Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized particles. Achieving a deep understanding and precise modelling of loess behavior necessitates comprehensive knowledge of the realistic 3D microstructure.
- Innovative 3D analysis of loess microstructure using μXCT and FIB-SEM.
- Detailed visualizat... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
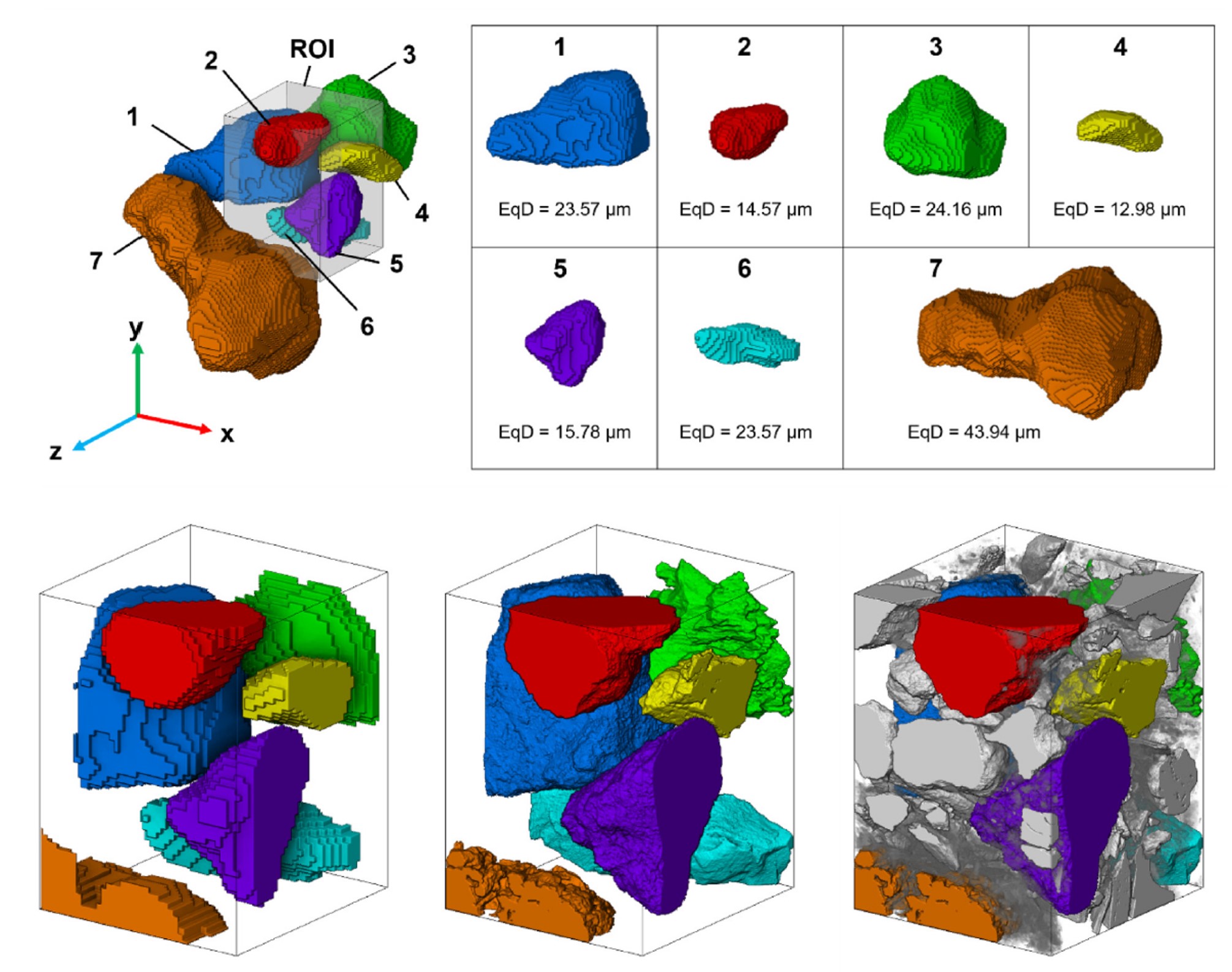
3D loess microstructure of loess, including skeleton particles as well as inter-particle bonding structures, was characterized through a correlative approach using μXCT and FIB-SEM
Loess, a Quaternary wind-blown deposit, is a problem soil that gives rise to frequent geohazards such as landslides and water-induced subsidence. The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized
skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized p... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
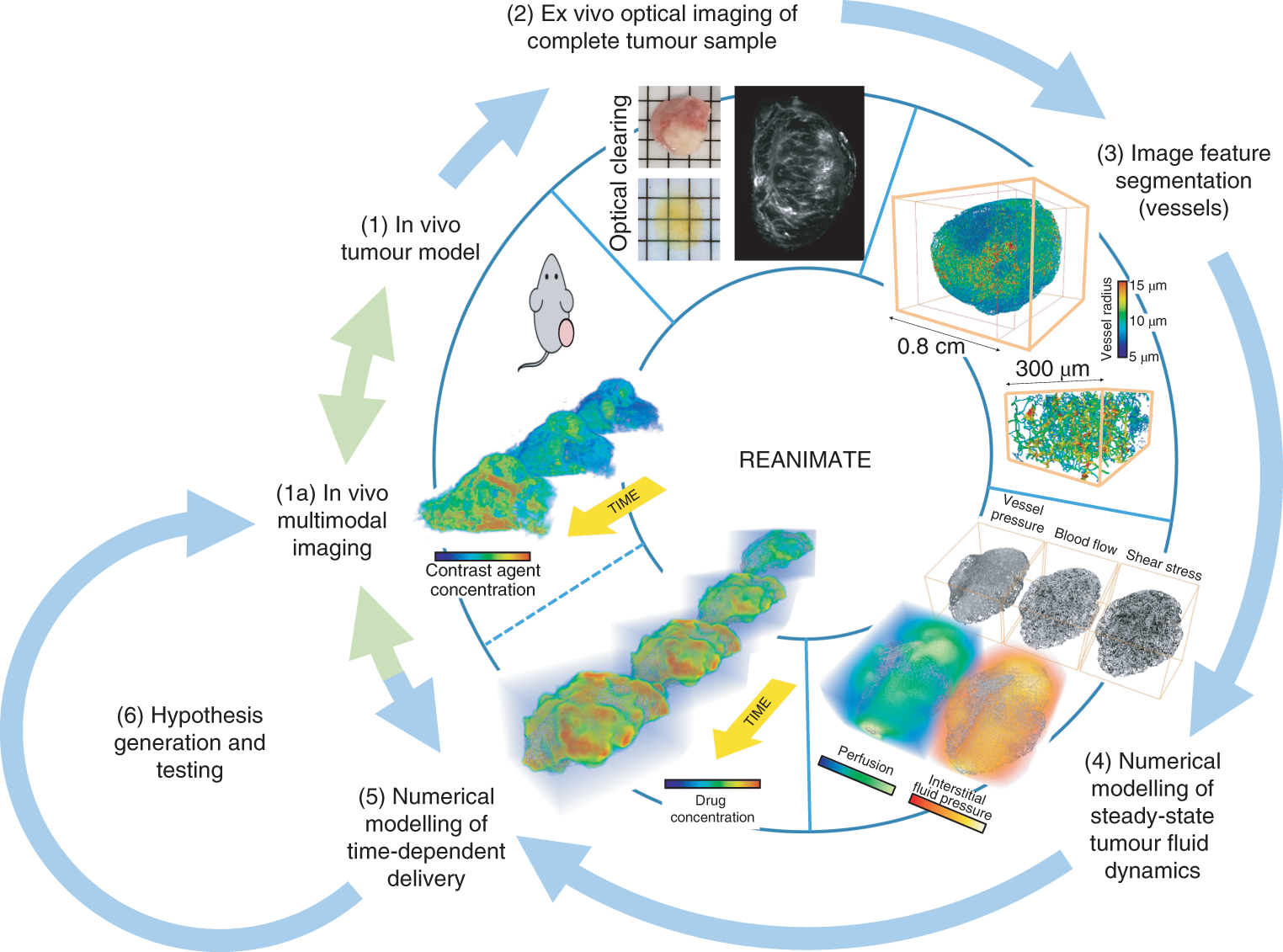
Understanding the uptake of a drug by diseased tissue, and the drug’s subsequent spatiotemporal distribution, are central factors in the development of effective targeted therapies. However, the interaction between the pathophysiology of diseased tissue and individual therapeutic agents can be complex, and can vary across tissue types and across subjects. Here, we show that the combination of mathematical modelling, high-resolution optical imaging of intact and optically cleared tumour tiss... Read more
Angela d’Esposito, Paul W. Sweeney, Morium Ali, Magdy Saleh, Rajiv Ramasawmy, Thomas A. Roberts, Giulia Agliardi, Adrien Desjardins, Mark F. Lythgoe, R. Barbara Pedley, Rebecca Shipley and Simon Walker-Samuel
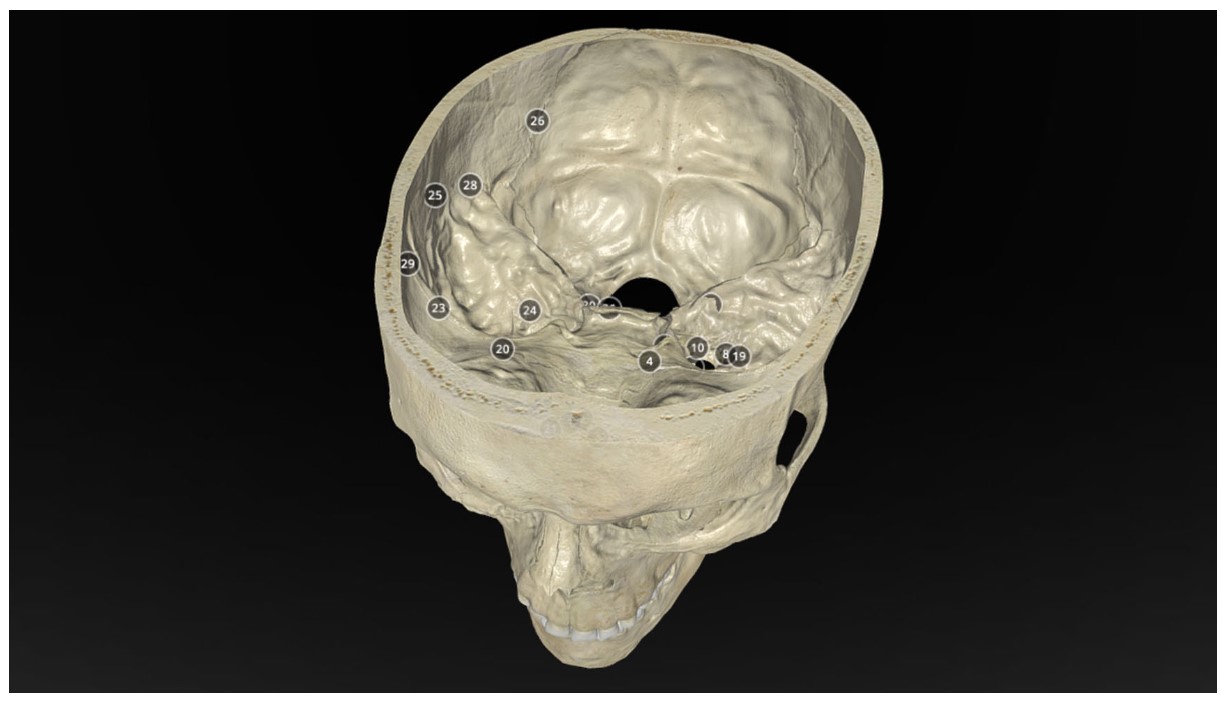
Operative Anatomy of the Human Skull: A Virtual Reality Expedition
Benjamin K Hendricks, MD Akash J Patel, MD Jerome Hartman Mark F Seifert, PhD Aaron Cohen-Gadol, MD, MSc, MBA
Revealing the mechanisms by which magneto-hydrodynamics disrupts solidification microstructures
A key technique for controlling solidification microstructures is magneto-hydrodynamics (MHD), resulting from imposing a magnetic field to solidifying metals and alloys. Applications range from bulk stirring to flow control and turbulence damping via the induced Lorentz force. Over the past two decades the Lorentz force caused by the interaction of thermoelectric currents and a magnetic field, a MHD phenomenon known as Thermoelectric Magnetohydrodynamics (TEMHD), was also shown to drive inter... Read more
B. Cai, A. Kao, E. Boller, O.V. Magdysyuk, R.C. Atwood, N.T. Vo, K. Pericleous, P.D. Lee
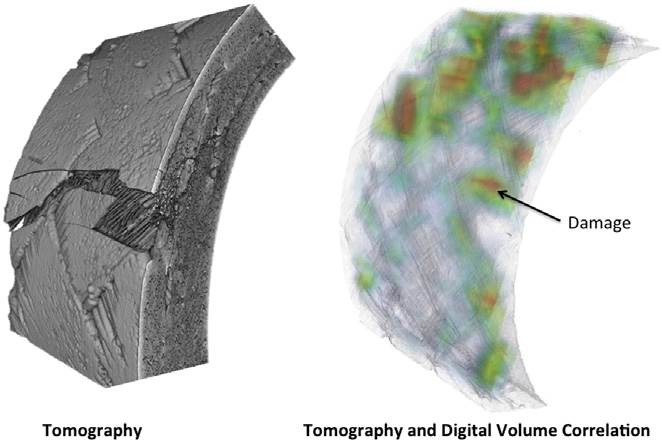
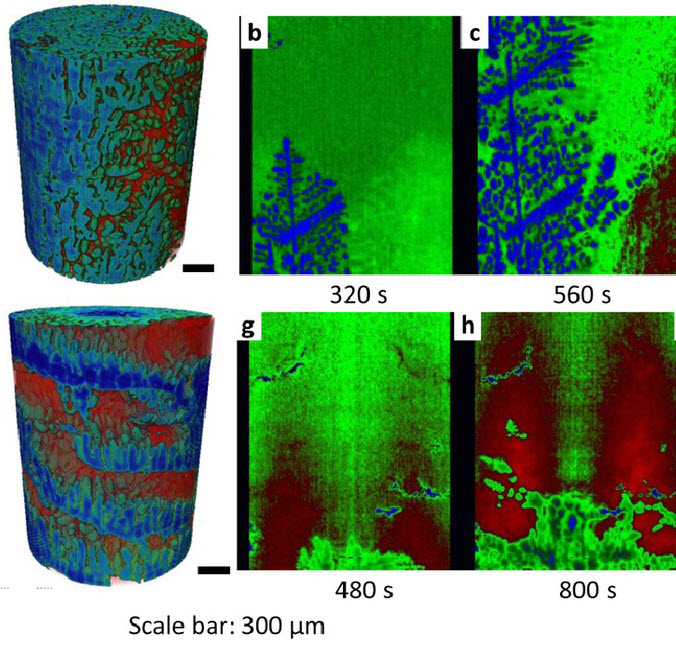
In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite
SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composites are candidate materials for fuel cladding in Generation IV nuclear fission reactors and as accident tolerant fuel clad in current generation plant.
Experimental methods are needed that can detect and quantify the development of mechanical damage, to support modelling and qualification tests for these critical components. In situ observations of damage development have been obtained of tensile and C-ring mechanical test specimens of a braided nuclear gr... Read more
L. Saucedo-Mora, T. Lowe, S. Zhao, P.D. Lee, P.M. Mummery, T.J. Marrow
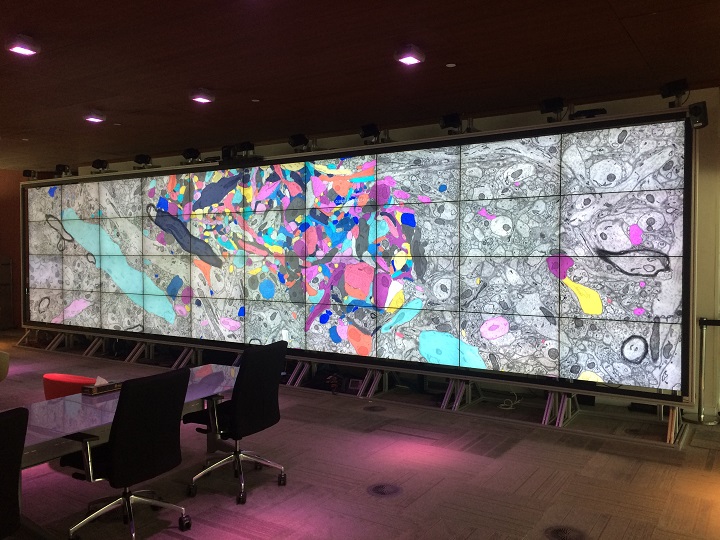

Insights into data with the KAUST Visualization Core Lab
Through collaboration, the KAUST Visualization Core Lab (KVL) team augments the efforts and domain expertise of KAUST researchers by providing complimentary technical knowledge with exploratory visualization and analytic tools.
KVL’s multi-year collaboration with KAUST Distinguished Professor P. Magistretti and research scientist C. Calì’s KAUST-EPFL Alliance for Integrative Modelling of Brain Energy Metabolism project—itself a collaboration with the Swiss Blue Br... Read more
By the KAUST Visualization Core Lab team and Caitlin Clark
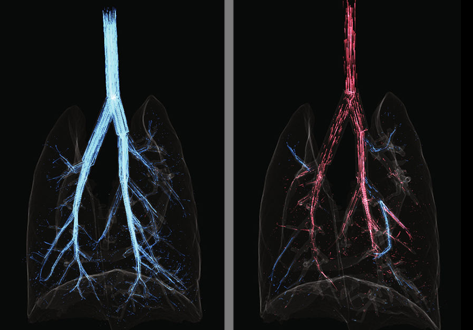
Cardiogenic Airflow in the Lung Revealed Using Synchrotron-Based Dynamic Lung Imaging
The beating heart is known to produce pressure and airflow oscillations in the lungs of mammals. This phenomenon is often disregarded as detailed measurement of its effects in the lung have hitherto not been possible. Previous studies have attempted to measure the effect of these oscillations on gas mixing. However, the results have proven inconclusive, due to the lack of a direct measurement tool capable of flow measurement throughout the entire bronchial tree. Here we present the first deta... Read more
Stephen Dubsky, Jordan Thurgood, Andreas Fouras, Bruce R. Thompson & Gregory J. Sheard
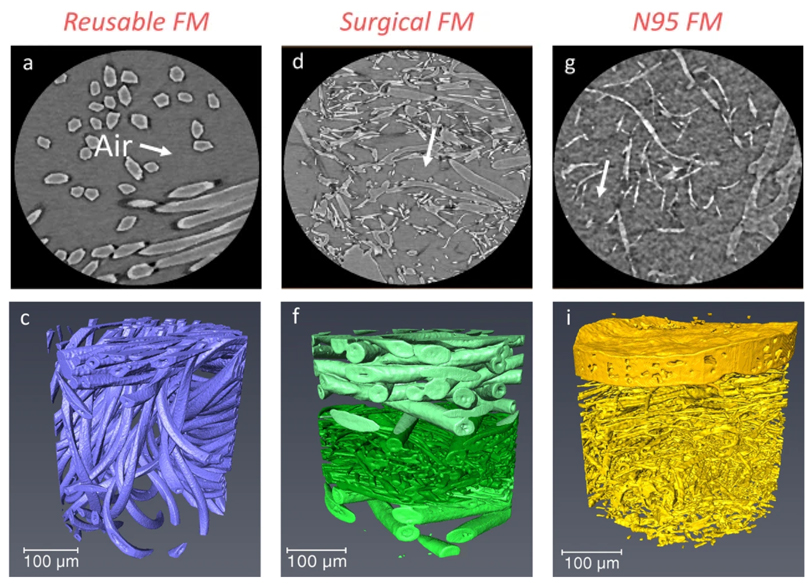
Microstructure analysis and image-based modelling of face masks for COVID-19 virus protection
Until March 2021, around 120 million coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infected cases and over 2.6 million deaths have been reported worldwide. […] Recent investigations have implied that face masks help to reduce the disease transmission and therefore slow down the growth of the epidemic curve. However, there are still ongoing debates on the efficacy of wearing masks […] since there is a general lack of information relating to the material structure of commonly used face masks.Read more
Wenjia Du, Francesco Iacoviello, Tacson Fernandez, Rui Loureiro, Daniel J. L. Brett & Paul R. Shearing
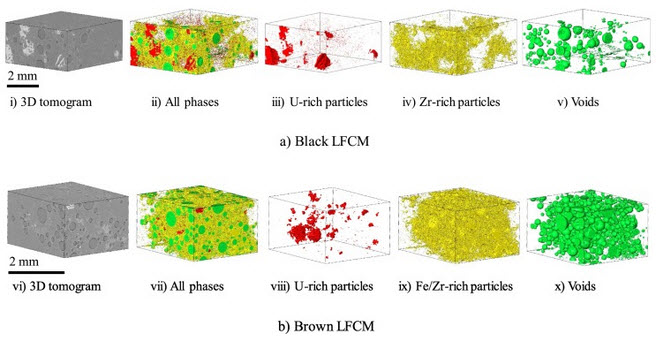
High market demands related to material quality and properties strongly influence redesigning of common safety loaded aluminum alloy castings. The quality of aluminum components and associated obtained mechanical properties are strongly dependent on the casting process and parameters, as well as on the chemical composition. Therefore, the redesigning of chemical composition of high-strength aluminum alloys becomes significant for safety critical structural components in automotive industry.Read more
Davor Stanić, Zdenka Zovko Brodarac, Letian Li
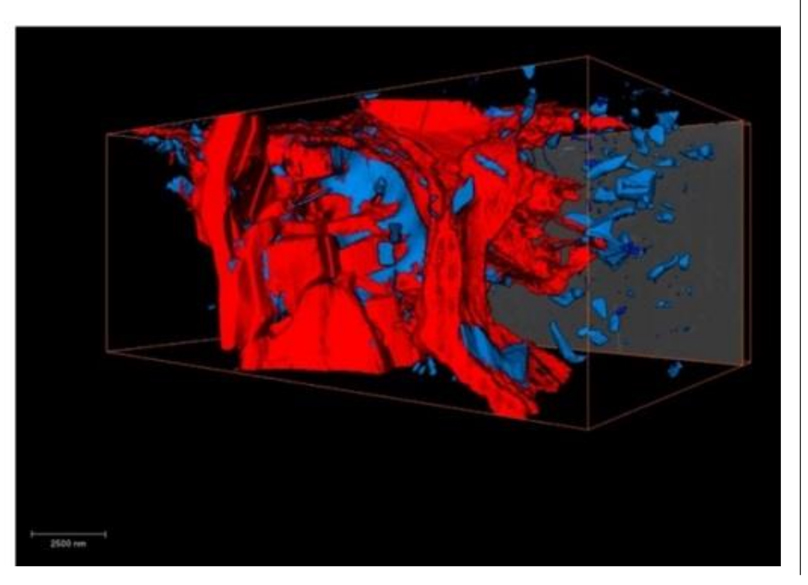
Decommissioning of the damaged Chernobyl nuclear reactor Unit 4 is a top priority for the global community. Before such operations begin, it is crucial to understand the behaviour of the hazardous materials formed during the accident. Since those materials formed under extreme and mostly unquantified conditions, modelling alone is insufficient to accurately predict their physical, chemical and, predominantly, mechanical behaviour. Meanwhile, knowledge of the mechanical characteristics of thos... Read more
C.Paraskevoulakos, J.P.Forna-Kreutzer, K.R.Hallam, C.P.Jones, T.B.Scott, C.Gausse, D.J.Bailey, C.A.Simpson, D.Liu, C.Reinhard, C.L.Corkhill, M.Mostafavi
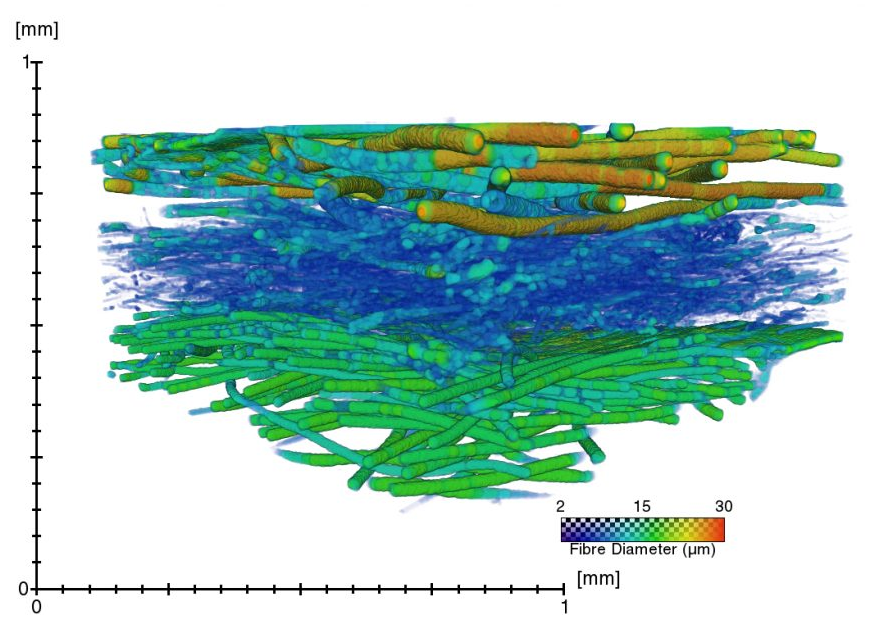
A virtual testing platform for filter materials and textile masks
In order to provide the population with consistent and science-based advice on preferred materials for face masks, we are characterizing the microstructure of different materials using X-ray microfocus computed tomography (microCT), and we use these datasets to simulate the pressure drop (i.e. measure for breathability). We validate our measurements with physically measured filter efficiency and pressure drop, and in this way, we try to develop a “virtual testing platform” for the charac... Read more
The ContrasTTeam of Prof. dr. Greet Kerckhofs, UCLouvain and MTM
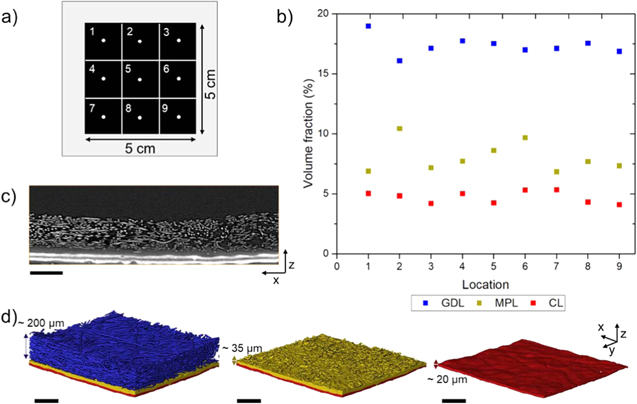
With the growing use of X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) datasets for modelling of transport properties, comes the need to define the representative elementary volume (REV) if considering three dimensions or the representative elementary area (REA) if considering two dimensions. The resolution used for imaging must be suited to the features of interest in the sample and the region-of-interest must be sufficiently large to capture key information. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells have a hier... Read more
Jennifer Hack et al 2020 J. Electrochem.
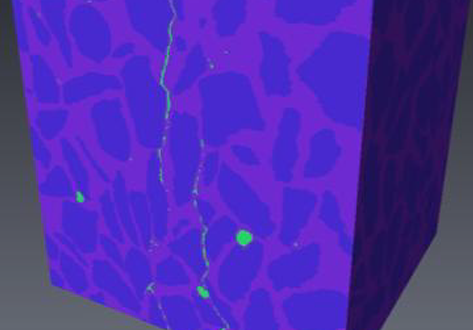
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
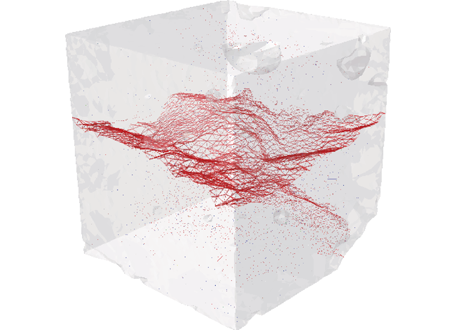
Three-Dimensional In Situ XCT Characterisation and FE Modelling of Cracking in Concrete
An improved understanding of 3D cracking in concrete can be achieved by multiscale experiments and numerical modelling based on realistic microstructures, for the development of materials with higher strength, durability, and fracture resistance.
Three-dimensional (3D) characterisation and modelling of cracking in concrete have been always of great importance and interest in civil engineering. In this study, an in situ microscale X-ray computed tomography (XCT) test was carried out to ... Read more
Wenyuan Ren, Zhenjun Yang, Rajneesh Sharma, Samuel A. McDonald, Paul M. Mummery
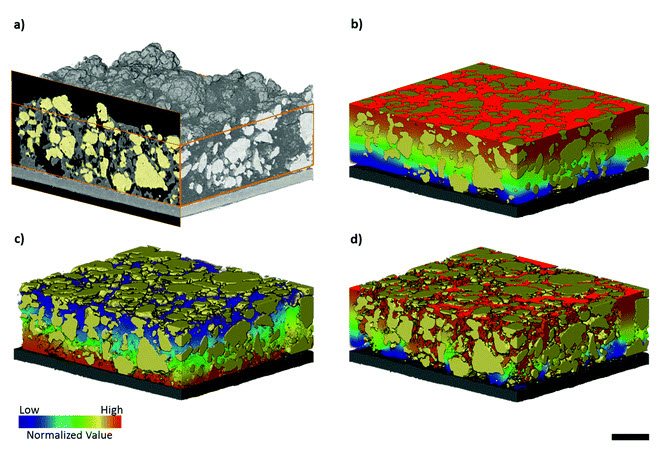
Three-dimensional image based modelling of transport parameters in lithium–sulfur batteries
An elemental sulfur electrode was imaged with X-ray micro and nano computed tomography and segmented into its constituent phases. Morphological parameters including phase fractions and pore and particle size distributions were calculated directly from labelled image data, and flux based simulations were performed to determine the effective molecular diffusivity of the pore phase and electrical conductivity of the conductive carbon and binder phase, D... Read more
Chun Tan, Matthew D. R. Kok , Sohrab R. Daemi , Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
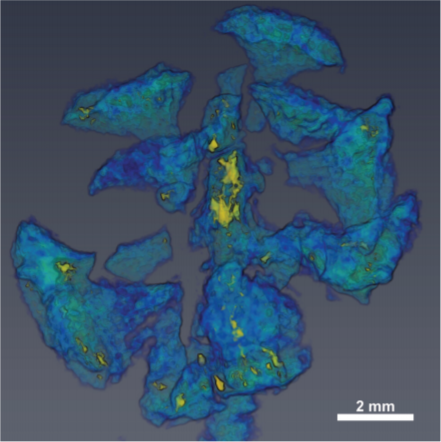
Computed tomography is an increasingly popular technique for the non-destructive study of fossils. Whilst the science of X-ray computed tomography (CT) has greatly matured since its first fossil applications in the early 1980s, the applications and limitations of neutron tomography (NT) remain relatively unexplored in palaeontology. These highest resolution neutron tomographic scans in palaeontology to date were conducted on a specimen of Austrosequoia novae-zeelandiae (Ettingshausen) Mays an... Read more
Chris Mays, Joseph J. Bevitt, and Jeffrey D. Stilwell
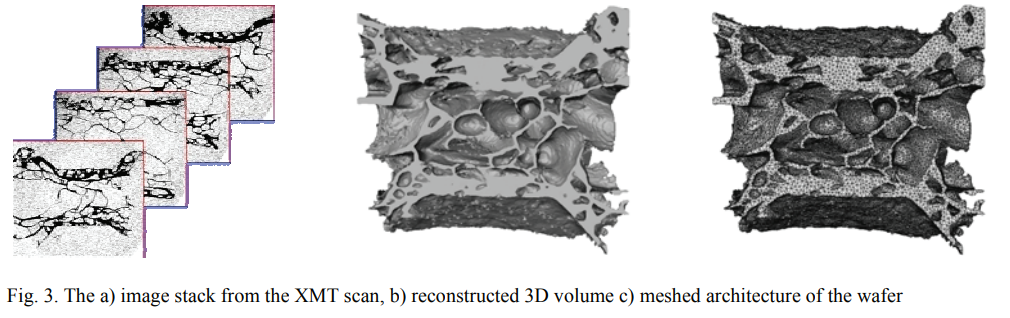
Modelling deformation and fracture in confectionery wafers
The aim of this research is to model the deformation and fracture behaviour of brittle wafers often used in chocolate confectionery products.
Three point bending and compression experiments were performed on beam and circular disc samples respectively to determine the ‘apparent’ stress-strain curves in bending and compression. The deformation of the wafer for both these testing types was observed in-situ within an SEM. The wafer is modelled analytically and numerically as a composi... Read more
Idris K. Mohammeda, Maria N. Charalambides , J. Gordon Williams , John Rasburn
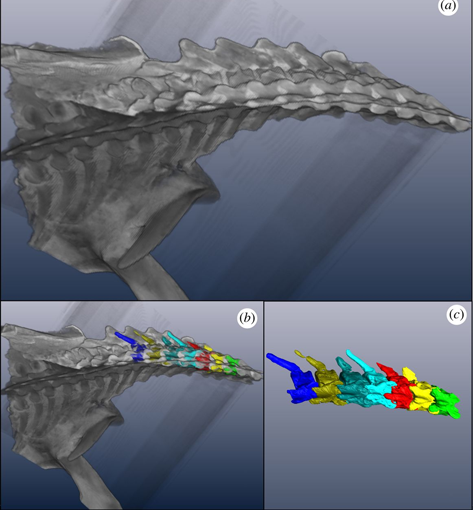
The elongate-necked aquatic plesiosaurs existed for 135 Myr during the Mesozoic. The function of this elongate neck is a point of debate. Using computed tomography and three-dimensional (3D) modelling, the range of motion (ROM) of the plesiosaur Nichollssaura borealis neck was assessed. To quantify the ROM, the intervertebral mobility was measured along the cervical vertebral column. This was done by manipulating the 3D models in the lateral and dorsoventral directions during two tri... Read more
Ramon S. Nagesan, Donald M. Henderson, Jason S. Anderson
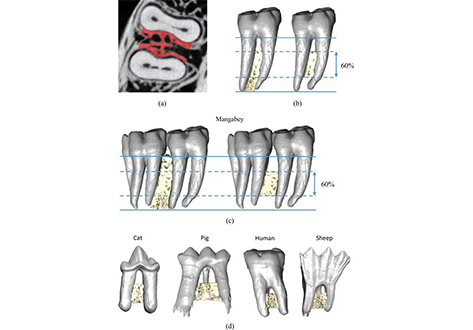
Mechanical adaptation of trabecular bone morphology in the mammalian mandible
Alveolar bone, together with the underlying trabecular bone, fulfils an important role in providing structural support against masticatory forces. Diseases such as osteoporosis or periodontitis cause alveolar bone resorption which weakens this structural support and is a major cause of tooth loss. However, the functional relationship between alveolar bone remodelling within the molar region and masticatory forces is not well understood. This study investigated this relationship by comparing m... Read more
Peter J. Watson, Laura C. Fitton, Carlo Meloro, Michael J. Fagan, Flora Gröning
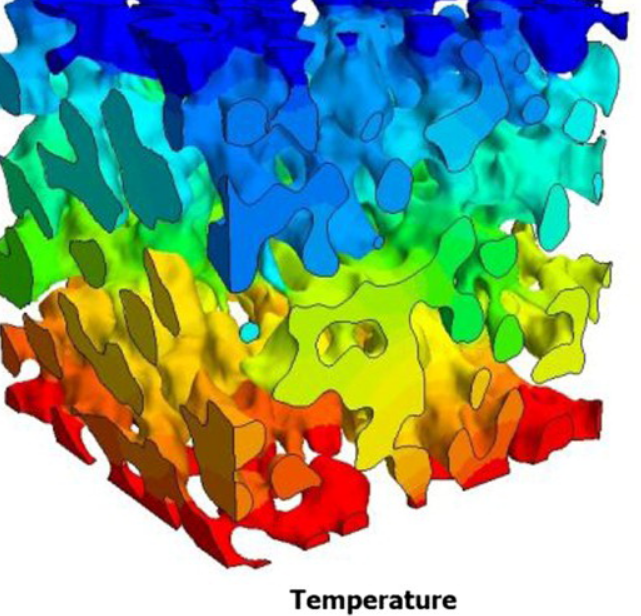
Tortuosity in electrochemical devices: a review of calculation approaches
Here, a review of tortuosity calculation procedures applied in the field of electrochemical devices is presented to better understand the resulting values presented in the literature. Visible differences between calculation methods are observed, especially when using porosity–tortuosity relationships and when comparing geometric and flux-based tortuosity calculation approaches.
Read more
Bernhard Tjaden, Dan J. L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing