Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
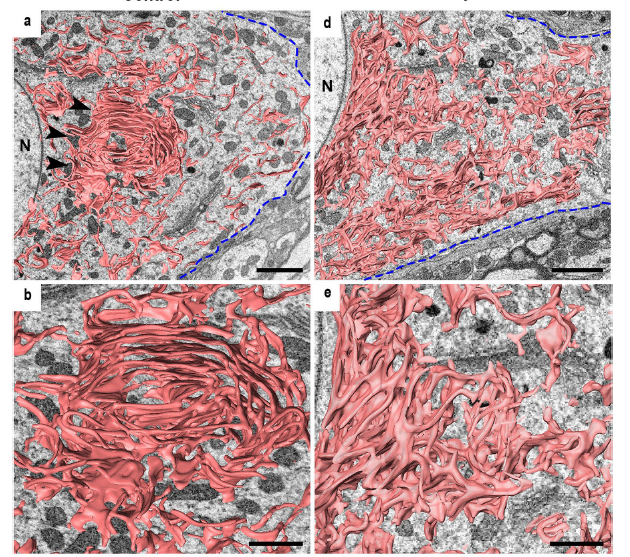
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) extends throughout a cell and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Changes in ER shape could provide a clue to explore the mechanisms that underlie the fate determination of neurons after
axon injury because the ER drastically changes its morphology under neuronal stress to maintain cellular homeostasis and
recover from damage. Because of their tiny structures and richness in the soma, the detailed morphology of the ER and... Read more
Mahmoud Elgendy,Hiromi Tamada, Takaya Taira, Yuma Iio, Akinobu Kawamura, Ayusa Kunogi, Yuka Mizutani, Hiroshi Kiyama
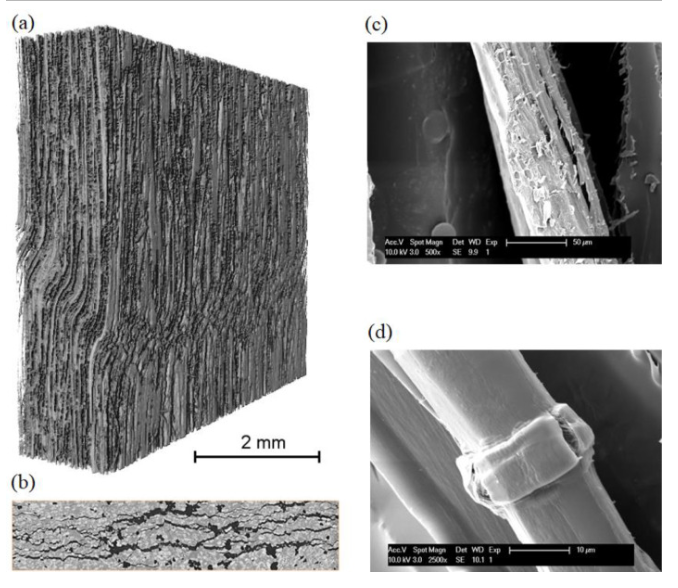
In this study, the researchers investigated the compressive failure mechanisms in flax fiber composites, a promising eco-friendly alternative to synthetic composite materials, through both numerical simulations and experimental analysis. They examined the reasons behind the low compressive strength in comparison to tensile strength, focusing on the compressive-to-tensile strength ratio. A novel thermodynamically consistent continuum damage micromechanics model was introduced to capture the ev... Read more
Vedad Tojaga, Alexandros Prapavesis, Jonas Faleskog, T. Christian Gasser, Aart W. van Vuure, Sören Östlund
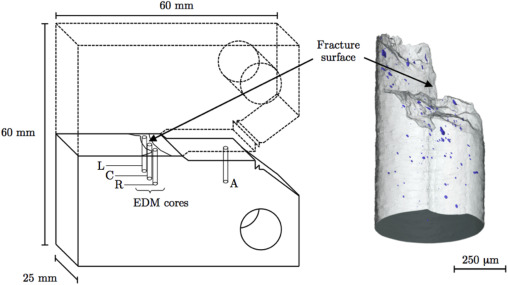
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) has been shown to reveal the true extent of ductile damage below the fracture surface of failed test specimens, which is often significantly underestimated when probed using 2D serial sectioning techniques and a microscope, since a single plane of material may only exhibit only a handful of resolvable voids.
In contrast XCT offers the capability to generate large datasets consisting of hundreds, if not thousands, of individually resolvable voids, where e... Read more
A. J. Cooper ; O. C. G. Tuck ; T. L. Burnett ; A. H. Sherry
Multi-modal plasma focused ion beam serial section tomography of an organic paint coating
Pigment distributions have a critical role in the corrosion protection properties of organic paint coatings, but they are difficult to image in 3D over statistically significant volumes and at sufficiently high spatial resolutions required for detailed analysis. Here we report, for the first time, large volume analytical serial sectioning tomography of an organic composite coating using a xenon Plasma Focused Ion Beam (PFIB) combined with secondary electron imaging, energy dispersive X-ray (E... Read more
Zhong Xiangli, M. Grace Burke, Philip J. Withers, Zhang Xun, Zhou Xiaorong, Timothy L. Burnett, Liu Yanwen, Stuart B. Lyon, Simon R.Gibbon
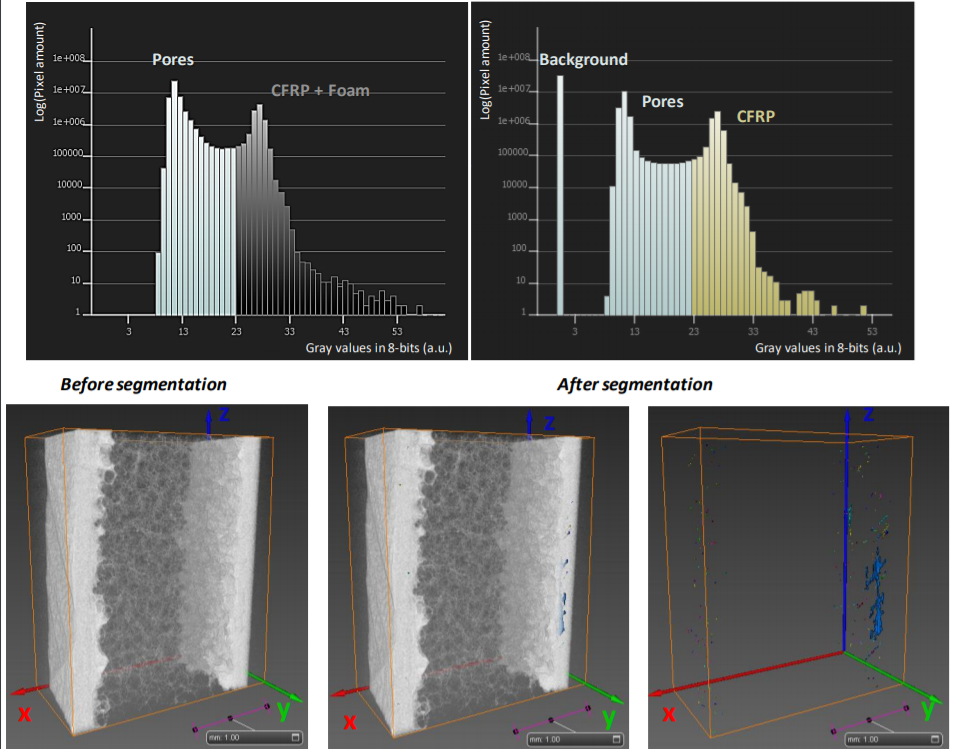
The aim of the current study is to propose a versatile, non-destructive inspection strategy to evaluate the structure of two different aircraft carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) -based composite configurations, which are widely used for structural elements, respectively layered composite and sandwich structure. X-ray computed tomography (CT) has been used as a flexible method for assessment of porosity levels in CFRP components in both types of configuration, permitting to investigate th... Read more
Elena Dilonardo, Michele Nacucchi, Fabio De Pascalis, Mauro Zarrelli, Cinzia Giannini
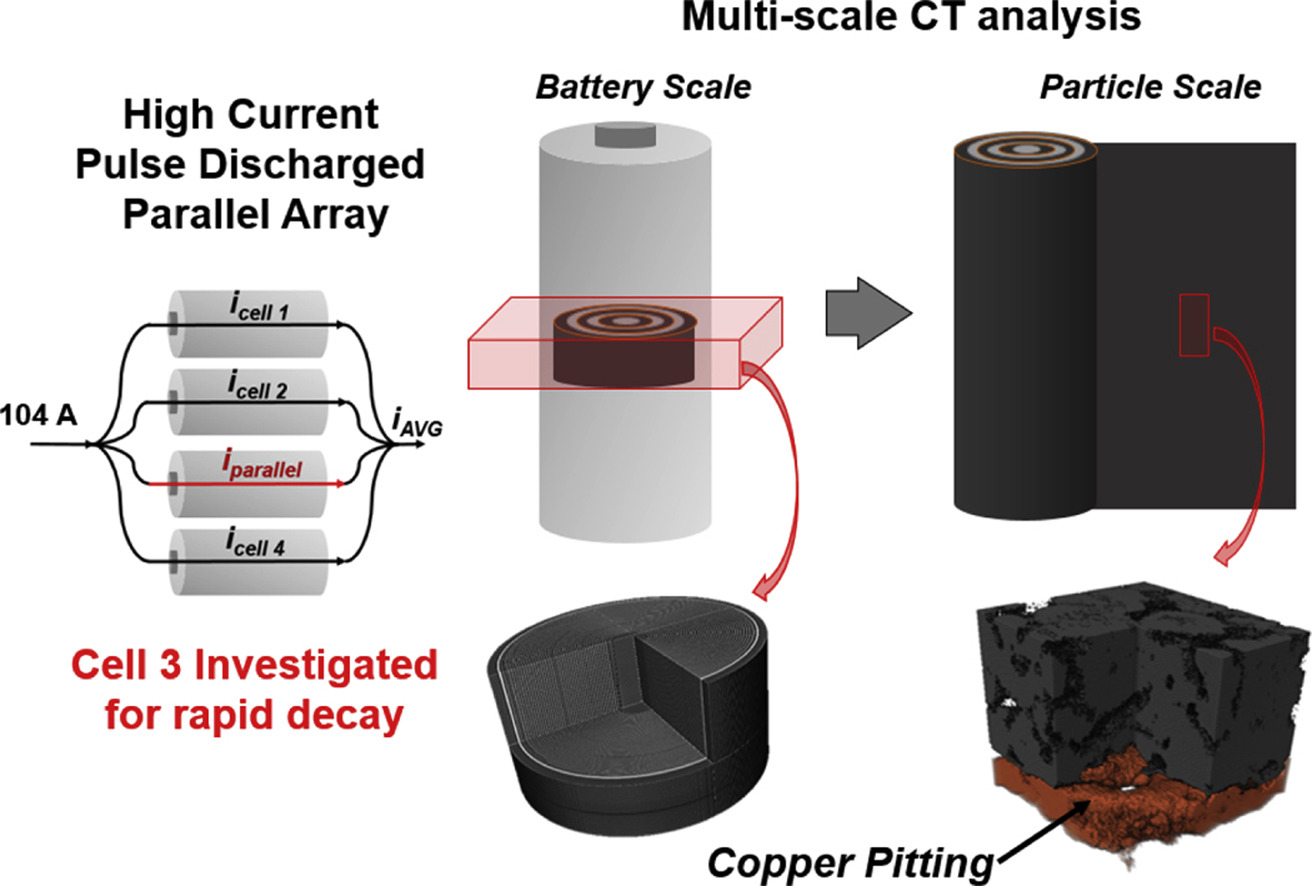
X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) across multiple length scales is utilized for the first time to investigate the physical abuse of high C-rate pulsed discharge on cells wired individually and in parallel.. Manufactured lithium iron phosphate cells boasting high rate capability were pulse power tested in both wiring conditions with high discharge currents of 10C for a high number of cycles (up to 1200) until end of life (<80% of initial discharge capacity retained). The parallel ass... Read more
Rachel Carter, Brett Huhman, Corey T. Love, Iryna V. Zenyuk
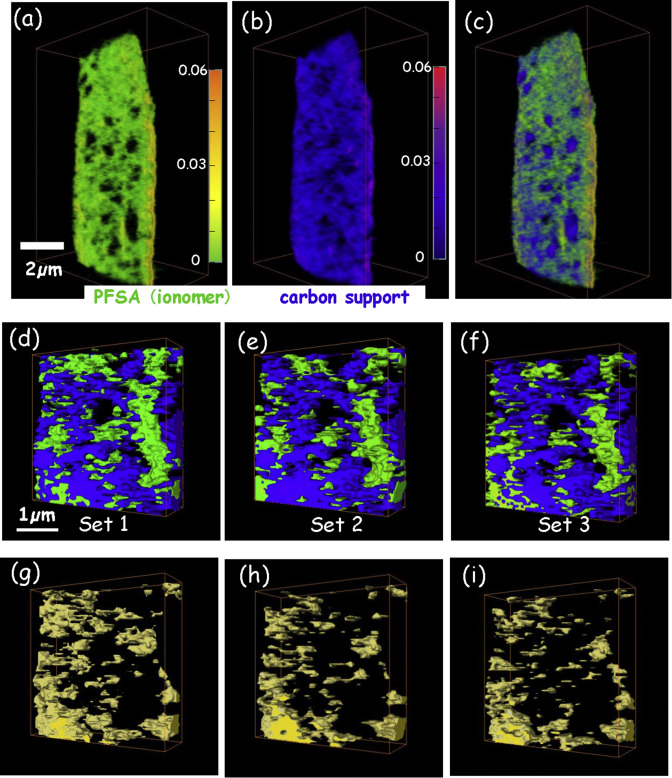
4D imaging – the three-dimensional distributions of chemical species determined using multi-energy X-ray tomography – of cathode catalyst layers of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEM-FC) has been measured by scanning transmission x-ray microscopy (STXM) spectro-tomography at the C 1s and F 1s edges. In order to monitor the effects of radiation damage on the composition and 3D structure of the perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) ionomer, the same volume was measu... Read more
Juan Wu, Lis G.A.Melo, Xiaohui Zhu, Marcia M.West, Viatcheslav Berejnov, Darija Susac, Juergen Stumper, Adam P.Hitchcock
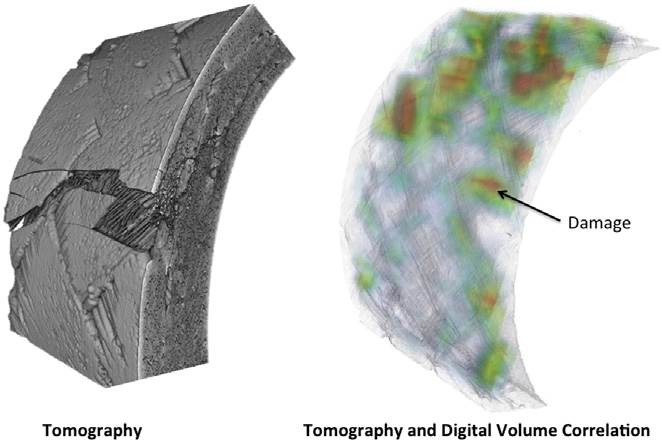
In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite
SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composites are candidate materials for fuel cladding in Generation IV nuclear fission reactors and as accident tolerant fuel clad in current generation plant.
Experimental methods are needed that can detect and quantify the development of mechanical damage, to support modelling and qualification tests for these critical components. In situ observations of damage development have been obtained of tensile and C-ring mechanical test specimens of a braided nuclear gr... Read more
L. Saucedo-Mora, T. Lowe, S. Zhao, P.D. Lee, P.M. Mummery, T.J. Marrow
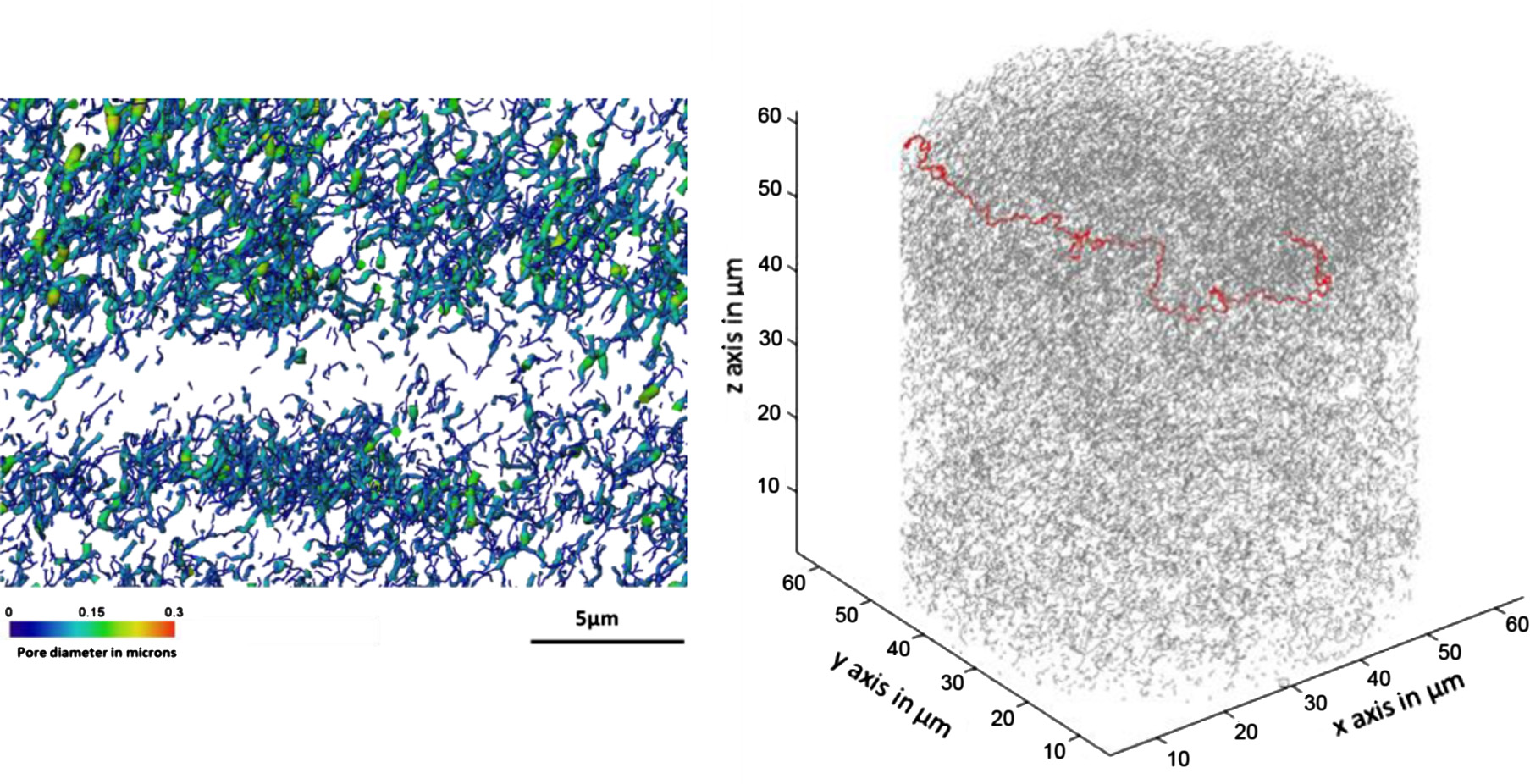
Microstructural analysis of TRISO particles using multi-scale X-ray computed tomography
TRISO particles, a composite nuclear fuel built up by ceramic and graphitic layers, have outstanding high temperature resistance. TRISO fuel is the key technology for High Temperature Reactors (HTRs) and the Generation IV Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) variant.
TRISO offers unparalleled containment of fission products and is extremely robust during accident conditions. An understanding of the thermal performance and mechanical properties of TRISO fuel requires a detailed knowledg... Read more
T. Lowe, R.S. Bradley, S. Yue, K. Barii, J. Gelb, N. Rohbeck, J. Turner, P.J. Withers
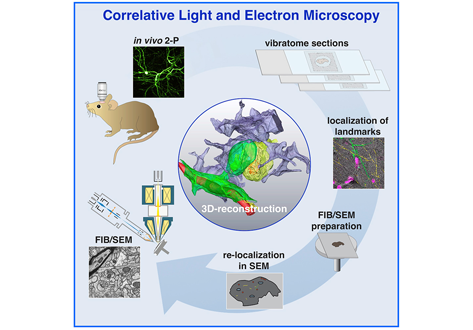
Label-free 3D-CLEM using endogenous tissue landmarks
We demonstrate feasibility of the workflow by combining in vivo 2-photon microscopy and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB/SEM) to dissect the role of astrocytic coverage in the persistence of dendritic spines.
Emerging 3D correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) approaches enable studying neuronal structure-function relations at unprecedented depth and precision. However, established protocols for the correlation of light and electron micrographs rely ... Read more
Manja Luckner,Steffen Burgold, Severin Filser, Maximilian Scheungrab, Yilmaz Niyaz, Eric Hummel, Gerhard Wanner, Jochen Herms
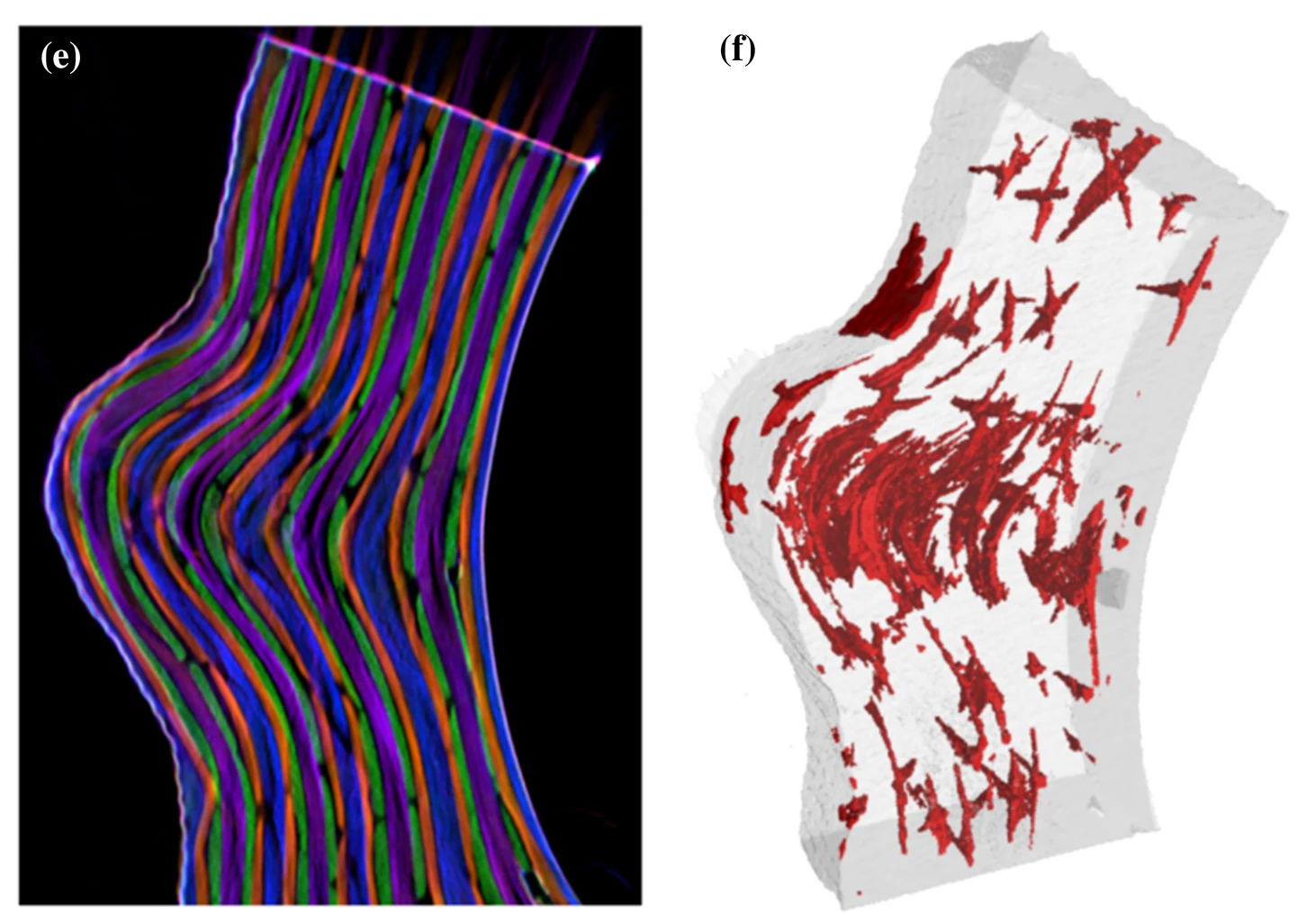
The high strength at moderate weight in combination with superior corrosion and fatigue properties makes carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) an attractive material for lightweight applications in aerospace. Nonetheless, besides several benefits, CFRP components also bear significant risks like a low resistance to impact damage. […] In this work, we present a multimodal approach to three-dimensionally quantify and visualize fiber orientation and resin-rich areas in carbon-fiber-reinf... Read more
Jonathan Glinz, Jan Šleichrt, Daniel Kytýř, Santhosh Ayalur-Karunakaran, Simon Zabler, Johann Kastner & Sascha Senck
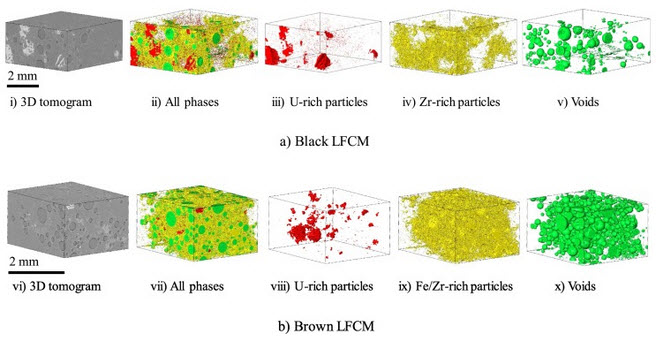
Decommissioning of the damaged Chernobyl nuclear reactor Unit 4 is a top priority for the global community. Before such operations begin, it is crucial to understand the behaviour of the hazardous materials formed during the accident. Since those materials formed under extreme and mostly unquantified conditions, modelling alone is insufficient to accurately predict their physical, chemical and, predominantly, mechanical behaviour. Meanwhile, knowledge of the mechanical characteristics of thos... Read more
C.Paraskevoulakos, J.P.Forna-Kreutzer, K.R.Hallam, C.P.Jones, T.B.Scott, C.Gausse, D.J.Bailey, C.A.Simpson, D.Liu, C.Reinhard, C.L.Corkhill, M.Mostafavi
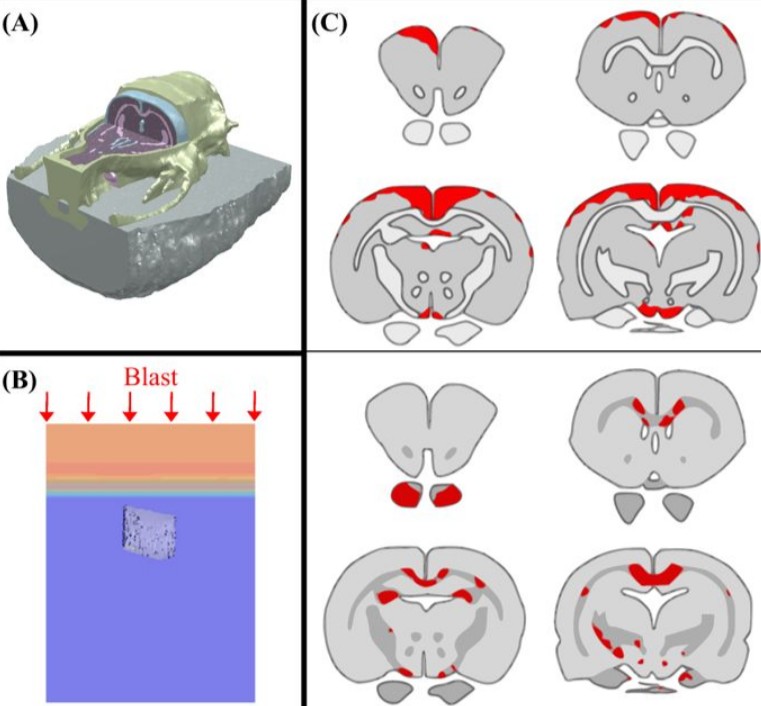
Cognition based bTBI mechanistic criteria; a tool for preventive and therapeutic innovations
Blast-induced traumatic brain injury has been associated with neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. To date, although damage due to oxidative stress appears to be important, the specific mechanistic causes of such disorders remain elusive. Here, to determine the mechanical variables governing the tissue damage eventually cascading into cognitive deficits, we performed a study on the mechanics of rat brain under blast conditions. To this end, experiments were carried out to analyse... Read more
Daniel Garcia-Gonzalez, Nicholas S. Race, Natalie L. Voets, Damian R. Jenkins, Stamatios N. Sotiropoulos, Glen Acosta, Marcela Cruz-Haces, Jonathan Tang, Riyi Shi & Antoine Jérusalem
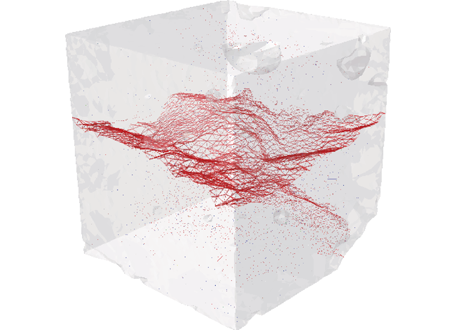
Three-Dimensional In Situ XCT Characterisation and FE Modelling of Cracking in Concrete
An improved understanding of 3D cracking in concrete can be achieved by multiscale experiments and numerical modelling based on realistic microstructures, for the development of materials with higher strength, durability, and fracture resistance.
Three-dimensional (3D) characterisation and modelling of cracking in concrete have been always of great importance and interest in civil engineering. In this study, an in situ microscale X-ray computed tomography (XCT) test was carried out to ... Read more
Wenyuan Ren, Zhenjun Yang, Rajneesh Sharma, Samuel A. McDonald, Paul M. Mummery
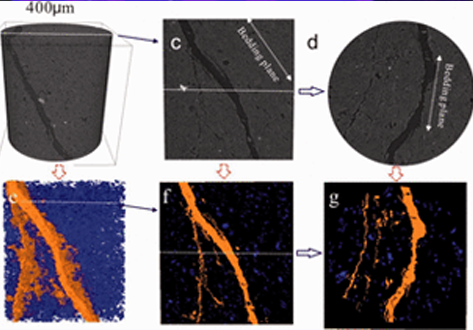
Experimental study on the cracking process of layered shale using X-ray microCT
The cracking process in Longmaxi formation shale was experimentally studied during uniaxial compressive loading. Both the evolution of the three-dimensional fracture network and the micromechanics of failure in the layered shale were examined as a function of the inclination angle of the bedding plane. To visualize the cracking process, the test devices presented here used an industrial X-ray CT scanner that enabled scanning during the uniaxial compressive loading. Scanning electron microscop... Read more
Institue of Geomechanic, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Laboratory of Shale Oil & Gas, Beijing, China
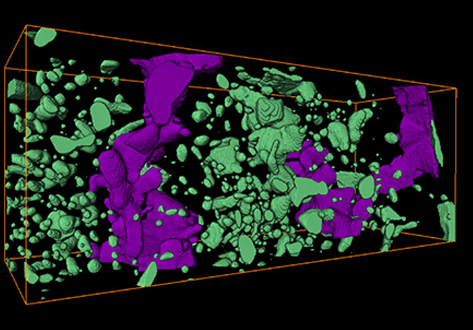
Fragmentation of wall rock garnets during deep crustal earthquakes
Deformation of the lithosphere by seismic slip along faults dissipates energy to the immediate surroundings as heat and elastic waves. Heat effects may occasionally cause frictional melting along the slip plane, leading to the formation of pseudotachylite, a characteristic fine-grained or glassy fault rock, interpreted as the quenched melt. Recently, it has been suggested that mechanical effects due to rapid loading, such as the formation of shiny “mirror” surfaces or pulverization of roc... Read more
Department of Geosciences, University of Oslo; Department of Earth Sciences, Utrecht University; Géosciences Montpellier, Université de Montpellier; Debye Institute for Nanomaterials Science, Utrecht University
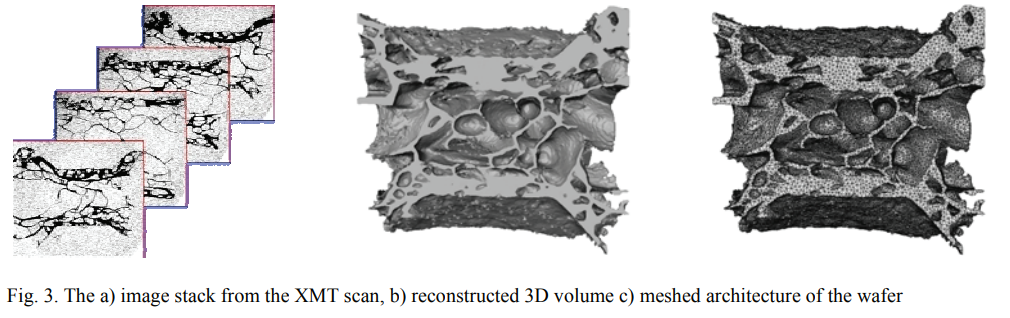
Modelling deformation and fracture in confectionery wafers
The aim of this research is to model the deformation and fracture behaviour of brittle wafers often used in chocolate confectionery products.
Three point bending and compression experiments were performed on beam and circular disc samples respectively to determine the ‘apparent’ stress-strain curves in bending and compression. The deformation of the wafer for both these testing types was observed in-situ within an SEM. The wafer is modelled analytically and numerically as a composi... Read more
Idris K. Mohammeda, Maria N. Charalambides , J. Gordon Williams , John Rasburn
The paper proposes a new experimental methodology, based on ultrasonic measurements, that aims at evaluating the anisotropic damage in woven semi-crystalline polymer composites through new damage indicators. Due to their microstructure, woven composite materials are characterized by an anisotropic evolution of damage induced by different damage mechanisms occurring at the micro or mesoscopic scales. In this work, these damage modes in polyamide 6.6/6-woven glass fiber reinforced composites ha... Read more
Pascal Pomarède, Fodil Meraghni, Laurent Peltier, Stéphane Delalande, Nico F. Declercq
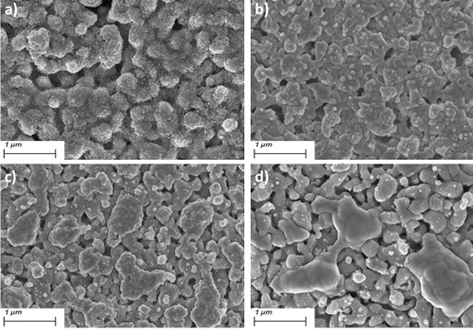
The electrochemical performance of Ni-YSZ SOFC anodes can quickly degrade during redox cycling. Mechanical damage at interfaces significantly decreases the number of active triple phase boundaries. This study firstly focuses on the sintering temperature impact on YSZ scaffold mechanical properties. The YSZ scaffold sintered at 1200 °C exhibited 56% Read more
B.Song; E.Ruiz-Trejo; N.P.Brandon
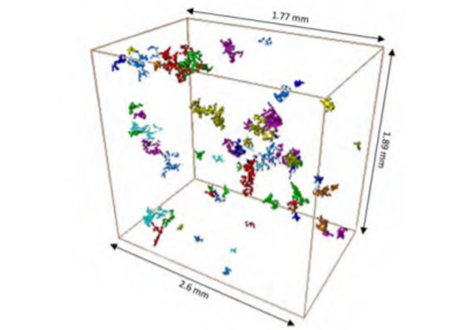
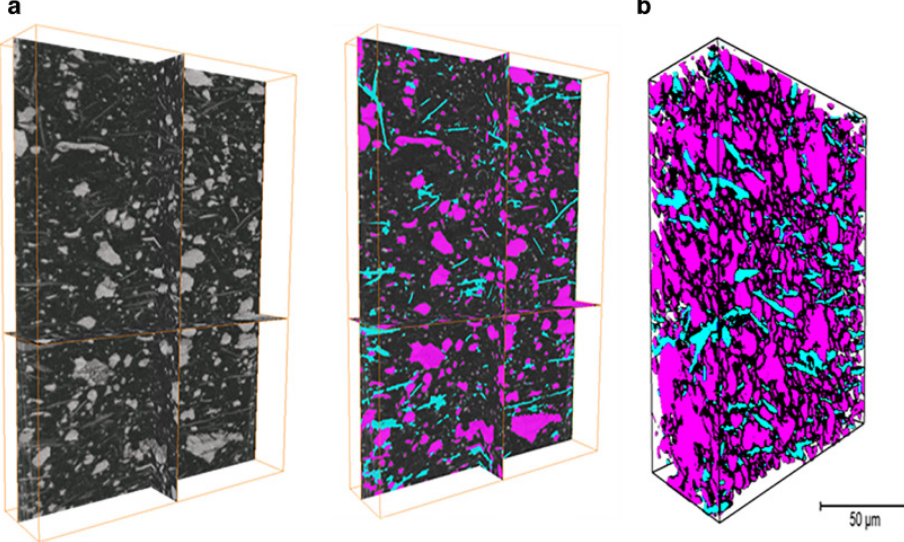
3D characterization of the fracture mechanisms of a Fe-rich Al-Si-Cu alloy
The effect of the defect size and morphology on the fatigue damage evolution was analysed in a recycled Al-Si-Cu alloy by micro-computed tomography and scanning electron microscopy. Fatigue tests were performed and the different crack initiation scenarios were characterized and classified. The interaction between shrinkage and gas pores was the key crack initiation mechanism and the ß-Al5FeSi particles did not play any role in the crack initiation phase. However, crack path analysis indicate... Read more
Angelika Brueckner-Foit, Inigo Bacaicoa, Martin Luetje, Marcel Wicke, Andreas Geisert, Martin Fehlbier
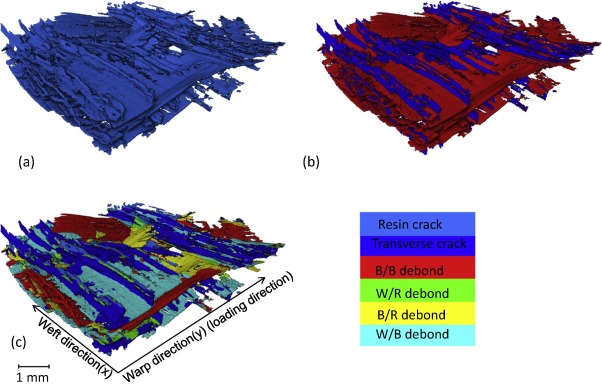
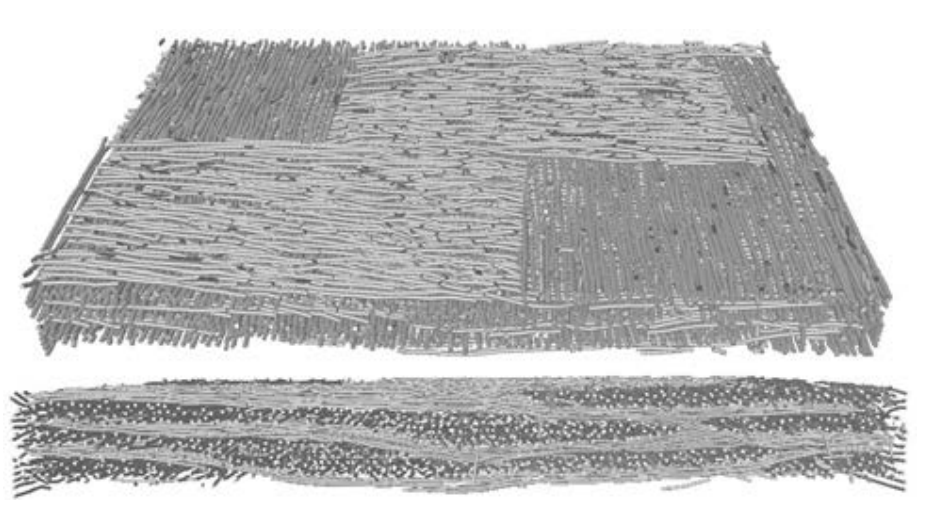
Three dimensional (3D) composites were proposed over 40 years ago in an attempt to overcome the shortcomings of 2D laminates, by incorporating fibres into the through-thickness direction. 3D weaving offer significant manufacturing benefits as well as creating versatile textiles having a range of 3D architectures.
The development of fatigue damage in a glass fibre modified layer-to-layer three dimensional (3D) woven composite has been followed by time-lapse X-ray computed tomograp... Read more
B. Yu, R. Blanc, C. Soutis, P.J. Withers