceramic and graphitic layers, have outstanding high temperature resistance. TRISO fuel is the key technology for High Temperature Reactors (HTRs) and the Generation IV Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) variant.
TRISO offers unparalleled containment of fission products and is extremely robust during accident conditions. An understanding of the thermal performance and mechanical properties of TRISO fuel requires a detailed knowledg... Read more
T. Lowe, R.S. Bradley, S. Yue, K. Barii, J. Gelb, N. Rohbeck, J. Turner, P.J. Withers
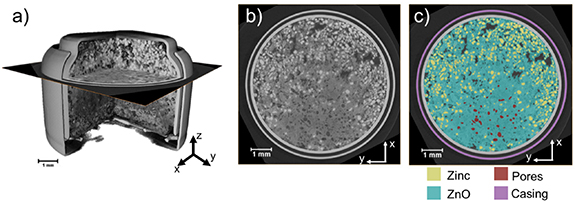
Given the urgent need to move to low-carbon technologies, batteries are being increasingly used in a range of applications. Lithium-ion batteries are the most widely used chemistry, but to meet the growing demand, there is a need to move beyond lithium towards alternative battery chemistries. Metal–air batteries are a group of such battery alternatives that hold promise, especially for stationary power and flexible electronics applications.
However, barriers to their widespread adopt... Read more
Jennifer Hack, Drasti Patel, Josh J Bailey, Francesco Iacoviello, Paul R Shearing, and Dan J L Brett
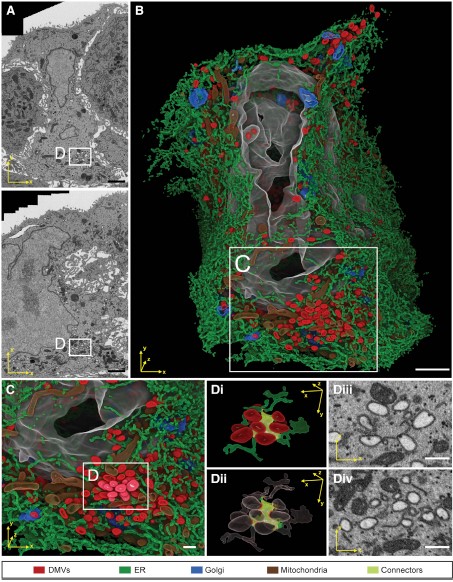
Integrative Imaging Reveals SARS-CoV-2-Induced Reshaping of Subcellular Morphologies
Cortese et al. use integrative imaging techniques to generate a publicly available repository of morphological alterations induced by SARS-CoV-2 in lung cells. Accumulation of ER-derived double-membrane vesicles, the viral replication organelle, occurs concomitantly with cytoskeleton remodeling and Golgi fragmentation. Pharmacological alteration of cytoskeleton dynamics restricts viral replication and spread.
Pathogenesis induced by SARS-CoV-2 is thought to result from both an inflamma... Read more
Mirko Cortese, Ji-Young Lee, Berati Cerikan, ..., Laurent Chatel-Chaix, Yannick Schwab, Ralf Bartenschlager
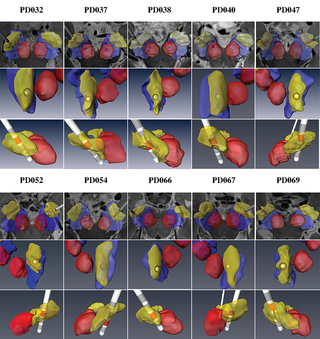
Patient-specific anatomical model for deep brain stimulation based on 7 Tesla MRI
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) requires accurate localization of the anatomical target structure, and the precise placement of the DBS electrode within it. Ultra-high field 7 Tesla (T) MR images can be utilized to create patient-specific anatomical 3D models of the subthalamic nuclei (STN) to enhance pre-surgical DBS targeting as well as post-surgical visualization of the DBS lead position and orientation. We validated the accuracy of the 7T imaging-based patient-specific model of the STN and m... Read more
Yuval Duchin, Reuben R. Shamir, Remi Patriat, Jinyoung Kim, Jerrold L. Vitek, Guillermo Sapiro, Noam Harel
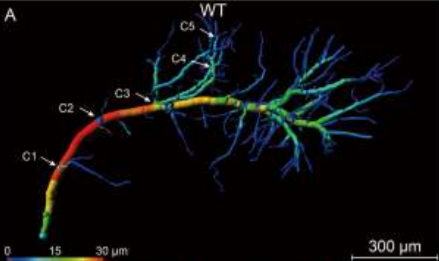
Accumulating evidence indicates the critical importance of cerebrovascular dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, systematic comparative studies on the precise brain vasculature of wild-type and AD model mice are still rare. Using an image optimization method for analyzing Micro-Optical Sectioning Tomography (MOST) data, we generated cross-scale whole-brain 3D atlases that cover the entire vascular system from large vessels down to smallest capillaries at ... Read more
Xiaochuan Zhang, Xianzhen Yin, Jingjing Zhang, Anan Li, Hui Gong, Qingming Luo, Haiyan Zhang, Zhaobing Gao, Hualiang Jiang
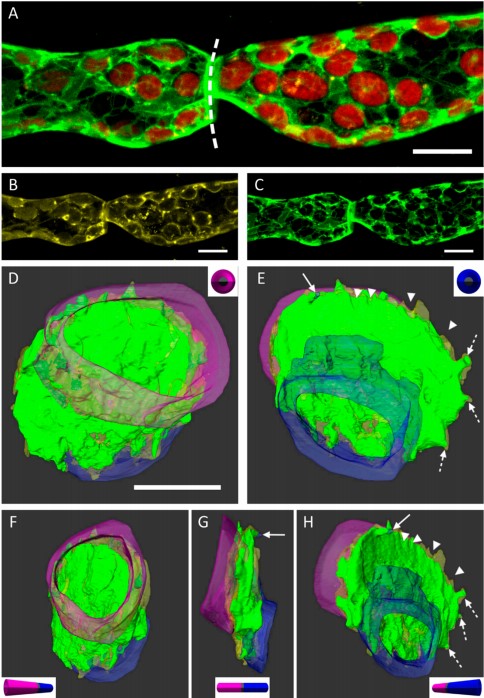
3D Dissection of Structural Membrane-Wall Contacts in Filamentous Moss Protonemata
Cell-to-cell contact is essential for communication and development of multicellular organisms. A prerequisite is the passage through membranes. That way, molecular exchange and information flow is regulated via hormones, membrane proteins and pores.
In plants, the rigid cell walls prevent large membrane contact areas between protoplasts. Only plasmodesmata, minute channels between adjacent cells, form direct connections. Often, molecular data of the proteins involved are manifold but t... Read more
Dominik Harant and Ingeborg Lang
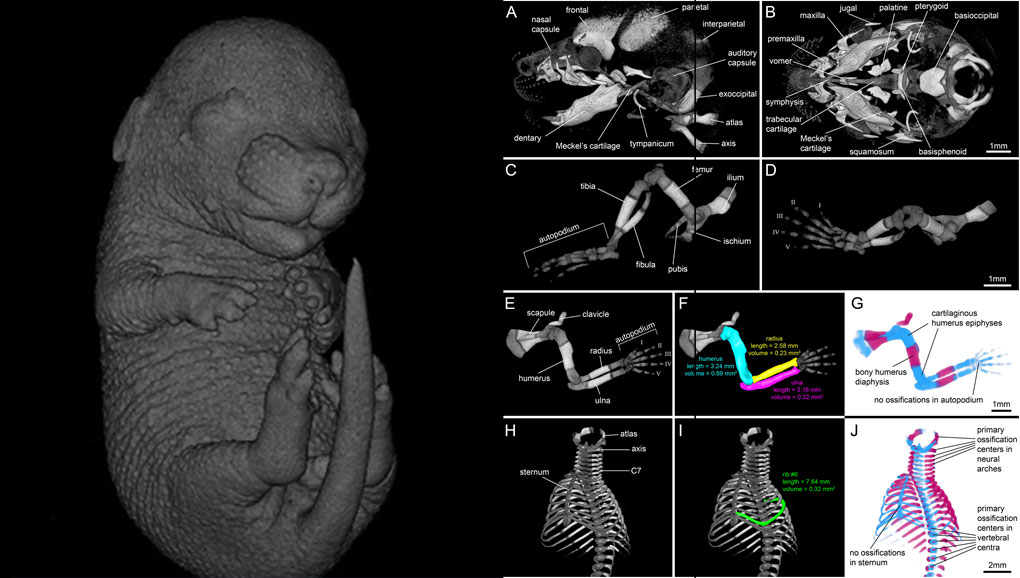
For decades, clearing and staining with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red has been the gold standard to image vertebrate skeletal development. Here, we present an alternate approach to visualise bone and cartilage based on X-ray microCT imaging, which allows the collection of genuine 3D data of the entire developing skeleton at micron resolution.
Our novel protocol is based on ethanol fixation and staining with Ruthenium Red, and efficiently contrasts cartilage matrix, as demonstrated in wh... Read more
Simone Gabner, Peter Böck, Dieter Fink, Martin Glösmann, Stephan Handschuh
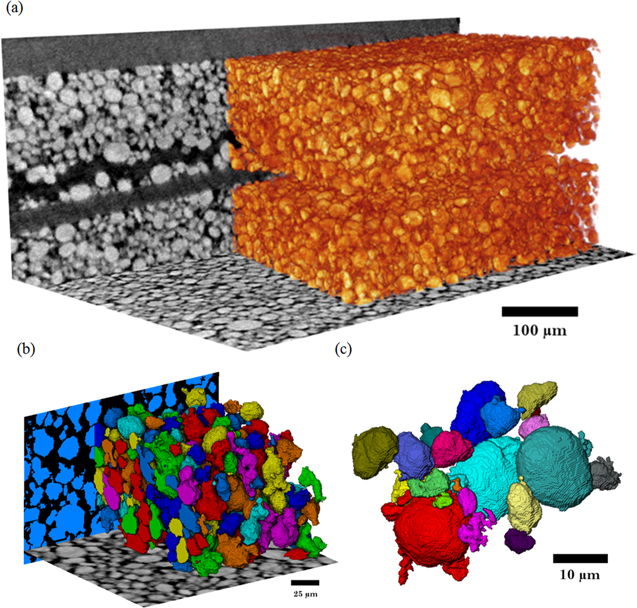
Thermal Runaway of a Li-Ion Battery Studied by Combined ARC and Multi-Length Scale X-ray CT
Lithium ion battery failure occurs across multiple length scales. In this work, the properties of thermal failure and its effects on electrode materials were investigated in a commercial battery using a combination of accelerating rate calorimetry (ARC) and multi-length scale X-ray computed tomography (CT). ARC measured the heat dissipated from the cell during thermal runaway and enabled the identification of key thermal failure characteristics such as onset temperature and the rate of heat g... Read more
Drasti Patel, James B. Robinson, Sarah Ball, Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
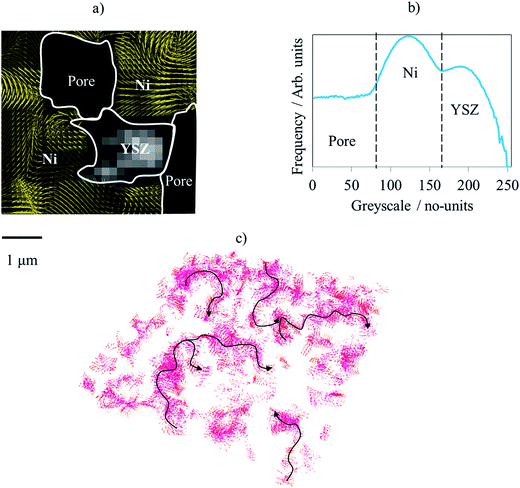
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
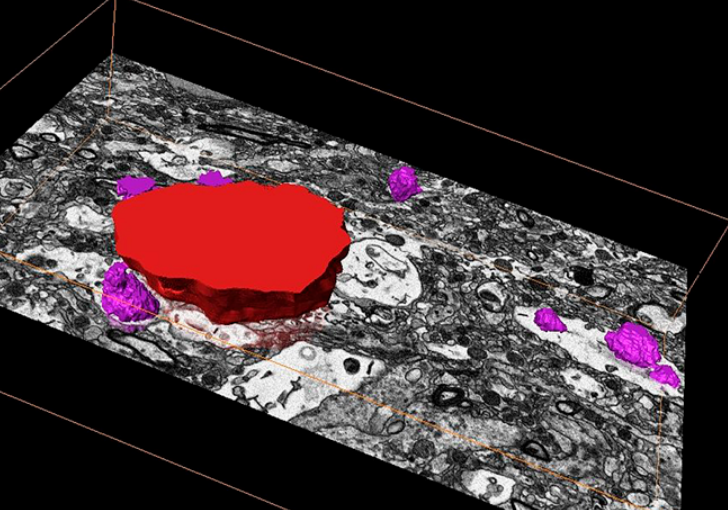
Corpora amylacea are cell-derived structures that appear physiologically in the aged human brain. While their histological identification is straightforward, their ultrastructural composition and microenvironment at the nanoscale have remained unclear so far, as has their relevance to aging and certain disease states that involve the sequestration of toxic cellular metabolites. Here, we apply correlative serial block-face scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron tomograp... Read more
Paula P. Navarro, Christel Genoud, Daniel Castaño-Díez, Alexandra Graff-Meyer, Amanda J. Lewis, Yvonne de Gier, Matthias E. Lauer, Markus Britschgi, Bernd Bohrmann, Stephan Frank, Jürgen Hench, Gabriel Schweighauser, Annemieke J. M. Rozemuller, Wilma D. J. van de Berg, Henning Stahlberg & Sarah H. Shahmoradian
Defect detection in 3D printed carbon fibre composites using X-ray Computed Tomography
X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) has become a vital tool for product quality inspection. The X-ray CT analysis of 3D printed composites, with a layer-by-layer structure of carbon fibre/polyamide and polyamide plies, demonstrates how the void content increases with an increasing number of consecutive carbon fibre layers. Not only the void content, but also the pore
network complexity increases, as more pore types are introduced into the sample. The PolyAmide (PA) matrix has an averag... Read more
Jeroen Soete1, Brice Badoux, Yentl Swolfs, Larissa Gorbatikh, Martine Wevers
The porous transport layer (PTL) is a vital component of the polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyser (PEMWE) as it is both a conduit for current distribution and mass transport. This study aims to examine the influence of the microstructure of the PTL on the performance of a PEMWE by the combination of ex-situ and in-situ techniques. Two PTLs with distinctly different mean pore diameter were characterized to determine key properties such as surface morphology, porosity, pore size dist... Read more
Jude O Majasan, Francesco Iacoviello, Paul R Shearing, Dan JL Brett
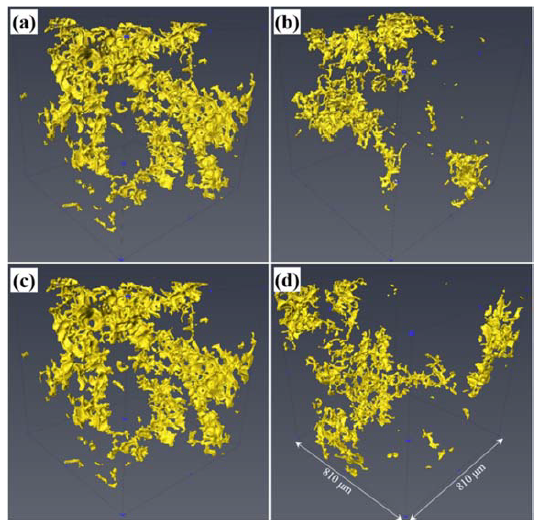
The effect of ultrasonic melting processing on three-dimensional architecture of intermetallic phases and pores in two multicomponent cast Al-5.0Cu 0.6Mn-0.5 Fe alloys is characterized using conventional microscopy and synchrotron X-ray microtomography. (…) The results show that ultrasonic melt processing (USP) significantly reduce the volume fraction, grain size, interconnectivity, and equivalent diameter of the intermetallic phases in both alloys. The volume fraction of pores in both ... Read more
Yuliang Zhao, Dongfu Song, Bo Lin, Chun Zhang, Donghai Zheng, Zhi Wang, Weiwen Zhang
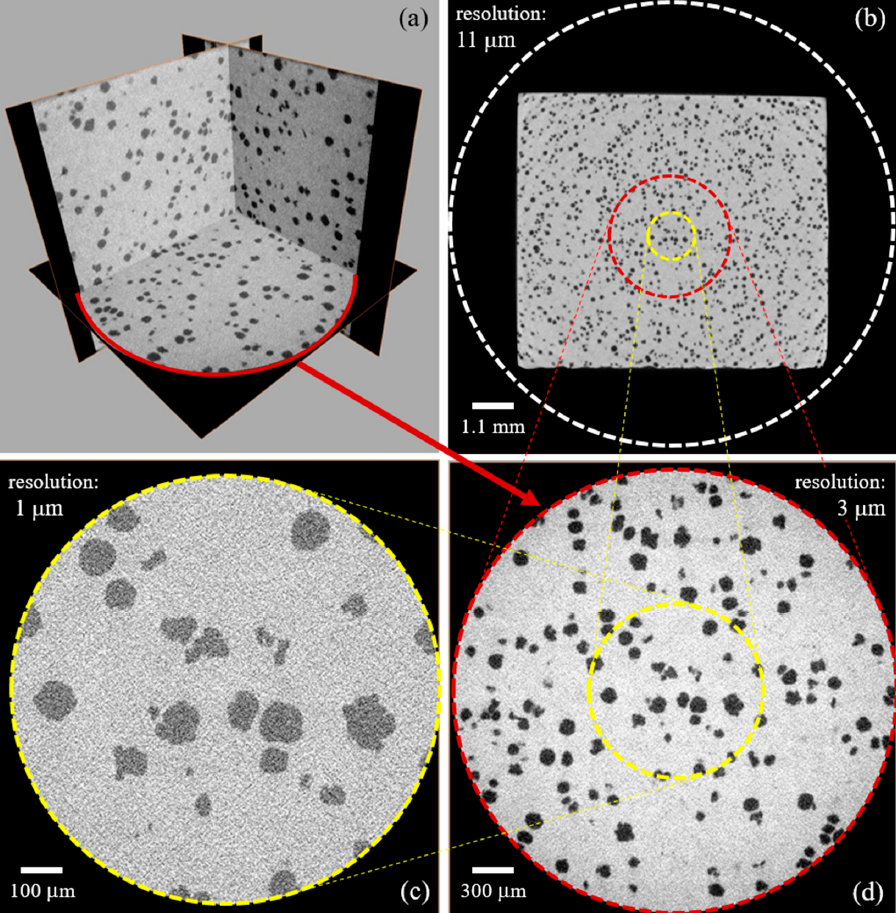
We describe in detail a methodology to estimate the effective elastic parameters of nodular cast iron, using micro-tomography in conjunction with multiscale finite elements. We discuss the adjustment of the image acquisition parameters, address the issue of the representative-volume choice, and present a brief discussion on image segmentation. In addition, the finite-element computational implementation developed to estimate the effective elastic parameters from segmented microstructural imag... Read more
Andre Pereira, Marcio Costa, Carla Anflor, Juan Pardal and Ricardo Leiderman
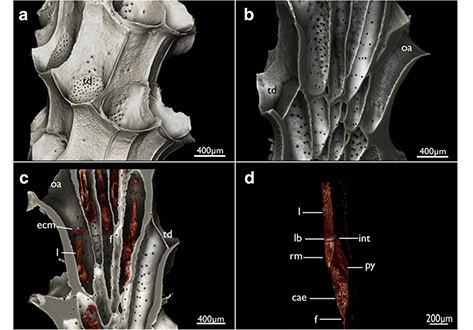
Cyclostome bryozoans are an ancient group of marine colonial suspension-feeders comprising approximately 700 extant species. Previous morphological studies are mainly restricted to skeletal characters whereas data on soft tissues obtained by state-of-the-art methods are still lacking. In order to contribute to issues related to cyclostome ground pattern reconstruction, we analyzed the morphology of the neuromuscular system Cinctipora elegans by means of immunocytochemical staining,... Read more
Thomas F. Schwaha, Stephan Handschuh, Andrew N. Ostrovsky, Andreas Wanninger
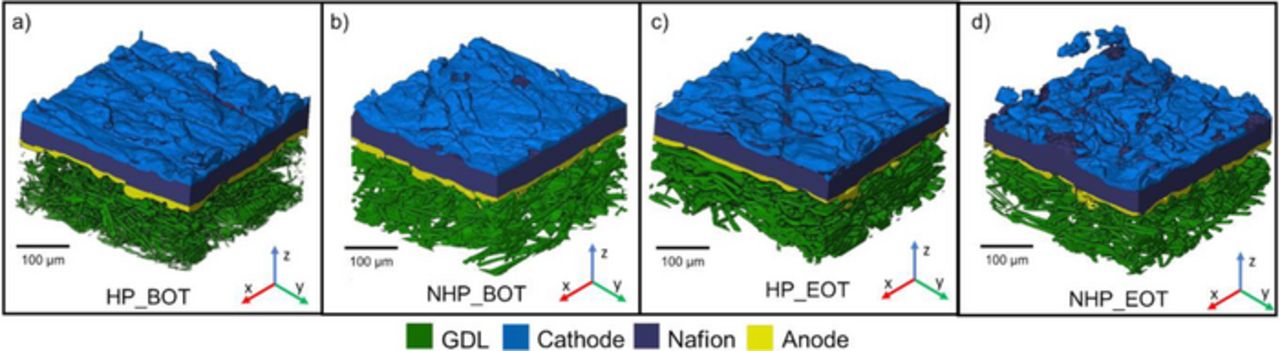
The most common means of fabricating membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) for polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) involves a hot-press step. The conditions used to perform the hot-press impacts the performance and durability of the fuel cell.
However, the hot-press process is not essential for achieving operational MEAs and some practitioners dispense with the hot-press stage altogether by using a self-assembled approach. By performing the integration of the components in-situ durin... Read more
Jennifer Hack, T. M. M. Heenan, F. Iacoviello, N. Mansor, Q. Meyer, P. Shearing, N. Brandon and D. J. L. Brett