Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
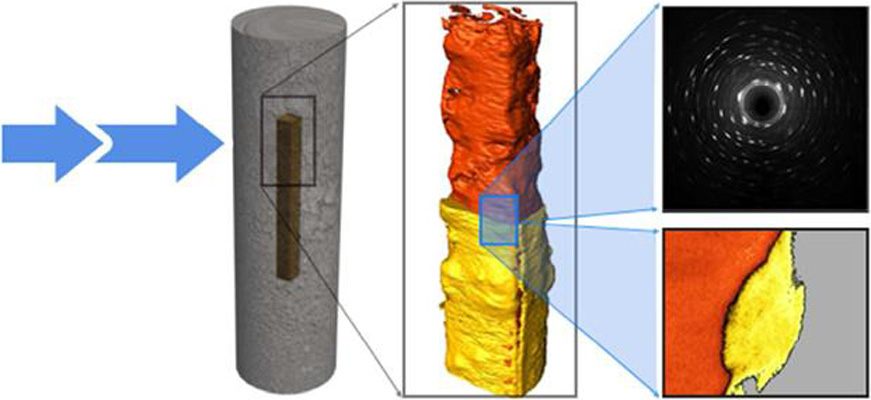
Nuclear waste viewed in a new light; a synchrotron study of uranium encapsulated in grout
How do you characterise the contents of a sealed nuclear waste package without breaking it open?
This question is important when the contained corrosion products are potentially reactive with air and radioactive. Synchrotron X-rays have been used to perform micro-scale in-situ observation and characterisation of uranium encapsulated in grout; a simulation for a typical intermediate level waste storage packet. X-ray tomography and X-ray powder diffraction generated both qualitative and ... Read more
C.A. Stitt, M. Hart, N.J. Harker, K.R. Hallam, J. MacFarlane, A. Banos, C. Paraskevoulakos, E. Butcher, C. Padovani, T.B. Scott
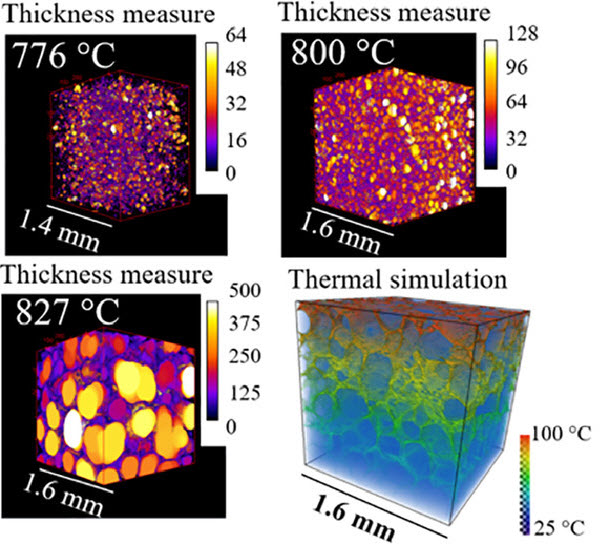
High-speed synchrotron X-ray imaging of glass foaming and thermal conductivity simulation
Glass foams are attractive thermal insulation materials, thus, the thermal conductivity (λ) is crucial for their insulating performance. Understanding the foaming process is critical for process optimization. Here, we applied high-speed synchrotron X-ray tomography to investigate the change in pore structure during the foaming process, quantifying the foam structures and porosity dynamically. The results can provide guidance for the manufacturing of glass foams. The 3D pore structures were a... Read more
Martin B. Østergaard, Manlin Zhang, Xiaomei Shen, Rasmus R. Petersen, Jakob König, Peter D. Lee, Yuanzheng Yue, Biao Cai
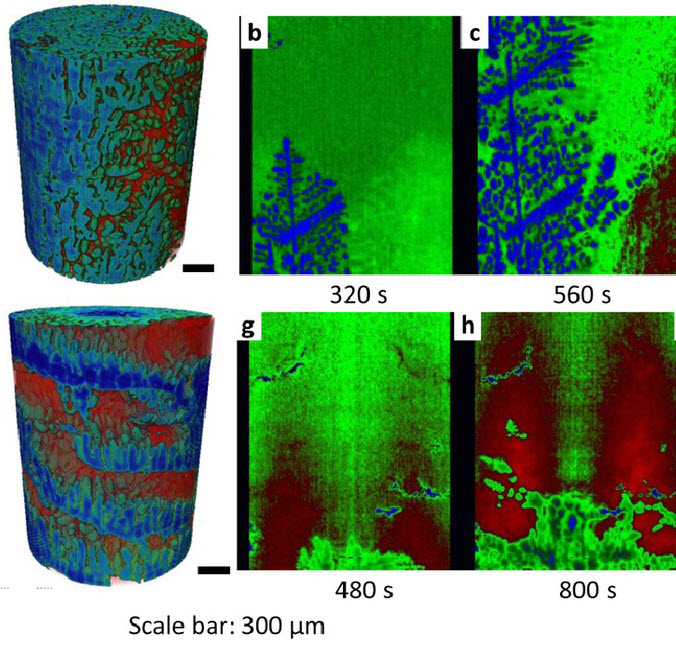
Revealing the mechanisms by which magneto-hydrodynamics disrupts solidification microstructures
A key technique for controlling solidification microstructures is magneto-hydrodynamics (MHD), resulting from imposing a magnetic field to solidifying metals and alloys. Applications range from bulk stirring to flow control and turbulence damping via the induced Lorentz force. Over the past two decades the Lorentz force caused by the interaction of thermoelectric currents and a magnetic field, a MHD phenomenon known as Thermoelectric Magnetohydrodynamics (TEMHD), was also shown to drive inter... Read more
B. Cai, A. Kao, E. Boller, O.V. Magdysyuk, R.C. Atwood, N.T. Vo, K. Pericleous, P.D. Lee
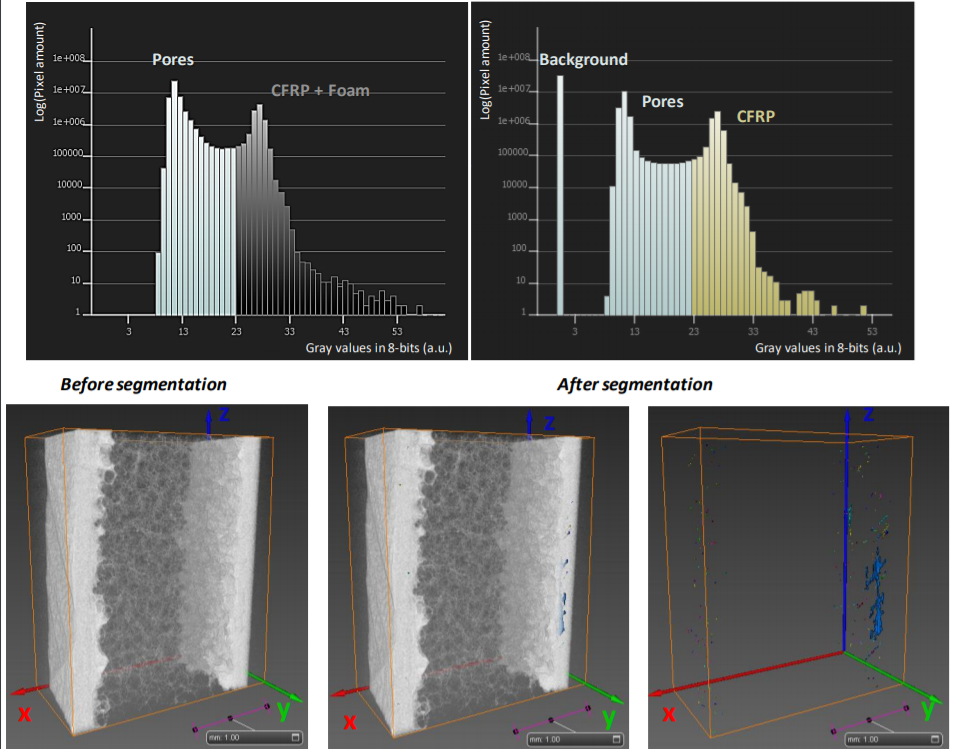
The aim of the current study is to propose a versatile, non-destructive inspection strategy to evaluate the structure of two different aircraft carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) -based composite configurations, which are widely used for structural elements, respectively layered composite and sandwich structure. X-ray computed tomography (CT) has been used as a flexible method for assessment of porosity levels in CFRP components in both types of configuration, permitting to investigate th... Read more
Elena Dilonardo, Michele Nacucchi, Fabio De Pascalis, Mauro Zarrelli, Cinzia Giannini
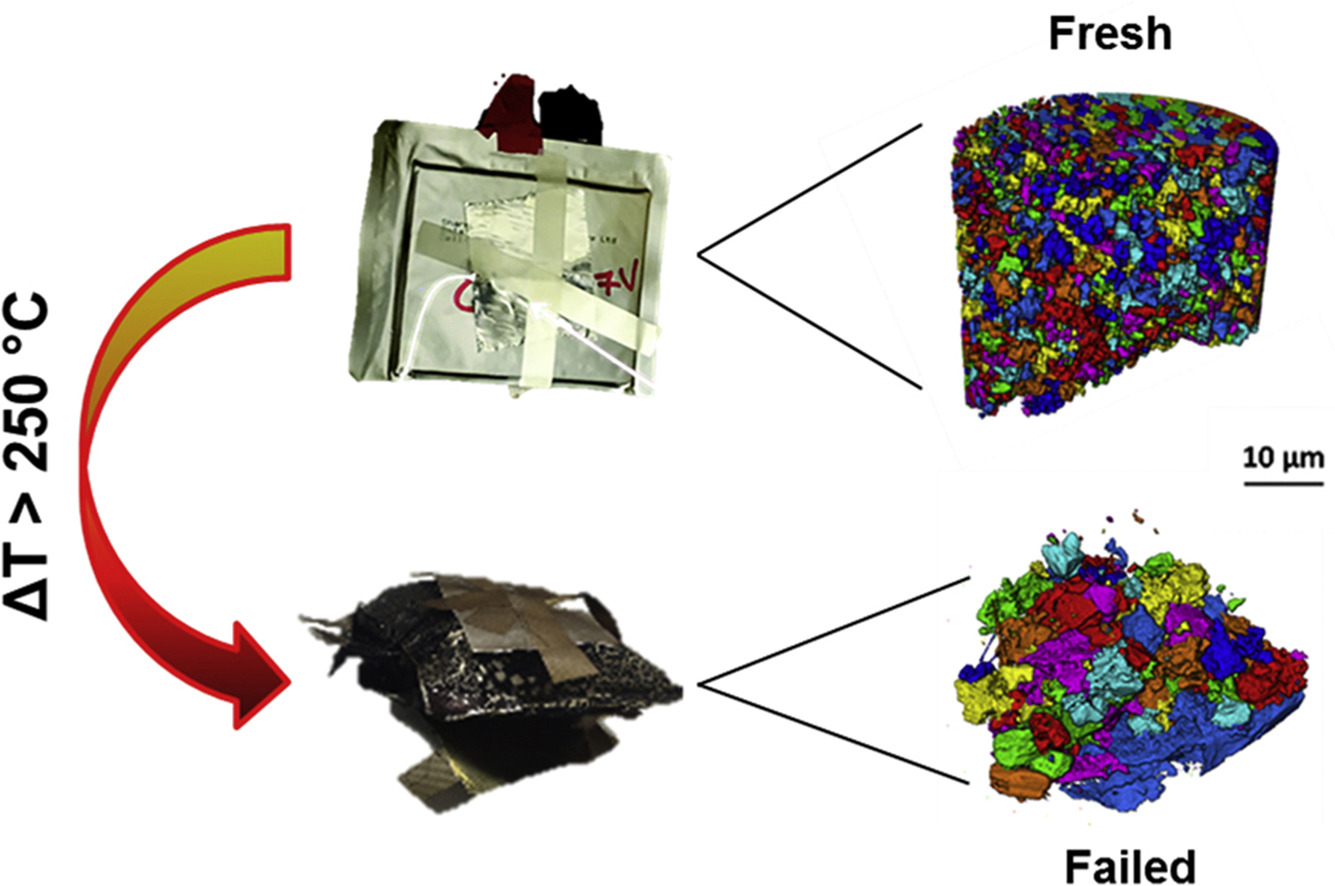
Multiscale tomographic analysis of the thermal failure of Na-Ion batteries
In recent years, the ability to examine the processes that cause the catastrophic failure of batteries as a result of thermal runaway has improved substantially. In this work, the effect of thermal runaway on the microstructure of the electrodes of a Na-ion battery is examined using X-ray computed tomography for the first time. The thermal failure induced via accelerating rate calorimetry enabled the examination of failed electrodes, which were subsequently compared with fresh s... Read more
Robinson, J. B., Heenan, T. M. M., Jervis, J. R., Tan, C., Kendrick, E., Brett, D. J. L., & Shearing, P. R.
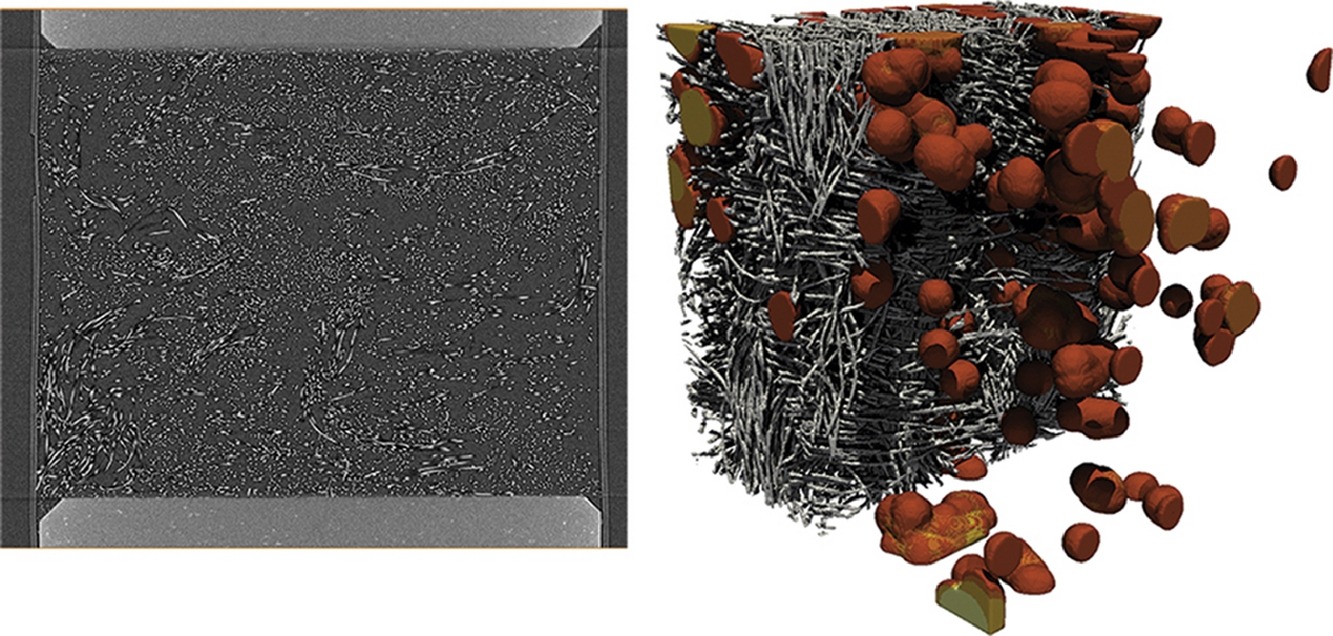
In situ compression and X-ray computed tomography of flow battery electrodes
Redox flow batteries offer a potential solution to an increase in renewable energy generation on the grid by offering long-term, large-scale storage and regulation of power. However, they are currently underutilised due to cost and performance issues, many of which are linked to the microstructure of the porous carbon electrodes used. Here, for the first time, we offer a detailed study of the in situ effects of compression on a commercially available carbon felt electrode. Visualisation ... Read more
Rhodri Jervis , Matt D.R. Kok , Tobias P. Neville , Quentin Meyer , Leon D. Brown , Francesco Iacoviello , Jeff T. Gostick , Dan J.L. Brett , Paul R. Shearing
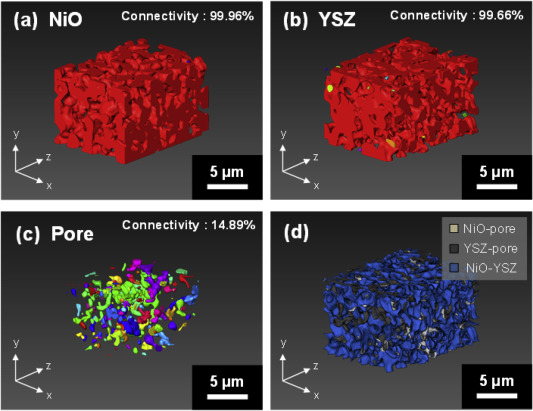
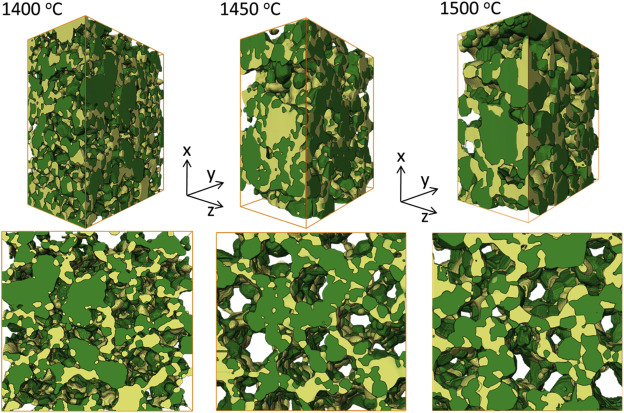
Nickel-yttria-stabilized zirconia (Ni-YSZ) cermet is widely used as an anode material in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs); however, Ni re-oxidation causes critical problems due to volume expansion, which causes high thermal stress. We fabricated a Ni-YSZ anode functional layer (AFL), which is an essential component in high-performance SOFCs, and re-oxidized it to investigate the related three-dimensional (3D) microstructural and thermo-mechanical effects. A 3D model of the re-oxidized AFL ... Read more
Jun Woo Kim, Kiho Bae, Hyun Joong Kim, Ji-won Son, Namkeun Kim, Stefan Stenfelt, Fritz B. Prinz, Joon Hyung Shim
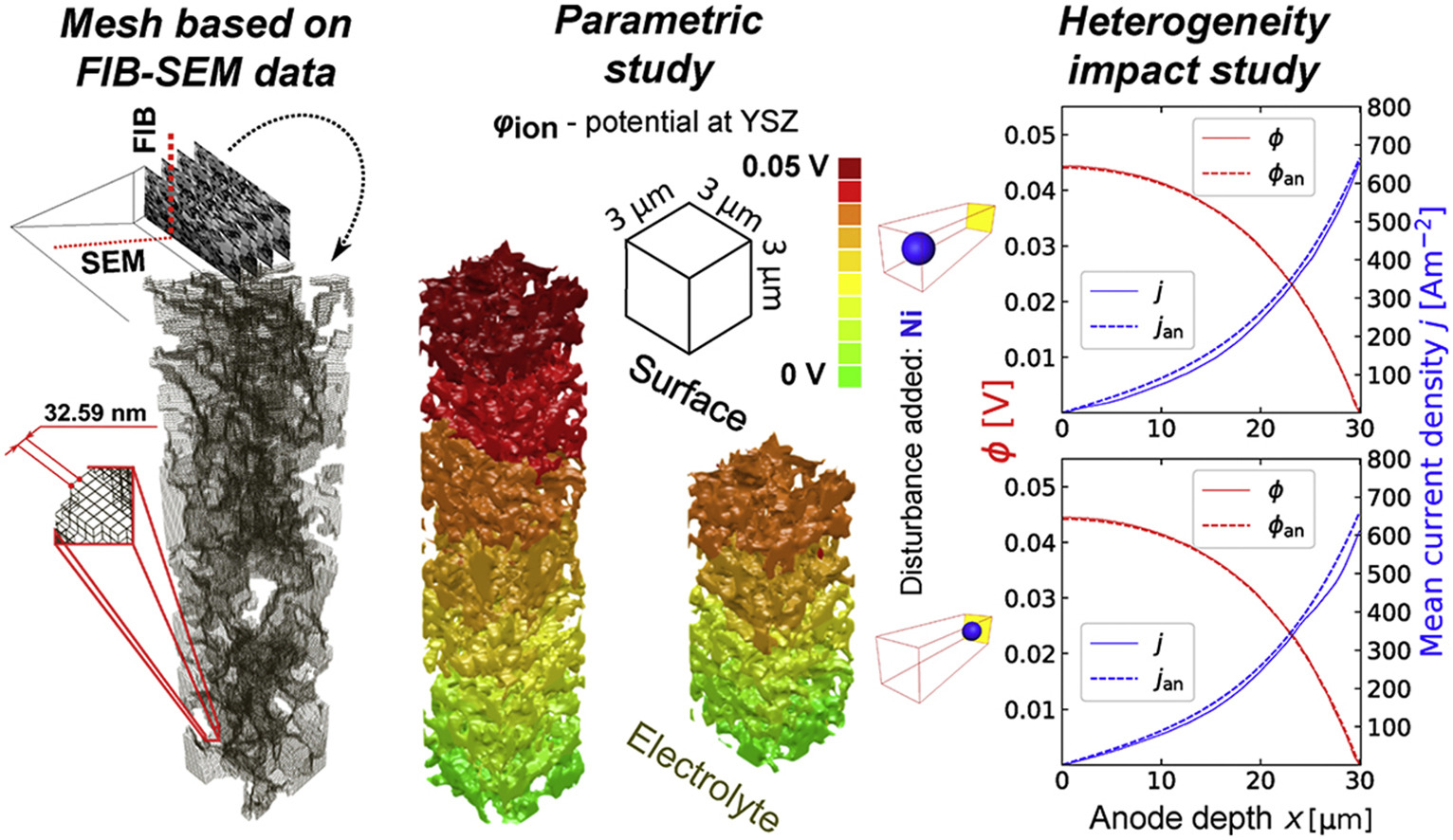
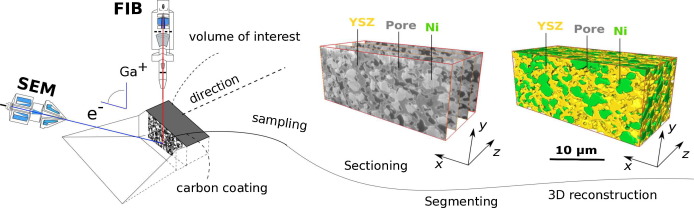
In this paper a fully three dimensional, multiphase, micro-scale solid oxide fuel cellanode transport phenomena numerical model is proposed and verified. The Butler-Volmer model was combined with empirical relations for conductivity and diffusivity – notably the Fuller-Shetler-Giddings equation, and the Fickian modelfor transport of gas reagents. FIB-SEM tomography of a commercial SOFC stack anode was performed and the resulting images were processed to acquire input data. ... Read more
Tomasz A. Prokop, Katarzyna Berent, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S.Szmyd, Grzegorz Brus
High performance anode with dendritic porous structure for low temperature solid oxide fuel cells
A dendritic porous supported microstructure simultaneously creates small pore size and broad gas diffusion pathways in a solid oxide fuel cell anode membrane. This microstructure also achieves pore sizes that reduce with increasing depth within the membrane without increasing the structure tortuosity. Such a microstructure supplies high triple phase boundary density, fast gas diffusion and low polarization resistance. Here we characterise the performance of a porous anode with such a dendriti... Read more
Xin Shao, William D.A. Rickard, Dehua Dong, Huu Dang , Martin Saunders, Aaron Dodd, Gordon Parkinson, Chun-Zhu Li
Growing popularity and rapid development of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) stem for their potential to become a gamechanger in the field of clean power generation technologies.
In this paper, a transient microstructure-oriented numerical simulation of a planar Direct Internal Reforming Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (DIR-SOFC) is delivered. The performance criteria in a direct steam reforming for a fuel starvation scenario are analyzed in order to optimize the underlying process. The proposed t... Read more
Maciej Chalusiak, Michal Wrobel, Marcin Mozdzierz, Katarzyna Berent, Janusz S. Szmyd, Shinji Kimijima, Grzegorz Brus
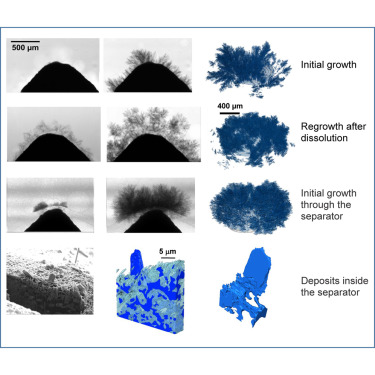
Alternative battery technologies are required to meet growing energy demands and address the limitations of present technologies. As such, it is necessary to look beyond lithium-ion batteries. Zinc batteries enable high power density while being sourced from ubiquitous and cost-effective materials. This paper presents, for the first time known to the authors, multi-length scale tomography studies of failure mechanisms in zinc batteries with and without commercial microporous separators. In bo... Read more
Vladimir Yufit, Farid Tariq David S. Eastwood Moshiel Biton Billy Wu Peter D. Lee Nigel P. Brandon
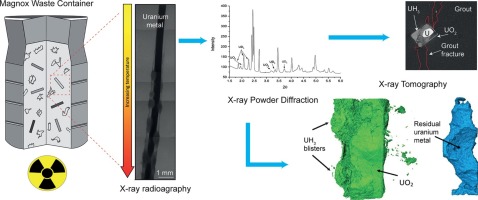
To accurately predict the initiation and evolution of uranium hydride potentially present in nuclear waste containers, studies of simulated conditions are required.
Here, for the first time, the uranium-deuterium reaction was examined in-situ, in real time, whilst within grouted media. A deuterium gas control rig and stainless steelquartz glass reaction cell were configured on a synchrotron beam line to collect X-ray diffraction and X-ray tomography data. It was found that deuteride fo... Read more
C.A. Stitt, C. Paraskevoulakos, N.J. Harker, A. Banos, K.R. Hallam, C.P. Jones, T.B. Scott
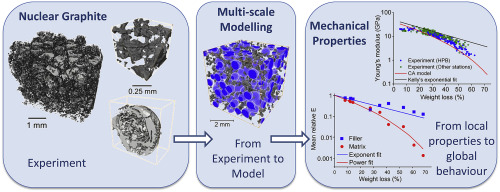
A multi-scale approach for fracture simulation, based on the Cellular Automata technique, has been developed and then applied to a nuclear graphite that is used in structural components of the UK Advanced Gas-cooled Reactors (AGR).
High resolution X-ray computed tomographs of Gilsocarbon grade
graphite, with up to 68% weight loss by radiolytic oxidation, provide quantitative descriptions of the porosity within its constitutive filler particles and their surrounding matrix. The st... Read more
Yelena Vertyagina, Thomas James Marrow
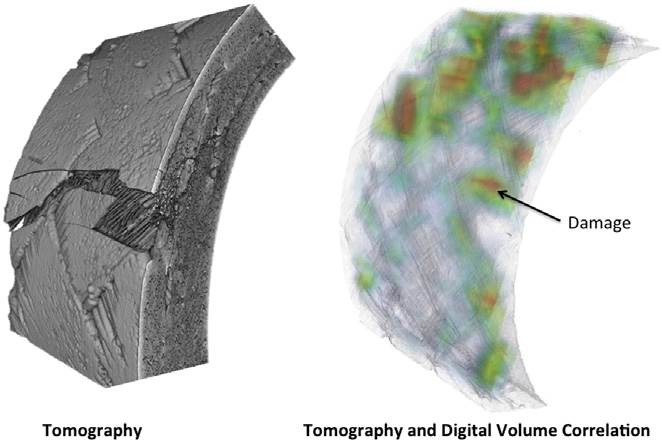
In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite
SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composites are candidate materials for fuel cladding in Generation IV nuclear fission reactors and as accident tolerant fuel clad in current generation plant.
Experimental methods are needed that can detect and quantify the development of mechanical damage, to support modelling and qualification tests for these critical components. In situ observations of damage development have been obtained of tensile and C-ring mechanical test specimens of a braided nuclear gr... Read more
L. Saucedo-Mora, T. Lowe, S. Zhao, P.D. Lee, P.M. Mummery, T.J. Marrow
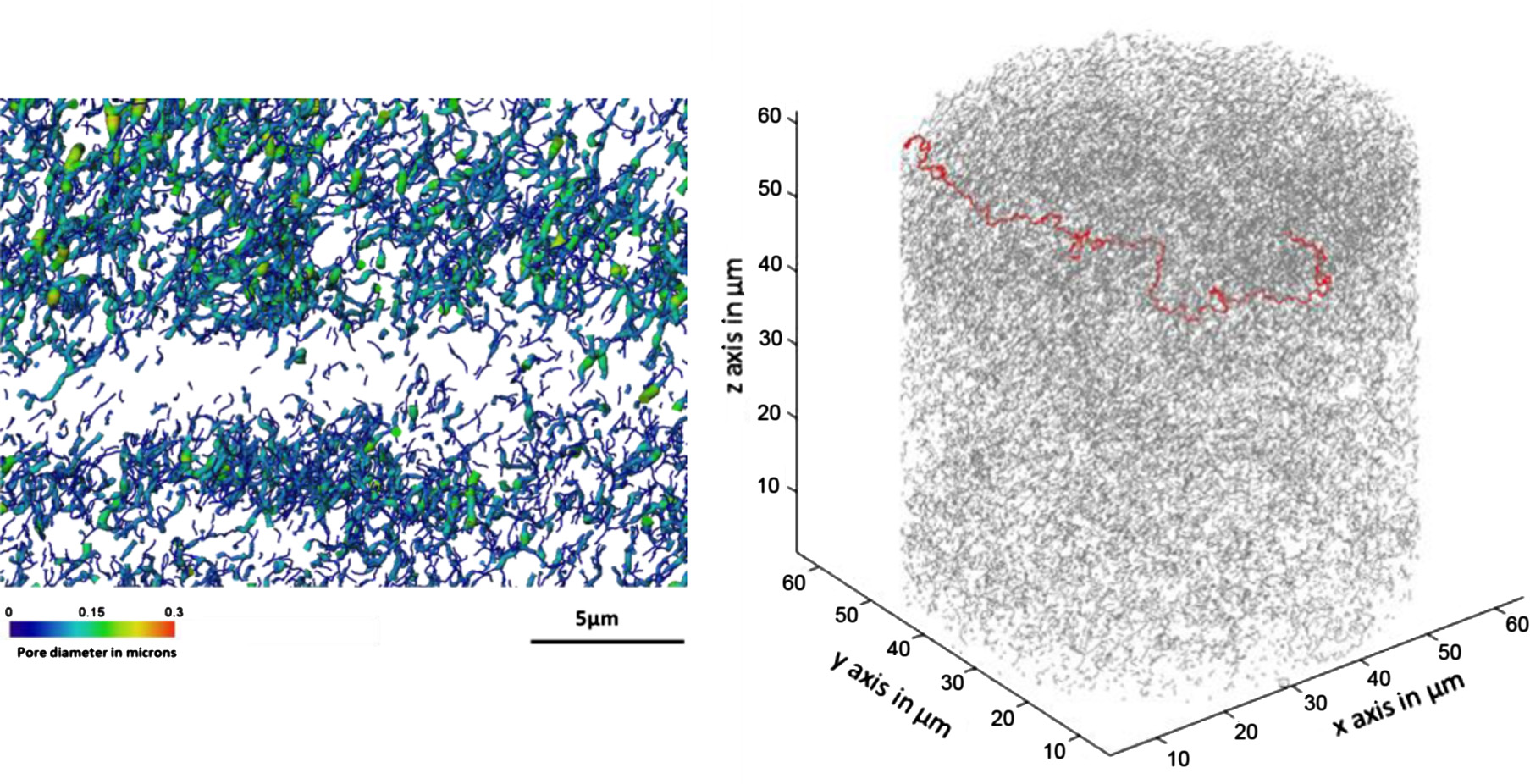
Microstructural analysis of TRISO particles using multi-scale X-ray computed tomography
TRISO particles, a composite nuclear fuel built up by ceramic and graphitic layers, have outstanding high temperature resistance. TRISO fuel is the key technology for High Temperature Reactors (HTRs) and the Generation IV Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) variant.
TRISO offers unparalleled containment of fission products and is extremely robust during accident conditions. An understanding of the thermal performance and mechanical properties of TRISO fuel requires a detailed knowledg... Read more
T. Lowe, R.S. Bradley, S. Yue, K. Barii, J. Gelb, N. Rohbeck, J. Turner, P.J. Withers
Endosseous oral implant is applied for orthodontic anchorage in subjects with multiple tooth agenesis. Its effectiveness under orthodontic loading has been demonstrated clinically and experimentally. This study investigates the deformation and stress on the bone and implant for different bite forces by three-dimensional (3D) finite element (FE) methods. A numerical simulation of deformation and stress distributions around implants was used to estimate the survival life for implants. The model... Read more
Hsin-Chung Cheng, Boe-Yu Peng, May-Show Chen, Chiung-Fang Huang, Yi Lin, and Yung-Kang Shen
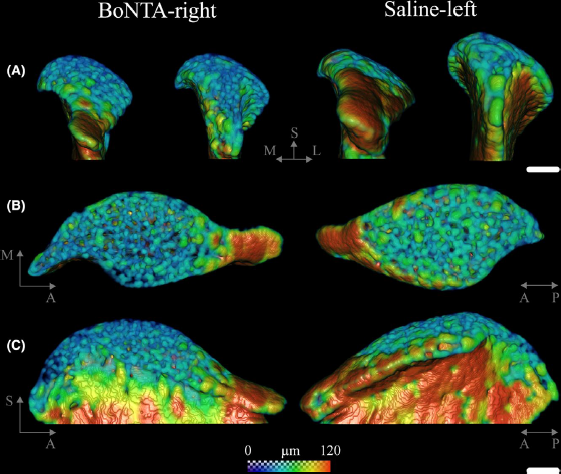
Masseter muscle function influences mandibular bone homeostasis. As previously reported, bone resorption markers increased in the mouse mandibular condyle two days after masseter paralysis induced with botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA), followed by local bone loss.
This study aimed to evaluate the bone quality of both the mandibular condyle and alveolar process in the mandible of adult mice during the early stage of a BoNTA‐induced masseter muscle atrophy, using a combined 3D histomorpho... Read more
Julián Balanta‐Melo, María Angélica Torres‐Quintana, Maximilian Bemmann, Carolina Vega, Constanza González, Kornelius Kupczik, Viviana Toro‐Ibacache, Sonja Buvinic
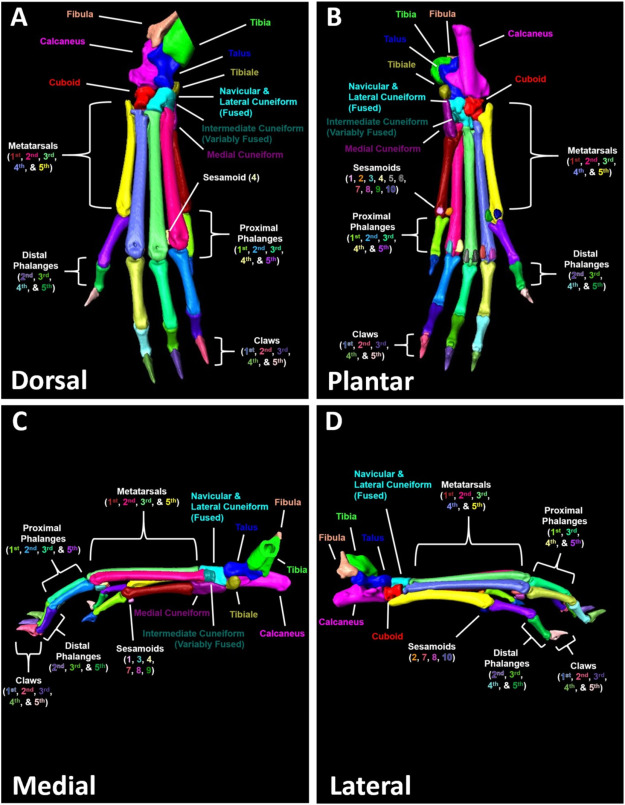
A high-throughput semi-automated bone segmentation workflow for murine hindpaw Micro-CT datasets
Micro-computed tomography (μCT) is a valuable imaging modality for longitudinal quantification of bone volumes to identify disease or treatment effects for a broad range of conditions that affect bone health. Complex structures, such as the hindpaw with up to 31 distinct bones in mice, have considerable analytic potential, but quantification is often limited to a single bone volume metric due to the intensive effort of manual segmentation. Herein, we introduce a high-throughput, user-friendl... Read more
H. Mark Kenney, Yue Peng, Kiana L.Chen, Raquel Ajalik, Lindsay Schnur, Ronald W.Wood, Edward M.Schwarz, Hani A. Awad
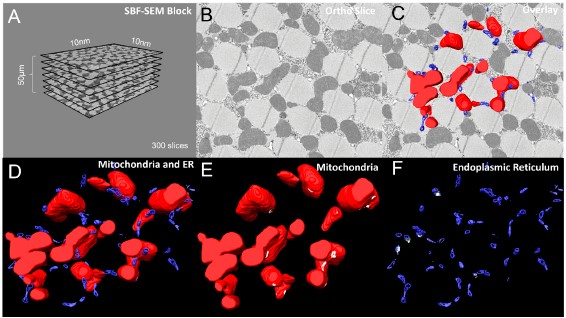
Protocols for Generating Surfaces and Measuring 3D Organelle Morphology Using Amira
High-resolution 3D images of organelles are of paramount importance in cellular biology. Although light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) have provided the standard for imaging cellular structures, they cannot provide 3D images.
However, recent technological advances such as serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) provide the tools to create 3D images for the ultrastructural analysis of org... Read more
Edgar Garza-Lopez, Zer Vue, Prasanna Katti, Kit Neikirk, Michelle Biete, Jacob Lam, Heather K. Beasley, Andrea G. Marshall, Taylor A. Rodman, Trace A. Christensen, Jeffrey L. Salisbury, Larry Vang, Margaret Mungai, Salma Ash Shareef, Sandra A. Murray, Jianqiang Shao, Jennifer Streeter, Brian Glancy, Renata O. Pereira1, E. Dale Abel, and Antentor Hinton, Jr.
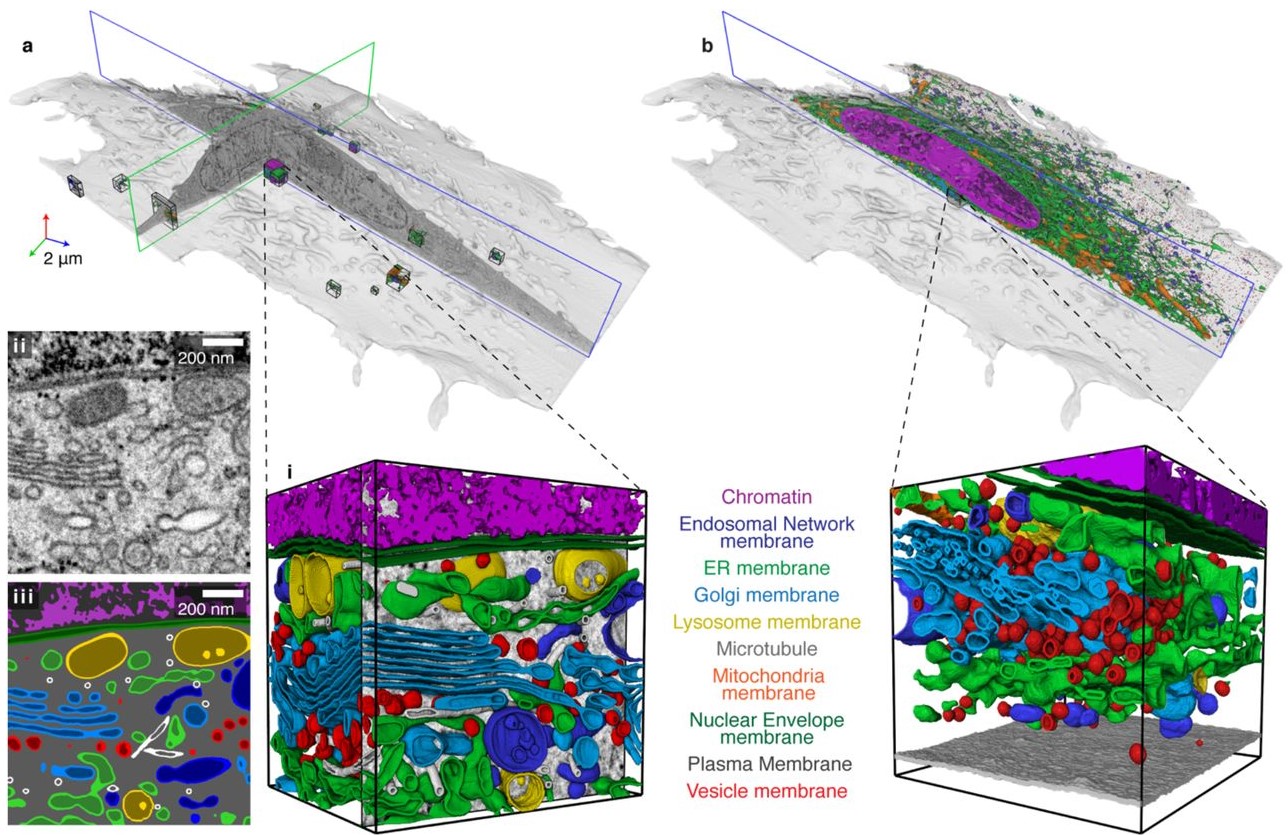
Automatic whole cell organelle segmentation in volumetric electron microscopy
Cells contain hundreds of different organelle and macromolecular assemblies intricately organized relative to each other to meet any cellular demands. Obtaining a complete understanding of their organization is challenging and requires nanometer-level, three-dimensional reconstruction of whole cells. Even then, the immense size of datasets and large number of structures to be characterized requires generalizable, automatic methods.
To meet this challenge, we developed an analy... Read more
Larissa Heinrich, Davis Bennett, David Ackerman, Woohyun Park, John Bogovic, View ORCID ProfileNils Eckstein, Alyson Petruncio, Jody Clements, C. Shan Xu, Jan Funke, Wyatt Korff, Harald F. Hess, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Stephan Saalfeld, Aubrey V. Weigel, COSEM Project Team
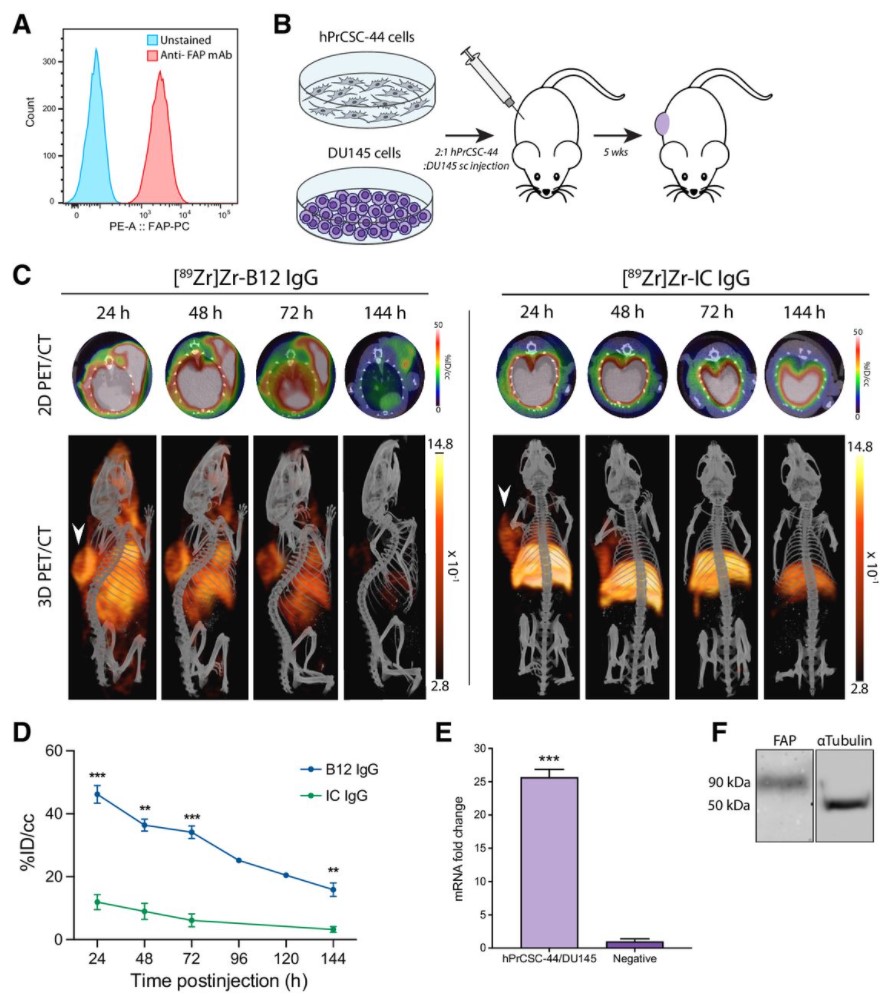
Malignant cells are surrounded by a complex and supportive tumor microenvironment that consists of immune cells, extracellular matrix, vasculature, and fibroblasts. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are the major cell type in the reactive stroma and are known to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis. Fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) is a transmembrane serine protease expressed by CAFs in the microenvironment of epithelial tumors.
Meta-analysis of FAP expression and clinical ... Read more
Hallie M. Hintz, Joseph P. Gallant, Donald J. Vander Griend, Ilsa M. Coleman, Peter S. Nelson and Aaron M. LeBeau